Evaluation
本文探討了評估演算法的不同方法,包括 Recall 和 Precision 、Top-k Precision 、Average Over Multiple Queries、Single Value Summaries、Mean Reciprocal Rank、Precision-Recall、F-score、User-Oriented Measure、Alternative Measures 和 Cost Matrix。
每個指標都有其特定的作用,例如 Recall 用於衡量系統可以檢索到的相關文件的比例,而 Precision 則可以衡量檢索到的文件有多少是正確的;Top-k Precision 能夠評估排列在前 k 名的文件的正確性;Average Over Multiple Queries 則能夠提供多個查詢的平均準確性;Single Value Summaries 則可以提供一個準確的單一值總結;Mean Reciprocal Rank 能夠衡量第一個結果的排名;Precision-Recall 則可以用於衡量不同類別的準確性,而 F-score 則能夠找出 precision 和 recall 之間的 tradeoff;Alternative Measures 能夠將預測與結果分為 True/False 的 Positive/Negative 四類,以及 Cost Matrix 能夠衡量錯誤結果的價值。
Recall and Precision
- Recall
- The fraction of the relevant documents (R) which has been retrieved
- Precision
- The fraction of the retrieved documents (A) which is relevant
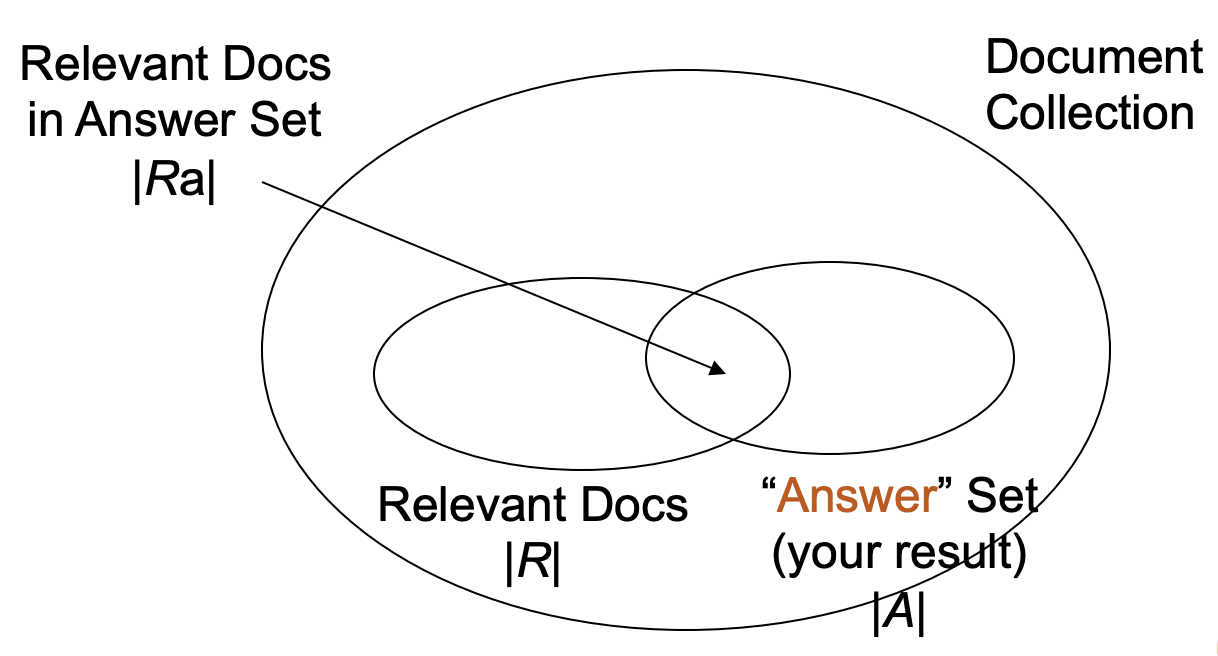
- Precision versus recall curve
- 通常 Recall 越高,會使 Precision 越低 (tradeoff)
- P = 100% at R = 10%
- P = 66% at R = 20%
- P = 50% at R = 30%
- 通常 Recall 越高,會使 Precision 越低 (tradeoff)
Top-k Precision (Precision at k, P@k)
- Precision evaluation in a ranking list
- The precision value of the top-k results
Top-1 = P@1,Top-3 = P@3- 前 5 筆有 2 筆中,P@5 = 2/5 = 40%

Average Over Multiple Queries
- Average precision at the recall level r
Interpolated precision
- What is interpolation mean ?

