Cellular Respiration
Cellular respiration 是指細胞如何將大的分子分解成一小份一小份,以及最後將分解出來的 energy 儲存為 ATP 的過程。細胞分解 glucose 的過程中,必須會進行 catabolic reactions,並且從高能量的環境轉變成低能量的環境,最後將 energy 釋放出來,其中一部分製造出 ATP 以及另一部分則消散為 heat。在整個過程中,electron carriers 就負責將 electrons 從一個物質轉移到另一個物質,帶動整個細胞呼吸的過程。
Introduction to cellular respiration
在 Energy and Enzymes 篇章裡有提到 ATP
- 細胞如何將甜美的 glucose 轉換成方便儲存使用的 ATP
- 必須要進行 catabolic reactions
- 意思是要將大的分子分解成一小份一小份
- 例如以下公式代表 glucose 在 oxygen 中被分解成 6 個 carbon dioxide 和 6 個 water molecules
Glucose bond 中的 energy 將透過分解被釋放
- 有的儲存為 adenosine triphosphate (ATP) 格式
- 有的消散為 heat
其中 ATP 可以"直接"透過 substrate-level phosphorylation 產生
- 由 phosphate group 找到 ADP 一起合成出來的
ATP 也可以"間接"產生
- 一些 glucose 的 electrons 運送到 electron carriers (small molecules)
- Carriers 帶著 electrons 來到細胞內的 mitochondrion
- 找到了 electron transport chain (protein)
- Electrons 就在 ETC 上面從 high energy 變成 low energy
- ultimately passed to oxygen (forming water)
詳細的說,ETC 上的 electrons 釋放的 energy 會用來 pump protons ()
- Pump 產生 electrochemical gradient
- 往 mitochondrion 內流的 H+ 會經過 ATP synthase (enzyme)
- 幫助合成 ATP
- 這個作用稱為 oxidative phosphorylation
- 往 mitochondrion 內流的 H+ 會經過 ATP synthase (enzyme)
下圖展示了 substrate-level 和 oxidative phosphorylation
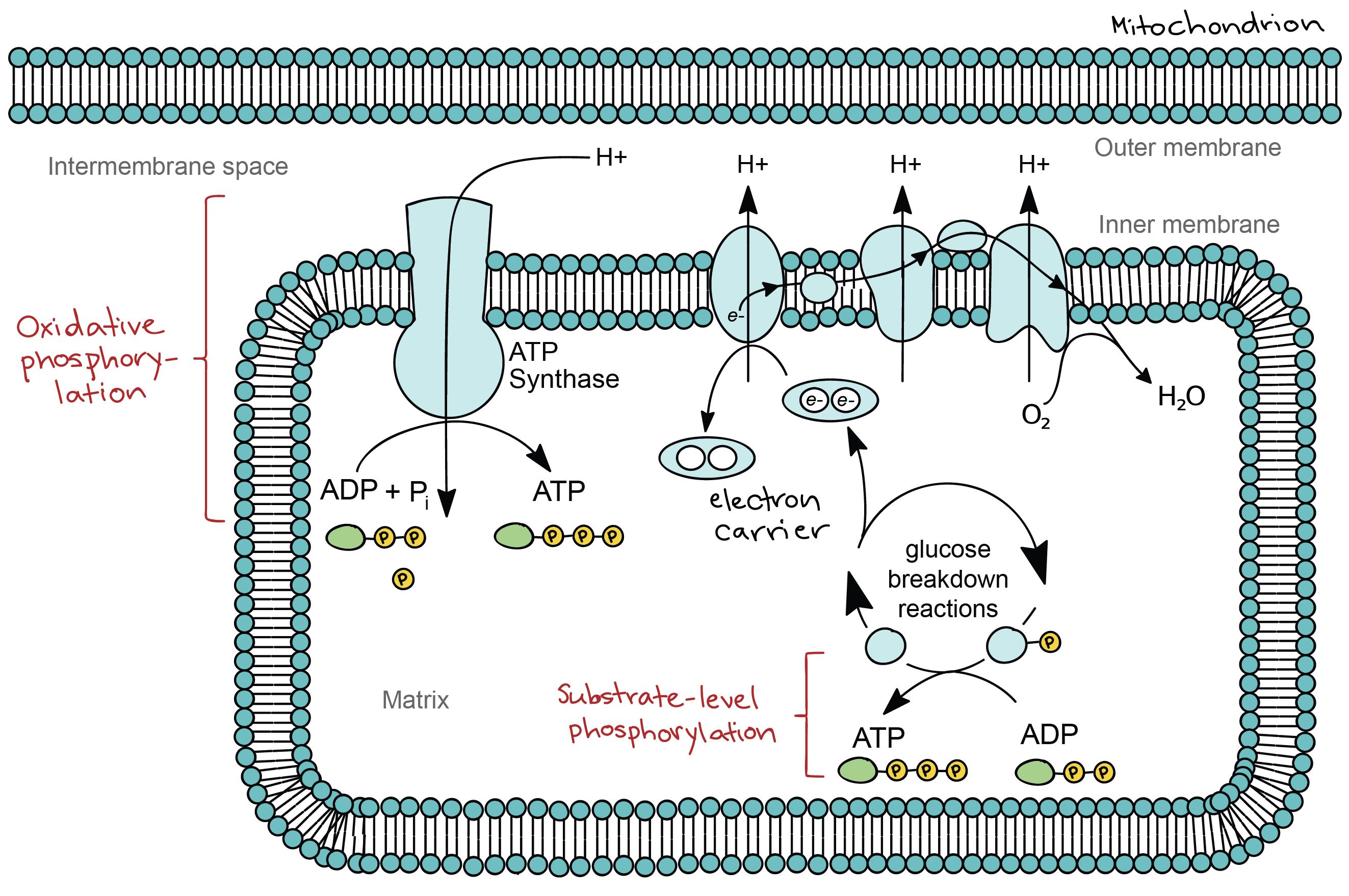
Glucose 等燃料透過上圖 electron transport chain 分解的過程,稱作 cellular respiration !
Electron carriers
負責載運 electrons 的 electron carriers 有兩種類型
- nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
- flavin adenine dinucleotide
當他們得到 electrons 時,順便會收下 hydrogen atoms 形成稍微不同的型式
丟掉 electrons 就會恢復原狀
這樣 gain/lost electrons 的反應又可以統稱為 redox reactions
Redox reactions
Cellular respiration 有非常多 electrons 互相 pass 的情況
- 所有包括 electron transfers 的統稱為 oxidation-reduction reactions (redox reactions)
- 失去或是無法繼續 hog electrons 的 molecules 就是被 oxidized
- 從被 oxidized molecules 獲得或 hog electrons 的 molecules 就是被 reduced
為何要區分「失去」跟「Hog」 electrons 呢,我們舉兩個例子 :
Magnesium chloride
我們用合成 magnesium chloride 來作為失去 electron 的例子
- 上面的 reaction 告訴我們
- magnesium atom 完全失去了 2 個 electrons
- 所以是 oxidized
- chlorine atoms 則完全接收了這 2 個 electrons
- 所以是 reduced
- magnesium atom 完全失去了 2 個 electrons
Water
我們另外用合成 water 來作為 hog electron 的例子
- 在外觀看起來沒有任何電子的轉移
- H atoms 原本就能很好的共享 electrons
- O atoms 也能很好的共用彼此 electrons
- 但因為成為 product 後跟原本 reactant 的 electron density 改變了 !
