ML System Design
我們將從建立一個 Spam Classifier 了解設計機器學習系統所需要注意的事情。這個 Classifier 將會教我們如何收集資料、撰寫 algorithm 並如何處理偏斜資料,以及如何利用 precision 和 recall 的概念來評估機器學習系統的準確度。最後,我們也會了解到如何利用大量的資料來提升演算法的準確度。
Prioritizing What to Work On
在訓練一個 spam classifier 時
通常會建立一個 10000 ~ 50000 entries 的 vector
裡面存放一些常見詞 for spam/not spam
每一個 entries words 出現在信中就標上 1,沒有出現就標上 0

所以在實作中,要怎麼樣增加 classifier 的 accuracy 呢 ?
- 收集大量資料 (例如 honeypot)
- 找出一些 sophisticated features (例如 email header 的 data 作為 features)
- 升級我們的 algorithm (例如辨識 misspelling in spam)
在實作中,很難決定哪一個才是最好的方法 ...
Error Analysis
所以在實作一個 machine learning project 時,推薦可以這樣做 :
- 快速製作一個簡單的 learning algorithm 然後早一點利用 cross validation set 測試
- Plot learning curves 到自己的 algorithm 來判斷下一步
- 手動測試 cross validation 的結果,來查看哪裡才是 algorithm 的弱點
舉個例子 :
- 500 個 emails 中我們誤判了 100 個
- 我們可以手動檢查這 100 個錯在哪裡
- 我們在針對錯的地方,加入新的 features
- 例如其中有 50 封都是釣魚信,代表我們要再增強辨識釣魚信的演算法
另外在實作時,也要習慣把實際數字記錄下來
例如我們是否要把 discount / discounts / discounted / discounting 視為一樣的意思
- 當沒有利用 steming 時 error 為 5%
- 利用 steming 時 error 為 3%
- steming + case detection 時 error 為 3.3%
所以就可以看出怎麼做才是最好的方法
Handling Skewed Data
假設我們有一個 logistic regression model
用來 predict y = 1 時為 cancer,y = 0 時沒有 cancer
這個 model 在 test set 預測了 99% 正確,只有 1% error
但結果後來發現,根本只有 0.5% 的病人有 cancer
代表我用一個演算法,全部都猜 0 還有更高的 0.5% 的正確率 !
function y = predictCancer(x)
y = 0; % ignore x, always equals to zero
return
這個 test set 就是一個 skewed classes
Error Matrices (Precision and Recall)
所以我們用一個 precision/recall 的 table 來檢驗一下正確率
這個方法可以避免 skewed classes
我們設定左邊為你的 predict class,而右邊為 actual class
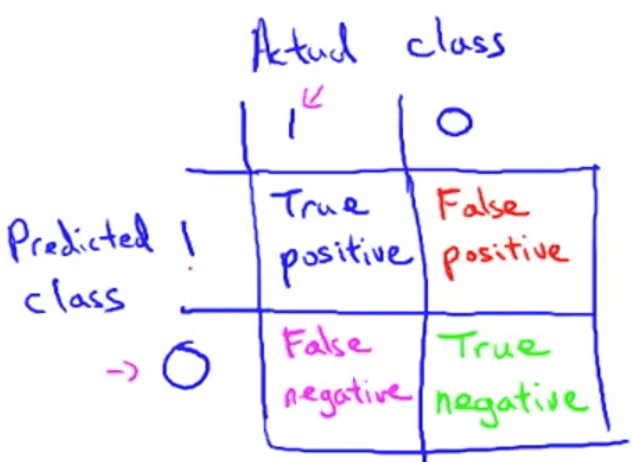
所以分別會有以下幾種結果
- True Positive : 猜 1 然後猜對
- False Positive : 猜 1 結果猜錯
- False Negative : 猜 0 結果猜錯
- True Negative : 猜 0 然後猜對
接下來我們就可以來計算 Precision 和 Recall
Precision
在 model 預測的猜測的 y = 1 中,有多少的 fraction 是真正為 1
簡單來說就是我猜 1 然後中獎的機率有多少啦
Recall
在真實情況下 y = 1 中,有多少是我猜對的
簡單來說就是 actual = 1 時,我剛好猜對 y = 1 的機率有多少
如此一來,就算你在 skewed classes 猜中 99%
但因為你的 Actual positives 很小很小
所以你的 recall 不是很小就是等於 0
就可以避免這種像 cheating 的結果出現
Trade Off Precision and Recall
其實我們是很難滿足 high precision 又 high recall 的
今天假設我們想要提高預測的準確度
我們將 logistic regression 改為 時 y = 1
所以 時 y = 0
這麼一來就可以非常有信心的預測成功
但也因為 threshold 設的太高,所以漏看了一些可能的 data
我們得到 higher precision, lower recall
那這時候我們改成 時 y = 1
而 時 y = 0
此時將不會漏看可能的 data
但精準度也變得很低
我們得到 lower precision, higher recall
畫成圖表,可能會出現這樣的結果

F score
現在假設我們設計出三個 algorithm (可能是一個 algorithm 用三種 threshold)
| Precision (P) | Recall (R) | Average | F-score | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Algorithm 1 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 0.45 | 0.444 |
| Algorithm 2 | 0.7 | 0.1 | 0.4 | 0.175 |
| Algorithm 3 | 0.02 | 1.0 | 0.51 | 0.0392 |
我們要怎麼判斷並取捨 precision 和 recall 的搭配呢
Average 顯然是不行的
因為使用 average 下,選擇的 Algorithm 3 雖然 recall 很高但 precision 極低
這邊可以使用一個算法叫做 F-score
他可以比 average 更有效的找出適當的 precision/recall 組合
Using Large Data Sets
“不是比較誰的 algorithm 比較好,而是比較誰有最多 data”
Useful test
- 當你把 input x 告訴一個那個領域的專家時,他能不能很好的預測出 y
- 如果可以,代表你的 input x 就是充足的
通常我們需要結合兩項重點
- 你的 learning algorithm 的 parameters 要充足
- 讓你的 很小
- 要使用大量的 training set
- 就不會 overfitting
- 所以
- 你的 learning algorithm 的 parameters 要充足
兩項結合在一起,代表 就可以很小