Gene Regulation
Gene Regulation 是指細胞如何決定在什麼時間、什麼地點啟動哪些 genes,以便細胞能夠多樣化的執行不同的事情。Gene Regulation 也會影響到 gene expression 的所有階段,例如 chromatin accessibility、transcription、RNA processing、RNA stability、translation 以及 protein activity 等。
Gene Regulation 會將特定的 genes 啟動,以及讓某些 genes 關閉,這也是為什麼即使細胞都具有一模一樣的 DNA,也會有獨一無二的 active genes 做不同的事情。Gene Regulation 也是透過一個 molecular pathway 觸發 gene expression 執行,而 transcription factors 是 Gene Regulation 的關鍵,會對特定 gene 扮演 activators 或 repressors 的角色。
Eukaryotic gene regulation
人體中的細胞其實都擁有一樣的 DNA instructions,但為什麼可以出現幾百多種類型 ? 答案是 gene regulation
- Gene regulation 會將特定 genes 啟動
- 所以就算細胞都擁有一模一樣的 DNA
- 也會有獨一無二的 active genes 做不同的事情
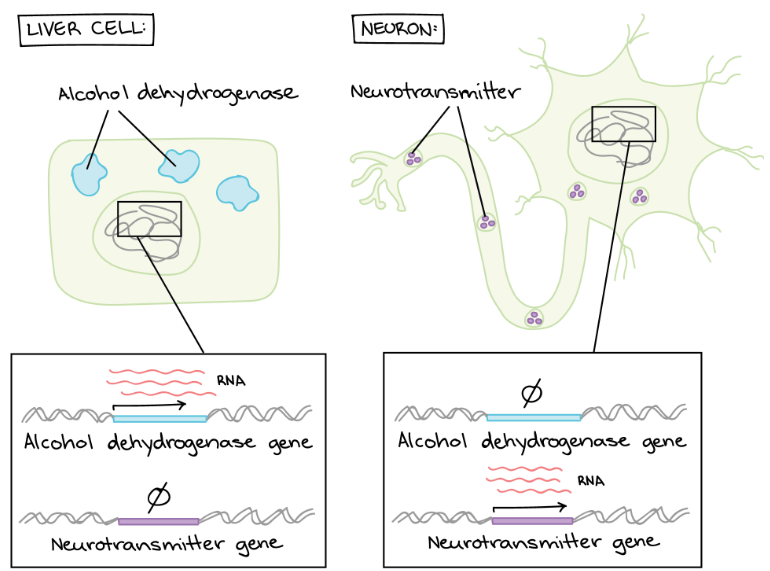
- 例如肝細胞為了要移除有毒物質
- 會啟動產生 alcohol dehydrogenase 的 genes
- 而神經細胞就不會啟動這個 gene
- 相反的神經細胞要傳遞訊息
- 會啟動 neurotransmitter 相關的 genes
- 而肝細胞就會關閉這個 gene
How do cells "decide" which genes to turn on?