- 因為 oxygen 有更強的 electronegative
- 所以變成 之後,變成 oxygen hog 2 個 electrons
所以儘管沒有 electron 的 gain/lost,我們還是能總結在反應過後
- O 有更多的 electron density,所以是 reduced
- H 降低了 electron density,所以是 oxidized
Biological Redox reactions (trick)
在 biology 中,有一個 trick 用來取代 electrons 來判斷 redox reactions
當含有 carbon 的 molecules 在 reaction 期間
- 獲得 H atoms 或失去 O atoms
- 那他就是 reduced (gain electrons or electron density)
當含有 carbon 的 molecules 在 reaction 期間
- 失去 H atoms 或獲得 O atoms
- 那他就是 oxidized (lost electrons or electron density)
用 glucose breakdown 舉例
- 在 glucose 時的 carbon 是有跟 H atoms 來往的
- 但變成 carbon dioxide 之後就沒有跟 H atoms 來往了
- 所以 glucose 應該是被 oxidized
- 在 glucose 時的 oxygen 沒有跟 H atoms 有來往
- 但變成 water 之後就有跟 H atoms 來往了
- 所以 oxygen 應該是被 reduced
為什麼在 biology 可以這麼草率判斷 oxidation/reduction ?
- 因為 H 通常會與 organic molecules 結合
- 例如 C, O, N, P
- 這些 atom 都比 H 擁有更大的 electronegative
- 所以當含有這些 atom 的 molecules 與 H 結合,自然多為 reduced
- 因為 O 原本其他主要 biological molecules 的 atoms 還要更加 electronegative
- 所以跟 O 結合的 molecules 的 electron 通常會被 O 給 hog 走
- 這些 molecules 就多為 oxidized
Why redox
Redox 的目的就是要從反應中獲得 energy 呀 !
- Electrons 在 less electronegative atoms 的時候會有 higher energy
- 例如在 C 或 H 身邊時
- Electrons 在 more electronegative atoms 的時候會有 lower energy
- 例如在 O 身邊時
所以從 glucose 到 oxygen 的過程,就是從 higher energy 轉換到 lower energy
- Energy 就會在轉換過程中一步一步的釋放出 energy
- Energy 就會被抓來作功或儲存
- Cellular respiration 的最終目標
- 就是將每個階段產生的 energy 轉換成 ATP 形式