- 下方的 (P, R) 分別為讀到第三個、第八個、第十五個時候
Single Value Summaries
- Average precision 可能會隱藏演算法中不正常的部分
- 需要知道對某特定 query 的 performance
- The single value should be interpreted as a summary of the corresponding precision versus recall curve
Average Precision
- Seen Relevant Documents
- obtained after each new relevant document is observed
- e.g.
- 此方法對於很快找到相關文件的系統是相當有利的
- 相關文件被排在越前面, precision 值越高
Mean Average Precision (MAP)
- Average of the precision value obtained for the top k documents
- each time a relevant doc is retrieved
- Avoids interpolation, use of fixed recall levels
R-Precision
- break-even point: recall = precision
- The precision at the R-th position in the ranking
- R : the total number of relevant documents of the current query
Comparison
RNRNN NNNRR
- MAP = (1 + 2/3 + 3/9 + 4/10) / 4 = 0.6
- RP(4) = 2/4 = 0.5
- (只看前四個)
NRNNR RRNNN
- MAP = (1/2 + 2/5 + 3/6 + 4/7) / 4 = 0.49
- RP(4) = 1/4 = 0.25
MRR: Mean Reciprocal Rank
- Rank of the first correct answer

Precision-Recall
| Class | Predicted | Correct? |
|---|---|---|
| orange | lemon | 0 |
| orange | lemon | 0 |
| orange | apple | 0 |
| orange | orange | 1 |
| orange | apple | 0 |
| lemon | lemon | 1 |
| lemon | apple | 0 |
| apple | apple | 1 |
| apple | apple | 1 |
Microaveraging
- 重視數量的差距
- Each Instance has equal weight
- Largest classes have most influence
Macroaveraging
- 每個 rank 都一樣重要
- Each Class has equal weight
P/R 適用性
- Maximum recall 需要知道所有文件相關的背景知識
- 平時不太可能得到標準答案,因為實際案例的 Recall 不好算
- Recall and precision 是相對的測量方式,兩者要合併使用比較適合
- Application dependent
F-score
The Harmonic Mean, F-measure
Example
Harmonic

User-Oriented Measure
- 在不同領域上可以修改 recall / precision 來進行不同評分
- e.g. coverage / novelty
- Coverage 越高,找到越多 user 期望文件
- Novelty 越高,找到越多使用者原本不知道的文件
- 這些評分都需要先經過繁雜的 labeling
Alternative Measures (confusion matrix)

- 將預測與結果分為 True/False 的 Positive/Negative 四類
- 可以改寫原本的 Recall / Precision
- Recall 又可稱為 Sensitivity
- 新增兩種測量方法
- Accuracy 就是所有猜對的機率
- Specificity 可以看作 Negative Recall
- Not useful, TN is always too large
Example