簡單來說,細胞將靠著內部和外部環境,來決定自己的 gene expression pattern
- Examples from inside the cell
- 從 mother cell 繼承的 proteins
- DNA 是否受損
- ATP 是否足夠
- Examples from outside the cell
- 其他 cells 給的訊號
- Extracellular matrix 的訊號
- Nutrient level
這些因素又是怎麼觸發 gene expression 執行 ? 答案是透過一個 molecular pathway
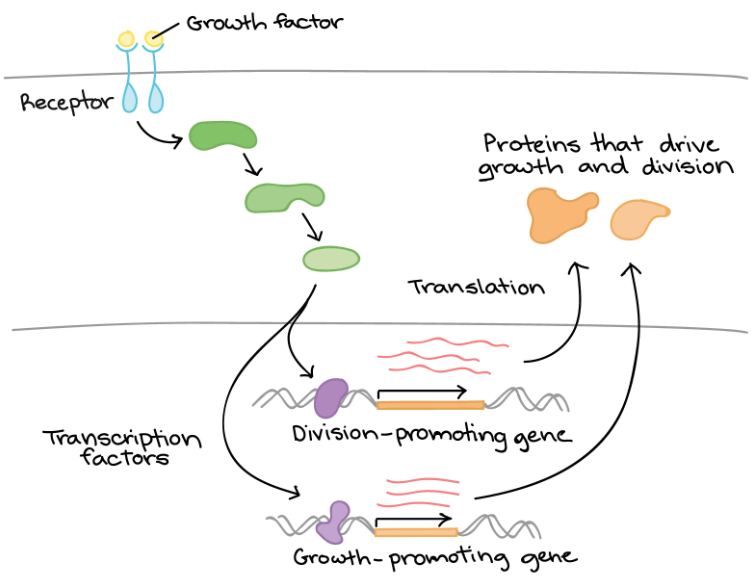
以上是細胞根據鄰居細胞給的 growth factors 來執行 gene expression
- 細胞透過表面的 receptor protein 偵測到 (結合) growth factor
- Receptor 改變形狀引起一連串的活動,啟動了 transcription factors (protein)
- Transcription factors 和 DNA 結合,讓 nucleus 開始執行分裂相關的 gene transcription
- 最終的產物就是幫助細胞分裂的 proteins
Regulation stages
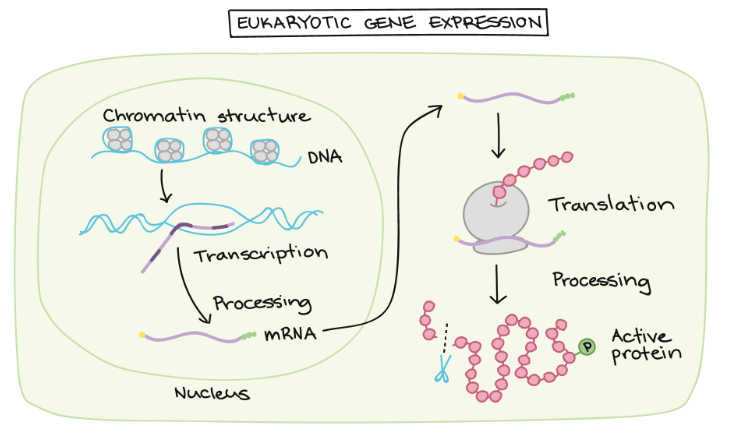
Gene regulation 幾乎出現在 gene expression 的每個階段
- Chromatin accessibility
- Chromatin 的架構可被調節
- 越 open (relax) 的 chromatin 越適合 transcription
- Transcription
- Transcription factors 會和特定 DNA sequences 結合
- 促進或壓抑 RNA transcription 的執行
- RNA processing
- Splicing, capping, adding poly-A tail 可被調節
- 是否要讓 RNA 離開 nucleus
- Alternative splicing 也可以製造出不同的 mRNAs
- RNA stability
- mRNA 在 cytosol 的壽命會影響到 proteins 製造的多寡
- miRNAs 會結合並除掉 (chop up) 特定的 mRNAs
- Translation
- Translation 的執行次數可以被 regulators 影響而增加或減少
- miRNAs 有時會檔住 translation
- Protein activity
- 被製作出來的 proteins 可以被修改
- 修改就會影響 protein 的行為和活動
其中最重要的是 transcription,後面幾個 regulation 幾乎都是在 transcription 時制定的 !