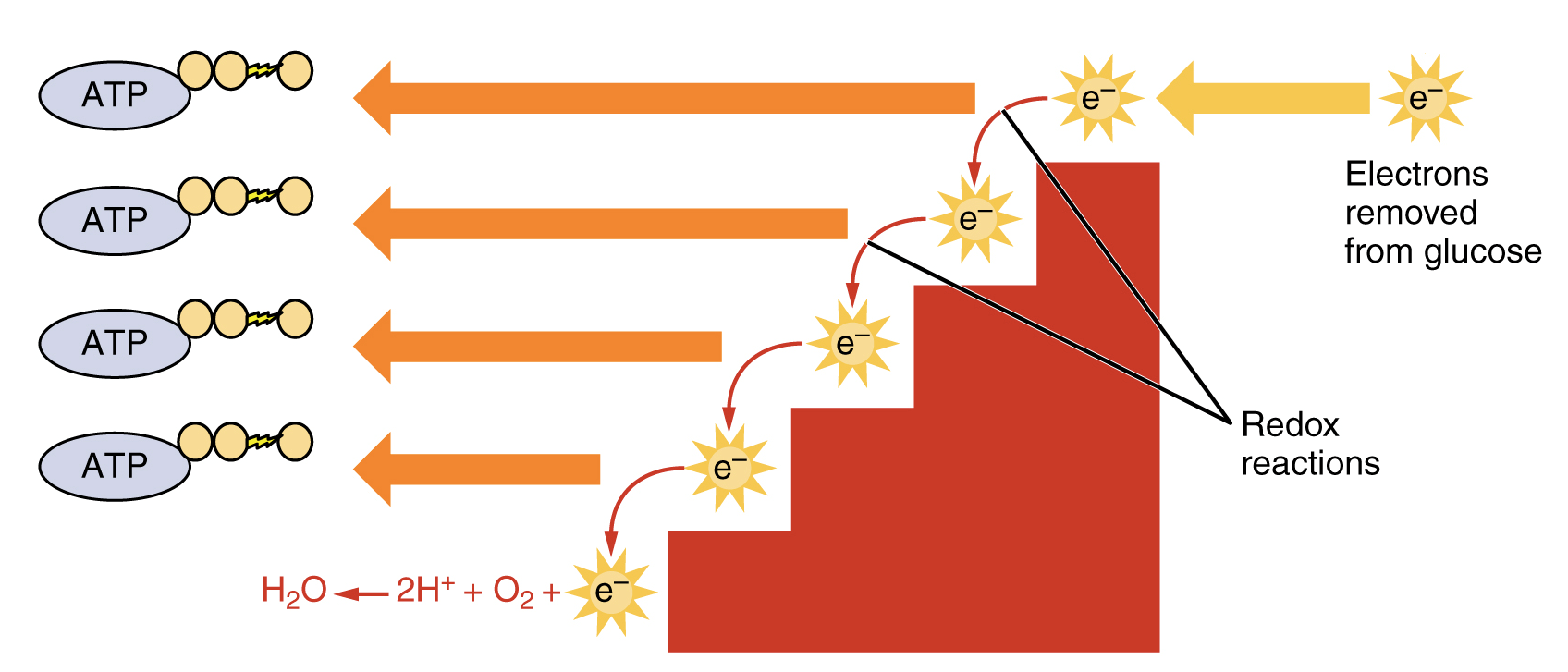
Steps of cellular respiration
Cellular respiration 有四大步驟,是地球中一種很美的 metabolic pathway (代謝途徑)
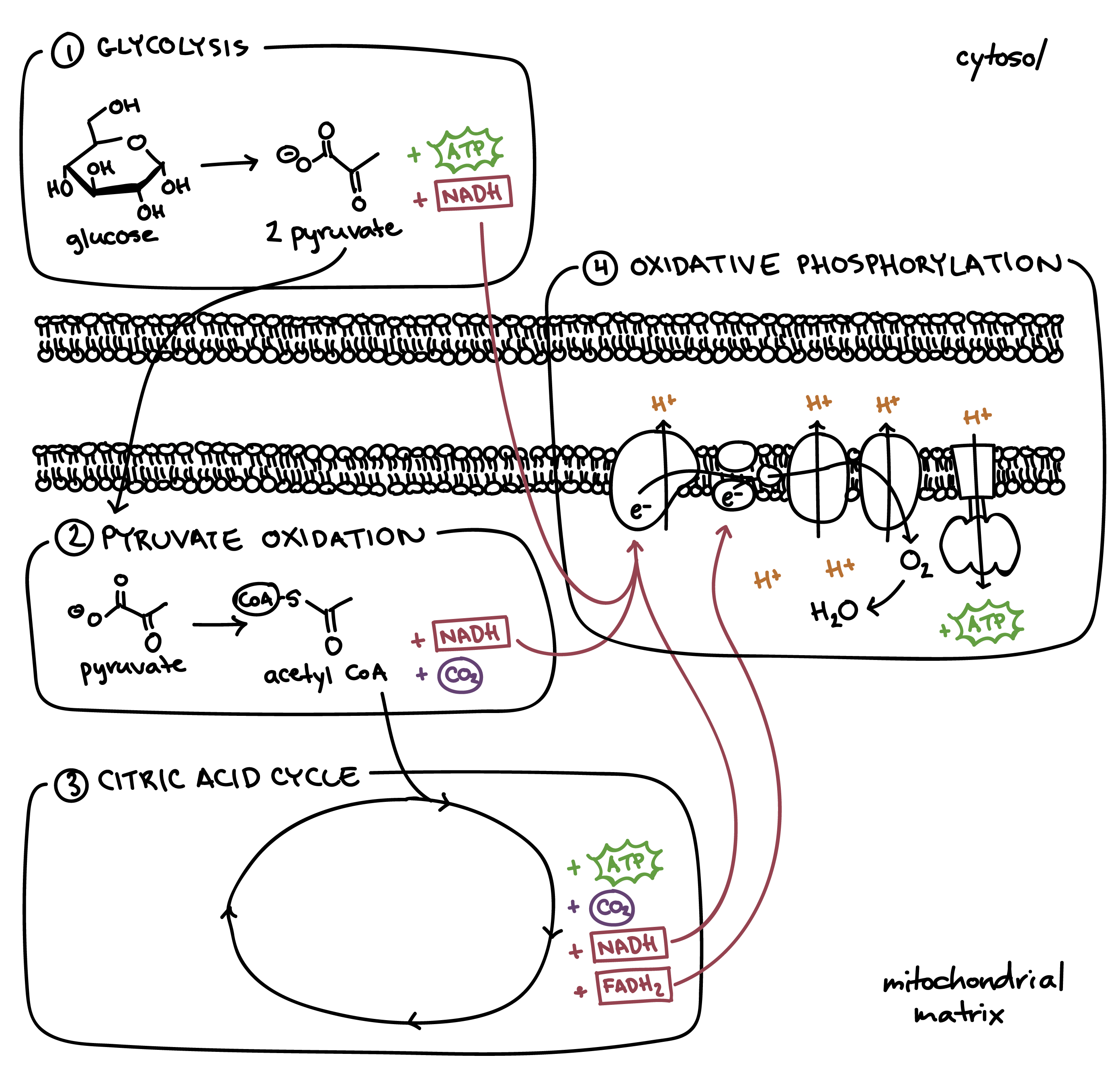
Cellular respiration 主要目標是將養分 (e.g., glucose) 轉化成能量 (e.g., ATP)
- 在 glucose 分解過程,會被拆解成 carbon dioxide, water 然後經過一些方法產出 ATP
- 有的 ATP 是直接被生產
- 有的 ATP 需透過 oxidative phosphorylation 來生產
- electrons 在 electron transport chain 移動產生的能量
- ETC 是 mitochondrion inner membrane 中一系列的 proteins
- electrons 來自 glucose,並由 electron carriers (NAD+, FAD) 運送到 ETC
- 所以會變成 NADH 跟 FADH2
- electrons 在 electron transport chain 移動產生的能量
現在來將四個步驟各別進行簡單的解釋
Glycolysis
- 將 glucose (6 carbon sugar) 進行一連串 chemical transformations
- 轉換成 2 個 molecules 叫做 pyruvate (3 carbon organic molecule)
- 並且直接產生出 ATP
- 而 NAD+ 獲得 electrons 變成 NADH
Pyruvate oxidation (Oxygen needed)
- 2 個 pyruvate 進入 mitochondrial matrix
- 結合 coenzyme A 形成 acetyl CoA (2 carbon molecule)
- 釋放出 carbon dioxide
- 而 NAD+ 一樣獲得 electrons 變成 NADH
Citric acid cycle (Oxygen needed)
- Acetyl CoA 結合一個 4 carbon molecule 進行一個 cycle 的 reactions
- 最終又產出一個 4 carbon molecule
- 直接產生 ATP
- 結合 electron 產生出 NADH, FADH2
- 釋放出 carbon dioxide
Oxidative phosphorylation (Oxygen needed, directly used)
- NADH 和 FADH2 來到 ETC 釋放出 electrons,變回 NAD+ 跟 FAD
- Electrons 移動釋放能量來 pump protons 形成 gradient
- 回到 matrix 的 protons 通過 ATP synthase (enzyme) 產生 ATP
- Oxygen 最終會和 electrons 形成水
因為後三個工程都需要用到 oxygen,所以在第一步 glycolysis 沒有使用 oxygen 的話,會變成 fermentation !