- 100% sensitivity 代表完全猜對所有生病的人
- 100% specificity 代表完全猜對所有健康的人
Limitation of Accuracy
- 想像 class 0 的 examples 有 9990 個
- 然後 class 1 的 examples 只有 10 個
- 我的模型全猜 class 0
- Accuracy = 9990/10000 = 99.9%
- 這個 acc 誤導我們,讓我們以為模型超強
Cost Matrix
- Cost matrix 和 confusion matrix 幾乎一樣
- 給 false negative 的 weight 加大
Example
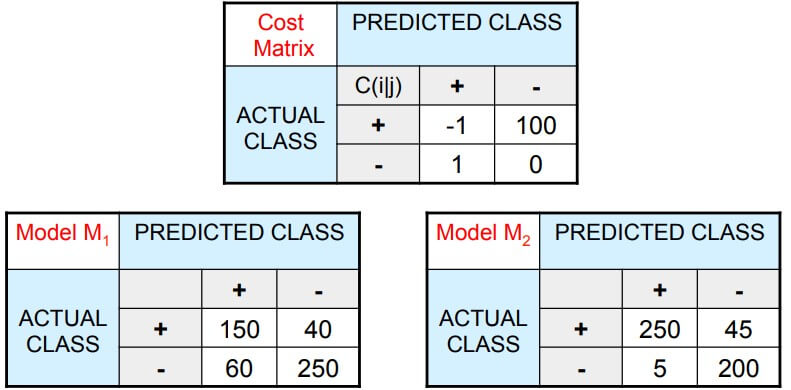
- 我們設置上面 matrix 為計算的標準
- False Negative (猜沒生病,但其實有生病) 的權重 Cost 為 100
- 左邊的預測可以得到
- acc =
- cost =
- 右邊的預測可以得到
- acc =
- cost =
- 可以發現雖然右邊 acc 較高,但 cost 也較高
- 很多情況,例如醫學上可能就不能容許 cost 較高情況出現
ROC
- ROC : Receiver Operating Characteristic
- ROC is a plot of sensitivity vs. 1-specificity for a binary classifier
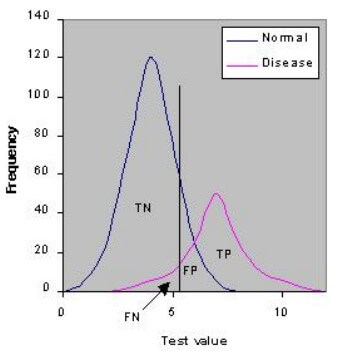
ROC curve
- ROC 的結果可以等同於 plot TP fraction vs. FP fraction
- the area under the ROC curve, or "AUC"
- AUC 越大,代表分類器正確率越高
Example
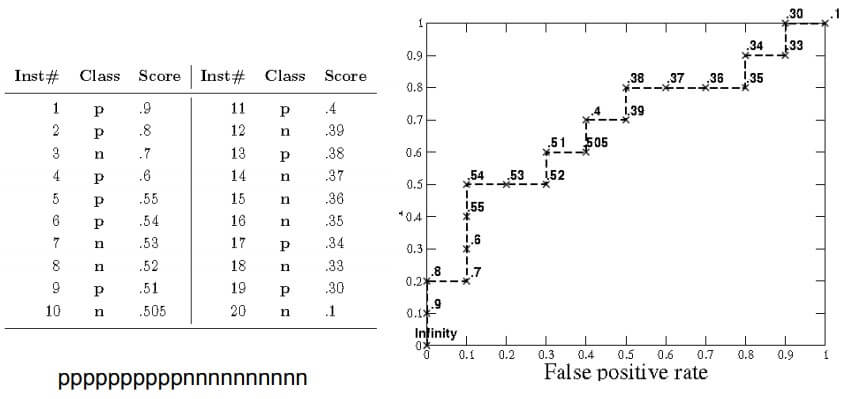
- 利用預先算好的結果 plot 到圖上
- True Positive 就往上走
- False Positive 就往右走
- 若是 ppppppppppnnnnnnnnnn 就會是一個 的形狀
Issues
- ROC curves are insensitive to changes in class distribution
- TPR and FPR are all strict columnar ratio
- 對於不 balance 的 data,產生的結果差不多,因為是參考 ratio
- ROC measures the ability of a classifier to produce good relative scores.
- need only produce relative accurate scores that serve to discriminate positive and negative instances
Questions
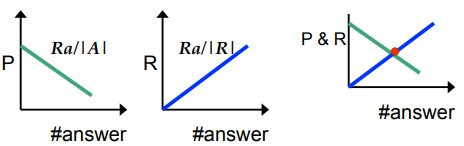
Q : What is the relationship between the value of F1 and the break-even point?
A : at break-even point F1 = P = R.
Q : Prove that the F1 is equal to the Dice coefficient of the retrieved and relevant document sets.
A :
Estimation Methods
- Holdout
- 2/3 train, 1/3 test
- Random subsampling
- Repeated holdout
- Cross validation
- Partition data into k disjoint subsets
- k-fold: train on k-1 partitions, test on the remaining one
- LOOCV: k=n (train on all data except 1 for test)
- Stratified sampling
- oversampling vs undersampling
- Bootstrap
- Sampling with replacement
Evaluate Ranked list
- The ground truth is ranked / partially preferred
- DCG
- Correlation coefficient measurement
Discounted Cumulative Gain (DCG)
- measures the usefulness, or gain, of a document based on its position in the result list
- The gain is accumulated cumulatively
- CG is independent with the result order
- DCG is dependent with the result order
- DCG at position p
- The is the graded relevance of the result at position i
Example
| Data | D1 | D2 | D3 | D4 | D5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Score | 2 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 |
Higher is more relevant, The score of order above is
The ideal order is 2, 2, 1, 0, 0
NDCG 將 DCG 正規化
Correlation coefficient measurement
Kendall-tau
- measure the association between two measured quantities
- where
- 找出所有任選兩個數字的前後關係
- e.g. Ground Truth = 12345, Result = 21534
- 前後關係維持一致的是 concordant
- 前後關係變不同的是 discordant
Cohen's Kappa
- 度量兩個評分者 (rater) 的 agreement
Example 1
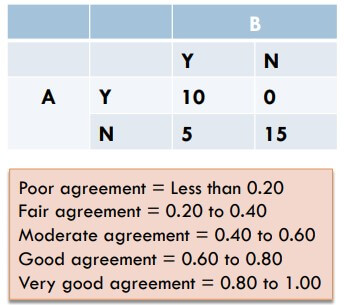
- 例如有 rater A 和 rater B
- 在 30 個投票中,共有 25 個 agreement
- 看起來很高,但有時候是因為很多 noise 導致 (例如選擇太 trivial)
- 解決方法就是減去 這個 random agreement
- 這個 代表的是兩人隨便亂猜就可以一致的機率
- 得到 a 和 e 的機率就可以算出上面的 kappa 值
- 所以 agreement 就從 0.83 下降至 0.66
Example 2
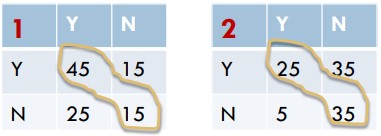
- 雖然兩題在未計算 kappa 之前的 agreement 都是 0.6
- 但計算完 kappa 後,可以發現右邊的 2 raters agreement 較好
Applicability
- each system need to use diff evaluation
- NDCG : sort data, ranking
- Recall : use with ground truth
- Top-1 precision : recommendation
- F1 : find the best in precision + recall tradeoff
- Novelty