Transcription factors
人類在 transcription 需要 basal (general) transcription factors 的幫助,才能將 RNA polymerase 放到 DNA promoter 的位置上
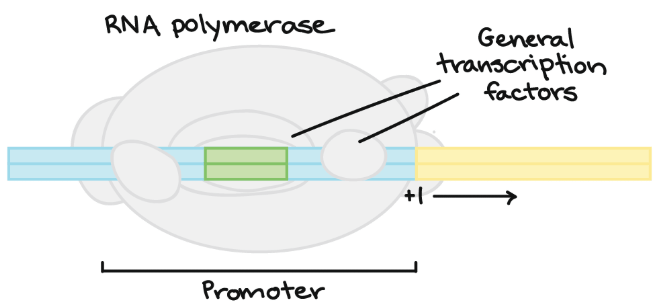
- Transcription factors 不只 general 一種
- 有非常多種類的 transcription factors
- 每種可能對應於特定的 genes
但這些 transcription factors 都會到目標的 DNA 上與之結合,促進或抑制 RNA polymerase 結合 promoter
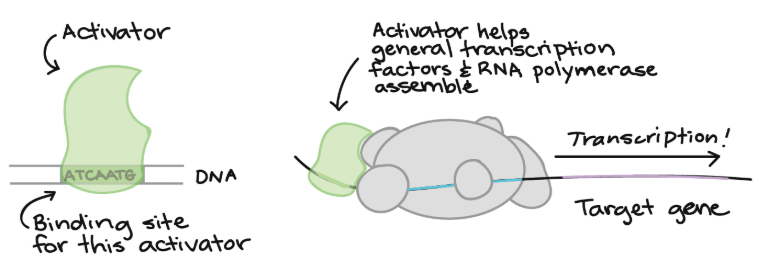
Activators
- 一些 transcription factors 是 activator
- 幫助 general transcription factors 和 RNA polymerase 更容易結合到 promoter 上面
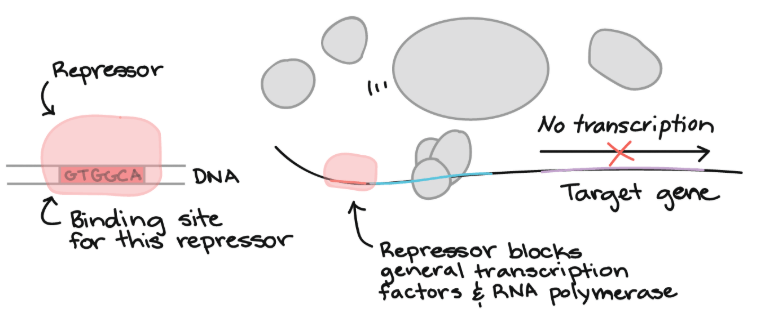
Repressors
- 一些 transcription factors 是 repressor
- 讓 general transcription factors 和 RNA polymerase 很難和 promoter 結合
- 有很多種方法阻止結合,以下是其中一種
Binding sites
- Transcription factors 通常非常靠近 gene's promoter
- 但也可以在 DNA 的其他地方,離 promoter 很遠
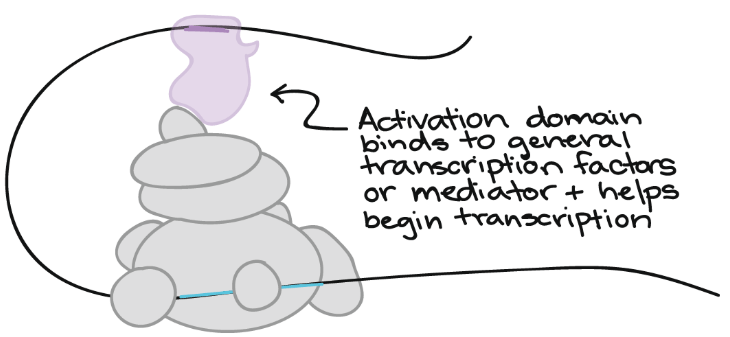
- 因為 DNA 非常有彈性
- 讓遠處的 transcription factors 可以透過 DNA 的變形接近 promoter
Turning genes on in specific body parts
有的 gene 會控制身體很多個地方的細胞,那 transcription factors 要如何和這種 gene 互動 ?