接下來我們將詳細認識這四個大工程
Glycolysis
人類、生物跟某些細菌一樣,在處理 glucose 代謝前的第一步一定是 glycolysis
- Glycolysis 將把 glucose (6 carbon) 拆成 2 個 pyruvate (3 carbon) molecules
- Glycolysis 在過程中會從 glucose 萃取 energy
- Glycolysis 不需要 oxygen 的參與就可進行
Glycolysis 總共有 10 個步驟,想要更詳細的知道其中的化學原理,可以參考 Steps of glycolysis, 但這邊我只想要了解簡單版本
- Glycolysis 在 cytosol 中進行,主要有兩階段
- Energy-requiring phase (下圖虛線上方)
- Energy-releasing phase (下圖虛線下方)
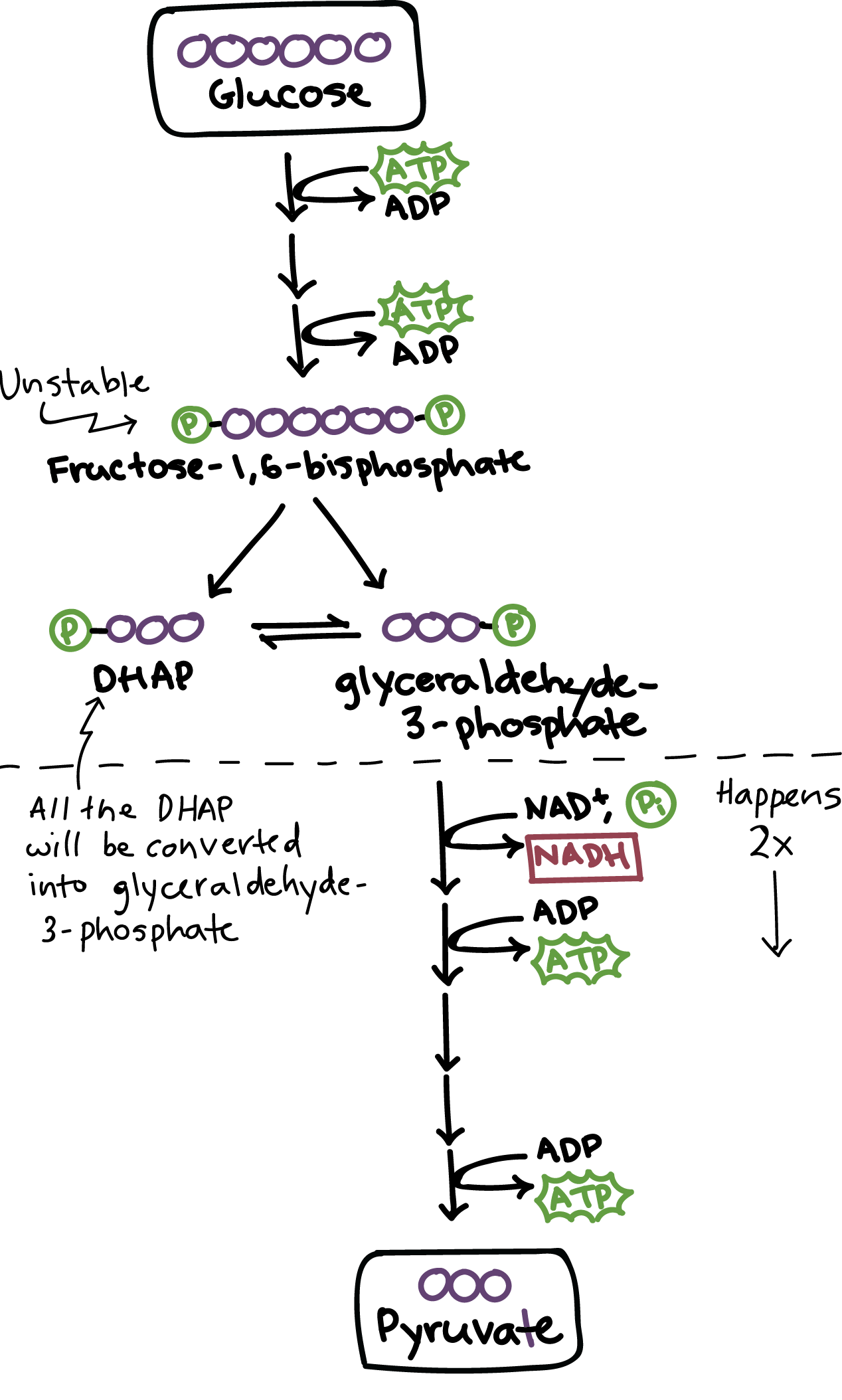
Energy-requiring phase
- Glucose 被重新排列,和 2 個 phosphate groups 結合
- 產生了新的 sugar 叫做 fructose-1,6-bisphosphate (unstable)
- 2 個 P 是從 ATP 變成 ADP 而來,所以 glycolysis 需要 2 個 ATP
- 因為不穩定,所以可以被拆成 2 個擁有 3 個 carbon 的 sugars
- 一個叫 glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate 可以接下去工作
- 一個叫 DHAP 不能工作下去,但他可以輕鬆轉換成 glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
- 所以最後會有 2 個 glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
Energy-releasing phase
- 在這個階段,每個 glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate 要變成 pyruvate 會經過一些反應
- 反應中將產生 2 個 ATP 和 1 個 NADH
- 所以共會產生 4 個 ATP 和 2 個 NADH
- 因為有 2 個 glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
Glycolysis 的所有反應都有獨自的 enzyme 來幫助催化
- 例如 phosphofructokinase 幫助 fructose-1,6-bisphosphate 進行催化
- 能根據細胞所需能量,調節 glycolysis 的速度
總結一下,在 Glycolysis 將 1 個 glucose:
- 轉成 2 個 pyruvates (3 carbon molecule)
- 花費 2 個 ATP 得到 4 個 ATP (淨生產是 2 個 ATP)
- 得到 2 個 NADH molecules
Pyruvate oxidation
Glycolysis 產生的 2 個 pyruvates 還可以透過 oxidation 被萃取出 energy
- Pyruvate oxidation 會在 mitochondria 最內部的 matrix 進行 (eukaryotes)
- 若是 prokaryotes 會在 cytoplasm 進行
- Oxidation 中,Pyruvate 會變成 Acetyl CoA
- Pyruvate 去除一個 carbon 並與 Coenzyme A 組合而成
- 產生 NADH
- 釋放 carbon dioxide
Acetyl CoA 將成為下一個工程 citric acid cycle 的燃料 !