- 這種 gene 可以會有多個 enhancers 或 silencers
- Enhancers 代表有多個給 activators 結合的 binding sites
- Silencers 代表有多個給 repressors 結合的 binding sites
以老鼠為例,有一個 gene 控制非常多身體的成長,叫做 Tbx4
- 所以 Tbx4 上就有多個 enhancers
- 每個 enhancers 對應不同的生長部位
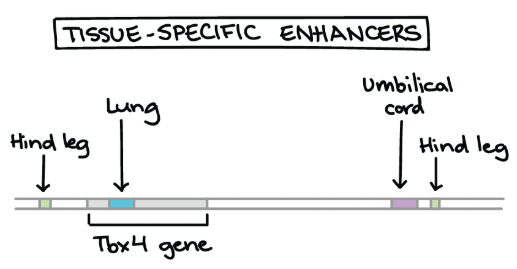
- 這種 enhancers 又叫做 tissue-specific enhancers
- 控制身體特定部位的 gene expression
- Tissue-specific enhancers 或 silencers 突變,是進化的關鍵
Transcription factors and cellular "logic"
很多 genes 會被多個 transcription factors 所控制,所以 factors 的組合會決定 gene 的啟動與否
- 透過 transcription factors 組合來控制 gene 又叫做 combinatorial regulation
- 例如下圖的 gene 只在 A, B 出現,而 C 不在時才會啟動
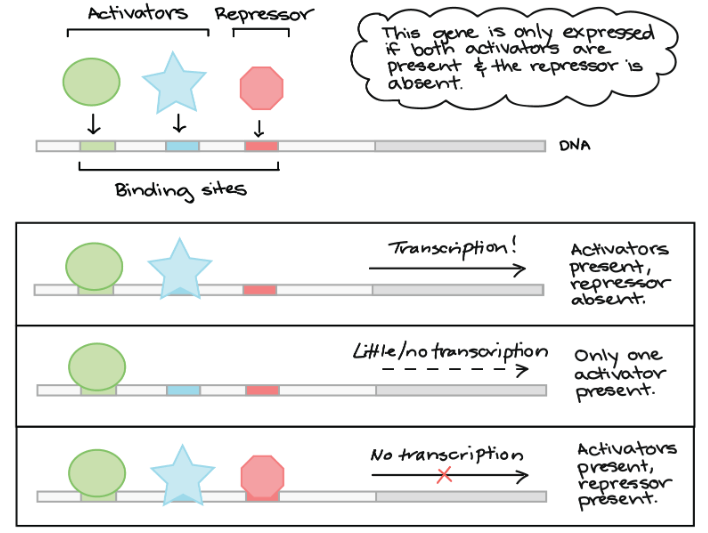
- 若 Activator A 只出現在 skin cells
- Activator B 在收到 growth factors 時出現,代表要 divide cell
- Repressor C 會在 DNA 損傷時出現
那這個 gene 就是在 "健康的" skin cells 中取得 growth factors 後控制細胞分裂的角色
Regulation after transcription
mRNA 在 transcription 後離開 nucleus 一樣能夠被調節,調節重點有兩個:
- Lifespan of mRNA in cytosol
- How readily the translation
microRNAs
有一個 regulators 叫做 small regulatory RNAs 被發現能調節上述兩個因子
- microRNAs (miRNAs) 是第一個被發現的 small regulatory RNAs
- miRNA 一樣被 transcribe 成 RNA molecules
- 釋出 22 nucleotides 的 small double-stranded fragment
- 其中一串就是 mature miRNA
- 將會跟特定 protein 結合成 microRNA-protein complex
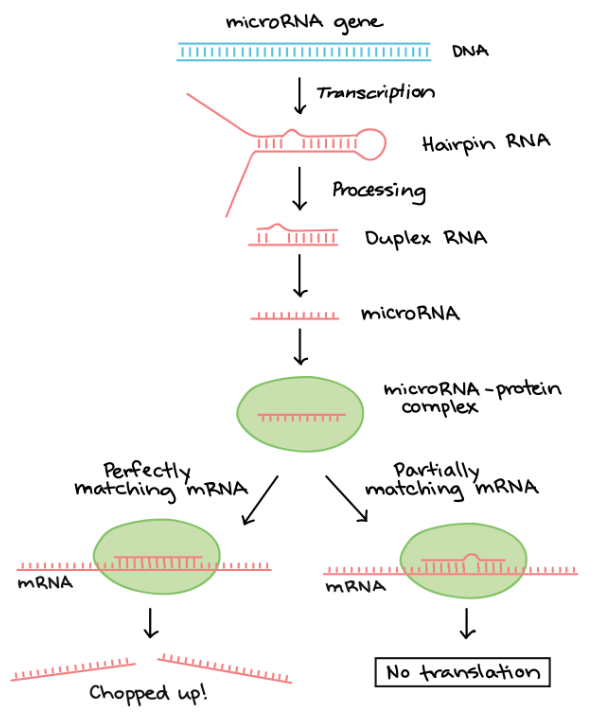