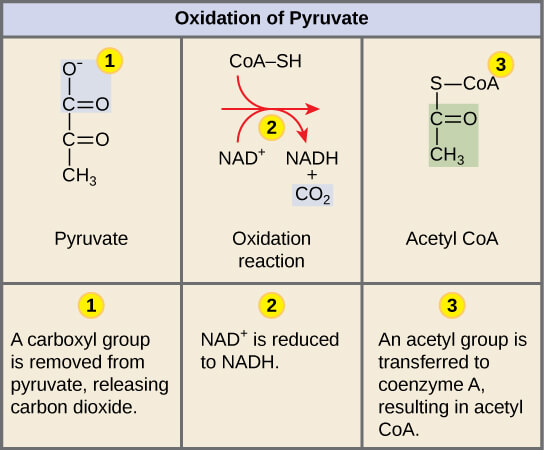
首先 carboxyl group (藍色) 將會從 pyruvate 提取出來
- carboxyl 會被作為 carbon dioxide 釋放
- 留下剩下的 2 個 carbon 部分
剩下的 2 個 carbon 部分會被 oxidized
- 失去的 electron 會和 NAD+ 形成 NADH
Oxidized 後的東西叫做 acetyl group (綠色)
- Acetyl group 和 Coenzyme A (CoA) 組合形成 acetyl CoA
- Acetyl CoA 其實是一個 carrier
- 運送 acetyl group 去 citric acid cycle
整個過程有一個大的 enzyme complex 叫做 pyruvate dehydrogenase complex 幫助
- Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex 由 3 個 enzymes 組成
- 有 60 個 subunits
- 調節 acetyl CoA 生成的速度
我們將 glycolysis 生成的 2 個 pyruvates 帶進 oxidation 總結可以得到:
- 2 個 acetyl CoA
- 2 個 NADH
- 2 個 carbon dioxide 釋放
- Glucose 的 6 個 carbon 有 2 個不見了
Citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle)
Citric acid cycle 是 cellular respiration 的核心,甚至有三個名字
- Citric acid cycle
- 第一個參與的東西是 citric acid (檸檬酸)
- Tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle
- 前兩個反應的媒介是 3 個 carboxyl groups
- Krebs cycle
- 發現者是 Hans Krebs
在 Citric acid cycle 會產生非常多的 NADH 和 FADH2 與幾個 ATP,這些 NADH, FADH2 將會在 ETC 被轉換成非常多的 ATP
Citric acid cycle 一樣在 mitochondria 的 matrix 執行 (Eukaryotes),或在 cytoplasm (Prokaryotes)
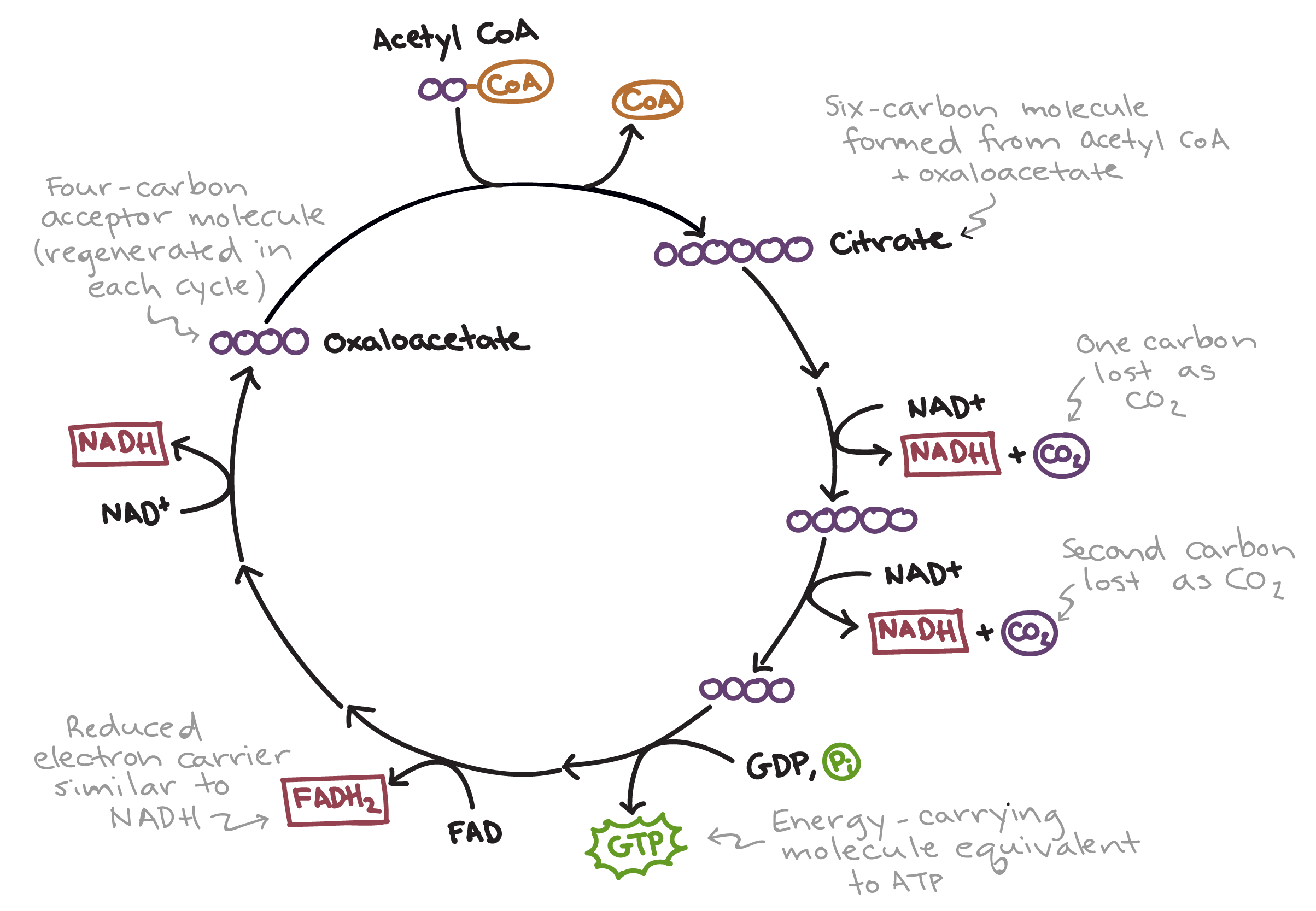
主要會有 8 大步驟形成封閉的迴圈,但這邊一樣簡單理解一下就好
- 首先 acetyl CoA 會和 oxaloacetate (4 carbon acceptor) 組成 citrate 並重新排列
- Citrate 就是 cycle 命名原因,有 6 個 carbon
- 接著會將 2 個 carbon 以 carbon dioxide 釋放掉
- 產生 2 次 NADH molecule
- 到這邊有一些 enzymes 非常重要,掌握了整個 cycle 的快慢
到這邊 carbon 從 6 變成 4 個,跟最終要變回的 oxaloacetate 一模一樣
- 接著進行反應產生 1 個 GTP (可以變成 ATP)
- 一次 FAD 變成 FADH2
- 一次 NAD+ 變成 NADH
- 變回 oxaloacetate
最後我們總結一下,一個 Glucose 在 Citric acid cycle 的收穫
- 因為 glucose 產生 2 個 acetyl CoA (from pyruvates) 所以每個都要乘以 2
- 進入 2 個 carbon 釋放 2 個 carbon dioxide * 2
- 產生 3 個 NADH * 2
- 產生 1 個 FADH2 * 2
- 產生 1 個 GTP (ATP) * 2
所以淨收穫是 6 個 NADH 和 2 個 FADH2 還有 2 個 ATP
想看更完整的化學反應可以參考下圖
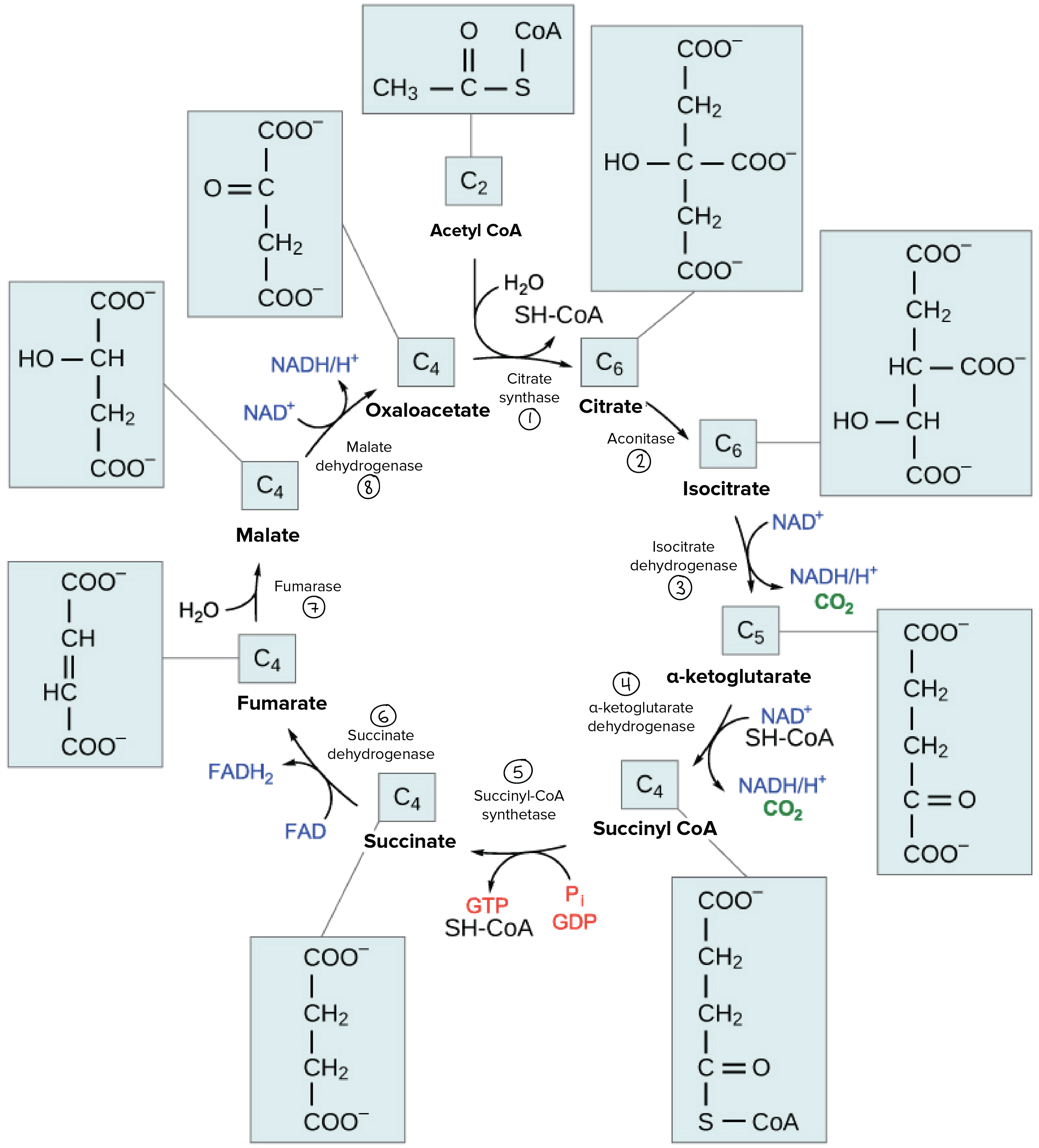
Oxidative phosphorylation
為什麼人沒呼吸、缺氧就會死掉 ? 跟 oxidative phosphorylation 有很大的關係
- Oxidative phosphorylation 需要 oxygen 才能運作
- 由兩大元件組成
- Electron transport chain
- electrons 在 molecules 之間進行 transfers
- 製造了 electrochemical gradient 的環境
- Chemiosmosis
- 利用 gradient 來產出 ATP
- Electron transport chain
- 由兩大元件組成
Oxygen 出現在 electron transport chain 的最後
- Oxygen 將領取 electrons 和 protons 來形成 water
- 如果沒有 oxygen (閉氣) 整個流程會停止
- ATP 就不再會由 chemiosmosis 產生
- 導致所有細胞都沒有 energy 能夠推動運作
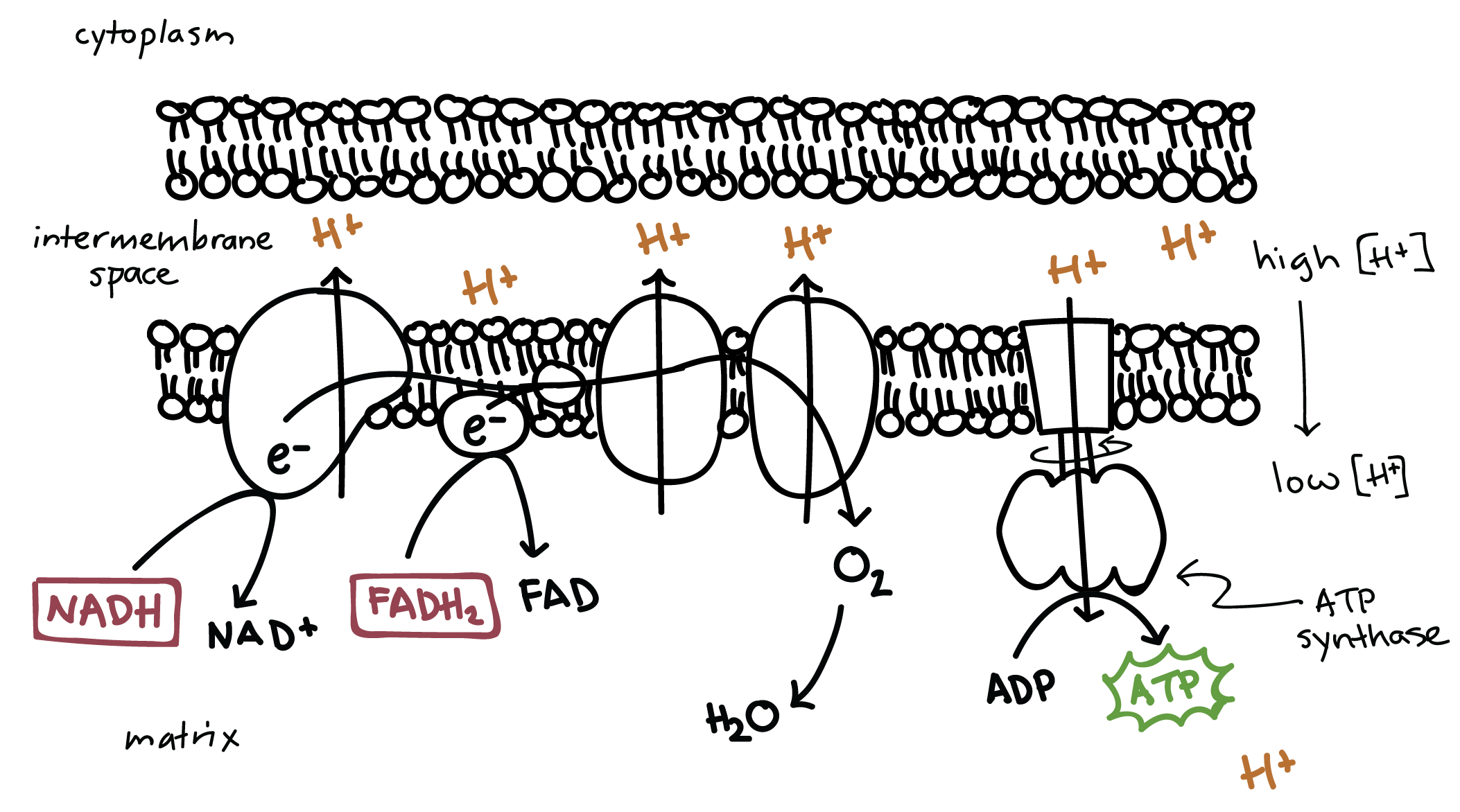
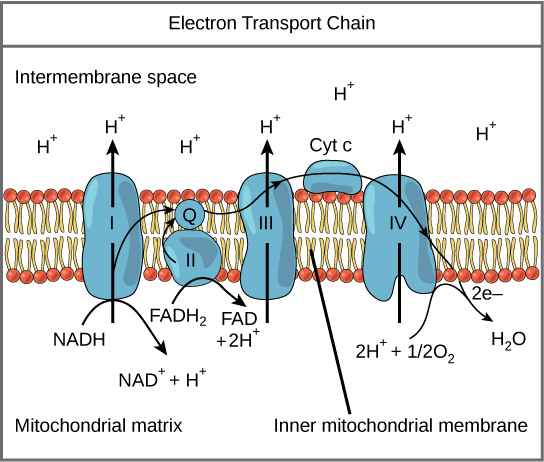
- 主角 electron transport chain (ETC) 是位在 mitochondria 的 inner membrane 中的一系列 proteins
- Electrons 將會在 transport chain 之間位移,進行一連串的 redox reactions
- 釋放出的 energy 將成為 proton gradient 作為 chemiosmosis 的利用工具
- Chemiosmosis 是產生 ATP 的 process
- electron transport chain 和 chemiosmosis 就是 oxidative phosphorylation 的核心
簡單來說,oxidative phosphorylation 過程可以用以下四點來解釋 :
Delivery of electrons by NADH and FADH2
- Respiration 前三步驟產生的 NADH 和 FADH2 終於能卸貨
- 把身上的 electrons 都放到 transport chain 的起點
- 然後變回 NAD+ 和 FAD 繼續回到其他地方工作
Electron transfer and proton pumping
- Electrons 在 chain 上從 higher energy 移動到 lower energy level
- 釋放的 energy 被用來 pump H+ ions
- H+ ions 離開 matrix 來到 intermembrane space
- 外部的 H+ 濃度大於內部,產生了 electrochemical gradient
Splitting of oxygen to form water
- 在 chain 的終點,這些 electrons 會和 molecular oxygen 結合產出水分子