miRNA 將會指引整個 protein complex 去和 mRNA 配對
- 若完全配對
- RNA-protein complex 中的 enzyme 就會把 mRNA 整個切掉
- 若配對有少部分錯誤
- 會代替 ribosome 和 mRNA 結合,停止 translation
Regulation of translation
Translation 的調節發生在 initiation
- Ribosome 為了正確與 mRNA 結合,需要很多 "helper" proteins
- 改變這些 helpers 的活動就是調節目標
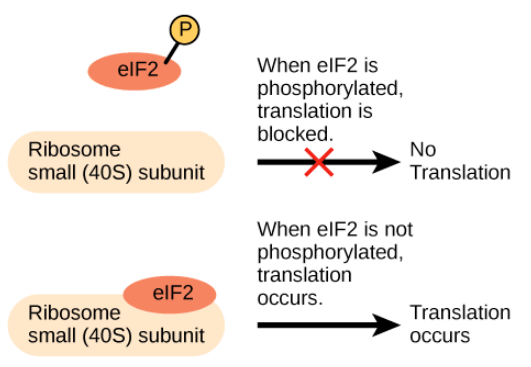
- 例如其中一個 protein 叫做 eukaryotic initiation factor-2 (eIF-2)
- eIF-2 必須要結合到 ribosome 的一個部位
- 當 eIF-2 被加上一個 phosphate group (been phosphorylation)
- 就無法幫助 ribosome 進行 translation
- 當 eIF-2 沒有被 phosphorylation
- 就可以進行 translation
- 當 eIF-2 被加上一個 phosphate group (been phosphorylation)
Proteins can be regulated after translation
產生的 protein 依然可以被調節,一些對 protein 的 edit 可以改變其行為及活動
- 有的 protein 可能需要被切開才能啟動
- e.g., insulin
- 有的 protein 則需要其他 chemical groups 加到身上
- e.g., methyl, phosphate, acetyl, ubiquitin
Phosphorylation
一個最常見的 post-translational modifications 就是 phosphorylation
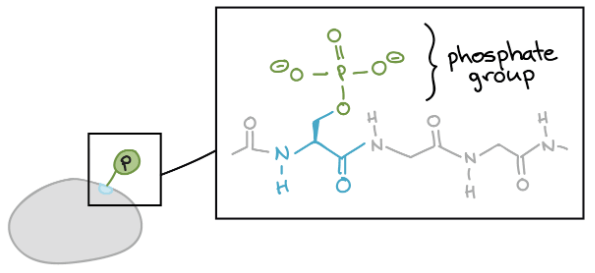
- Phosphate group 依附到 protein 上
- 可能造成 protein 被 activated 或 deactivated 甚至改變行為
- 前面說到的 eIF-2 就是一個例子
Ubiquitination
Ubiquitination 則是 protein 和 chemical marker ubiquitin 結合的現象
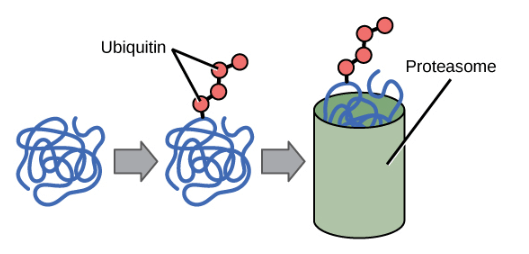
- Ubiquitin-tagged proteins 會被帶到 proteasome
- 拆解成 components 回收利用
- Ubiquitination 控制了細胞中 protein 的 persistence