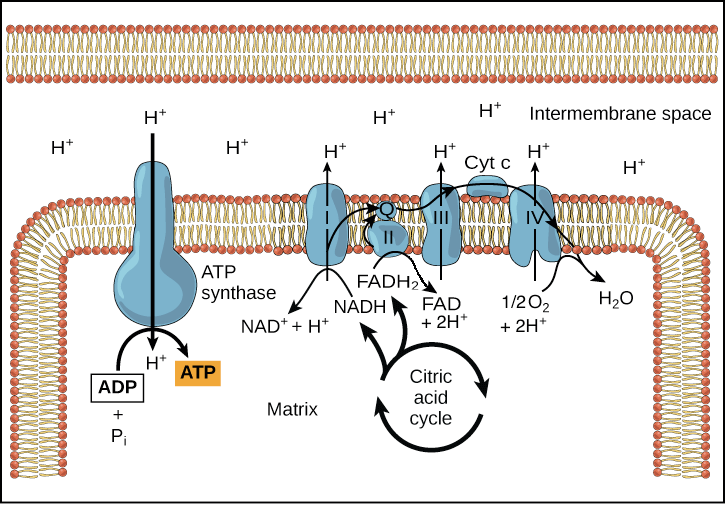
Gradient-driven synthesis of ATP
- H+ ions 隨著 gradient 移回 matrix
- 他們會通過一種 enzyme 叫做 ATP synthase
- 將 ADP 合成為 ATP
以上只是對過程的簡單解釋,詳細過程只用下面兩張圖帶過
- The electron transport chain
- Chemiosmosis
ATP yield
- 現在來統整一下 ATP 的總收益
- 根據研究, 4 個 H+ ions 進行 pump 可以產生 1 個 ATP
- 一個 NADH 所帶的 electrons
- 約可產生 10 H+ ions 來 pump 產生約 2.5 個 ATP
- 一個 FADH2 所帶的 electrons
- 約可產生 6 H+ ions 來 pump 產生約 1.5 個 ATP
- 一個 NADH 所帶的 electrons
| Stage | Direct products | Ultimate ATP yield (net) |
|---|---|---|
| Glycolysis | 2 ATP | 2 ATP |
| 2 NADH | 3-5 ATP | |
| Pyruvate oxidation | 2 NADH | 5 ATP |
| Citric acid cycle | 2 ATP/GTP | 2 ATP |
| 6 NADH | 15 ATP | |
| 2 FADH2 | 3 ATP | |
| Total | 30-32 ATP |
- 因為 glycolysis 是在 cytosol 發生
- NADH 無法直接來到 mitochondria 內部,需要額外的 shuttle system
- 人體細胞有的需要利用 FADH2 來幫助
- 所以只能產生 3 個 ATP
- 有的細胞能用 NADH 幫助
- 所以能產生 5 個 ATP
- 細菌一律在 cytosol 進行,所以一定產生 5 個 ATP
- 人體細胞有的需要利用 FADH2 來幫助
- NADH 無法直接來到 mitochondria 內部,需要額外的 shuttle system
另外 30-32 ATP 甚至有點高估,因為 energy 有時會直接供應其他地方使用
Fermentation and anaerobic respiration
酵母是如何將大麥麥芽發酵成啤酒 ? 肌肉如何處理無氧運動 ? 都跟在 cytoplasm 發生的以下兩件事有關
- 這兩件事皆發生於 aerobic cellular respiration 無法進行時
- Aerobic = oxygen using
- 也就是 oxygen 不在 electron transport chain 的最後幫忙
- 這些 fermentation pathways 主要組成由
- Glycolysis 和一些額外的 reactions 接在一起
- 例如 yeast 的額外 reactions 會產生 alcohol
- 而 muscle 的額外 reactions 會產生 lactic acid (乳酸)
- Glycolysis 和一些額外的 reactions 接在一起
但並不是所有的 fermentation 都是 anaerobically (non-aerobic) 來進行
- 有的 bacteria, archaea 直接利用別的東西來取代在 ETC 尾巴的 oxygen
- 例如使用 sulfate 作為 acceptor
- 這種方法稱為 anaerobic cellular respiration
Fermentation
- Fermentation (Anaerobic pathway)
- Non-oxygen-requiring pathway
- 唯一有萃取 energy 的工作只有 glycolysis
- 產生的 NADH 無法用正常的 ETC 程序消回原本的 NAD+
- 所以接續的工作 (extra reactions) 主要目標是將 NADH 變回 NAD+
- 讓 NADH 的 electrons 丟入一些 organic molecule (e.g., pyruvate)
- 如此就可以確保足夠的 NAD+ 能繼續進行 glycolysis
Lactic acid fermentation
- NADH 直接將 electrons 傳給 pyruvate 就是 lactic acid fermentation
- 會產生 lactate 作為 byproduct
- Lactate 是 lactic acid 被 deprotonated 後的樣子
- 會產生 lactate 作為 byproduct

- 常見的 lactic acid fermentation
- Bacteria 產生 yogurt 時
- Red blood cells (因為沒有 mitochondria)
- Muscle cells (只在 oxygen 太少的情況)
- lactic acid 會被 bloodstream 傳送回 liver
- 變回 pyruvate 然後由 cellular respiration 正常使用
Alcohol fermentation
- NADH 會將 electrons 傳給 pyruvate 的衍生物,然後產生 ethanol (乙醇)
- 是一個兩步驟的 process
- 首先 pyruvate 的 carboxyl group 被提出釋放成 carbon dioxide
- 產生 2 個 carbon 的 acetaldehyde (乙醛)
- NADH 再將 electrons 丟給 acetaldehyde
- 產生出 ethanol
- NADH 就可以變回 NAD+
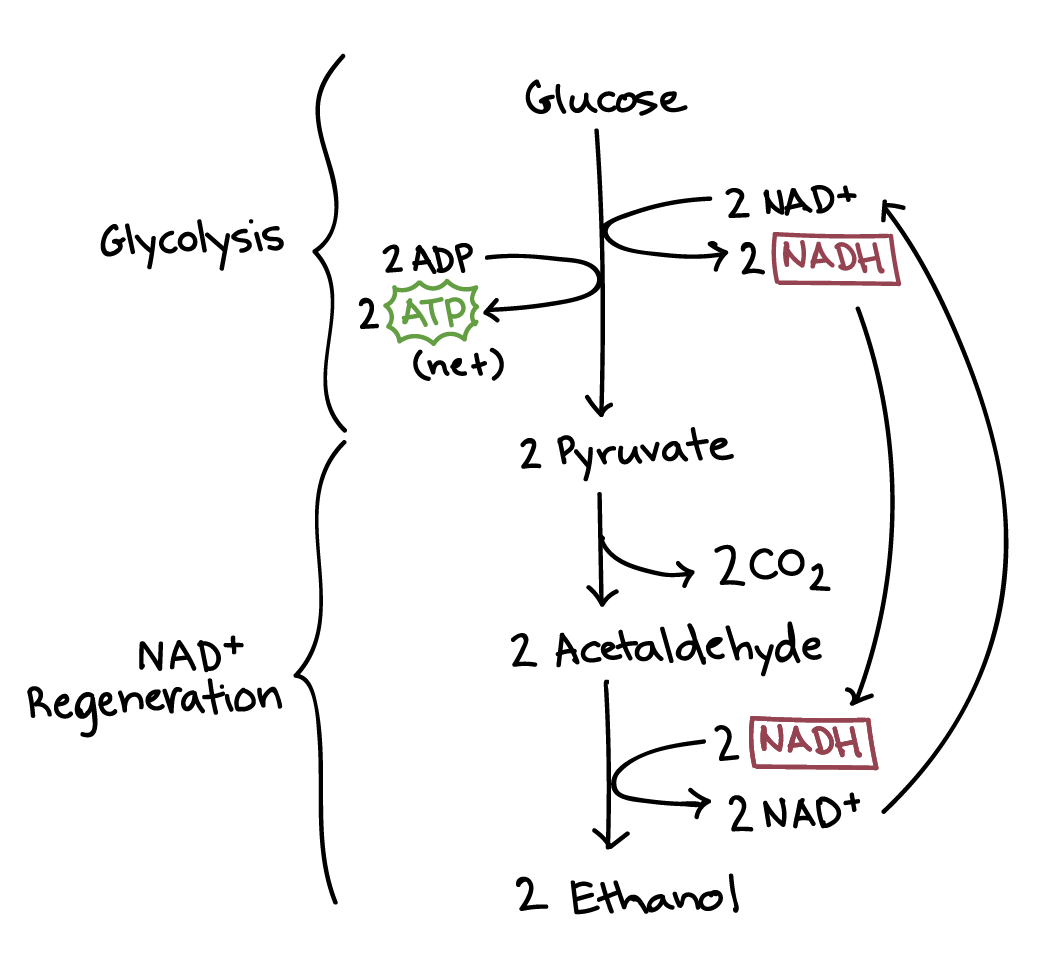
- 由 yeast 主導 alcohol fermentation 產出的 ethanol 常見於 beer, wine
- 但過多的 alcohol 對 yeast, human 都有害
- 所以 yeast 的 ethanol tolerance 約在 5% 到 21%
Facultative and obligate anaerobes
很多 Bacteria 和 archaea 可以分成兩大種類 : facultative anaerobes 和 obligate anaerobes
- Facultative anaerobes (facultative: 兼性)
- 可以切換 aerobic 和 anaerobic respiration
- 只要根據 oxygen 的多寡就可以改變
- Oxygen 足夠時就用 aerobic respiration 產生足夠的 ATP
- Oxygen 不夠時還能用 anaerobic respiration 維持生命
- Obligate anaerobes (obligate: 專性)
- 必須只使用 anaerobic respiration 才能生存
- Oxygen 甚至會殺掉這類型的微生物
- 例如 clostridium bacteria
- 還有目前也有許多種 multicellular 的深海生物被發現是 obligate anaerobes