Sequence Pattern
本文主要介紹了 Sequence Pattern Mining,它是一種用於找出在時間軸上 Item 之間的 Association Rule 的方法,而我們將一般 Dataset 加上 Timeline 來取得 Sequence Data Table,並且使用 Apriori-based SP algorithm (GSP) 等算法來找出所有的 Frequent Subsequence,再來提出了 Episode Mining 以及 FreeSpan 和 PrefixSpan 演算法,以更有效率的方式找出 Frequent Subsequence。
Sequence Data
在前一章節的 Association Analysis 中,itemset 都是固定一筆一筆所出現。若我們想要更了解 Item 之間的 association rule,勢必要加上時間軸,得到順序與因果關係。我們可以將一般 Dataset 加上 Timeline 取得 sequence data table
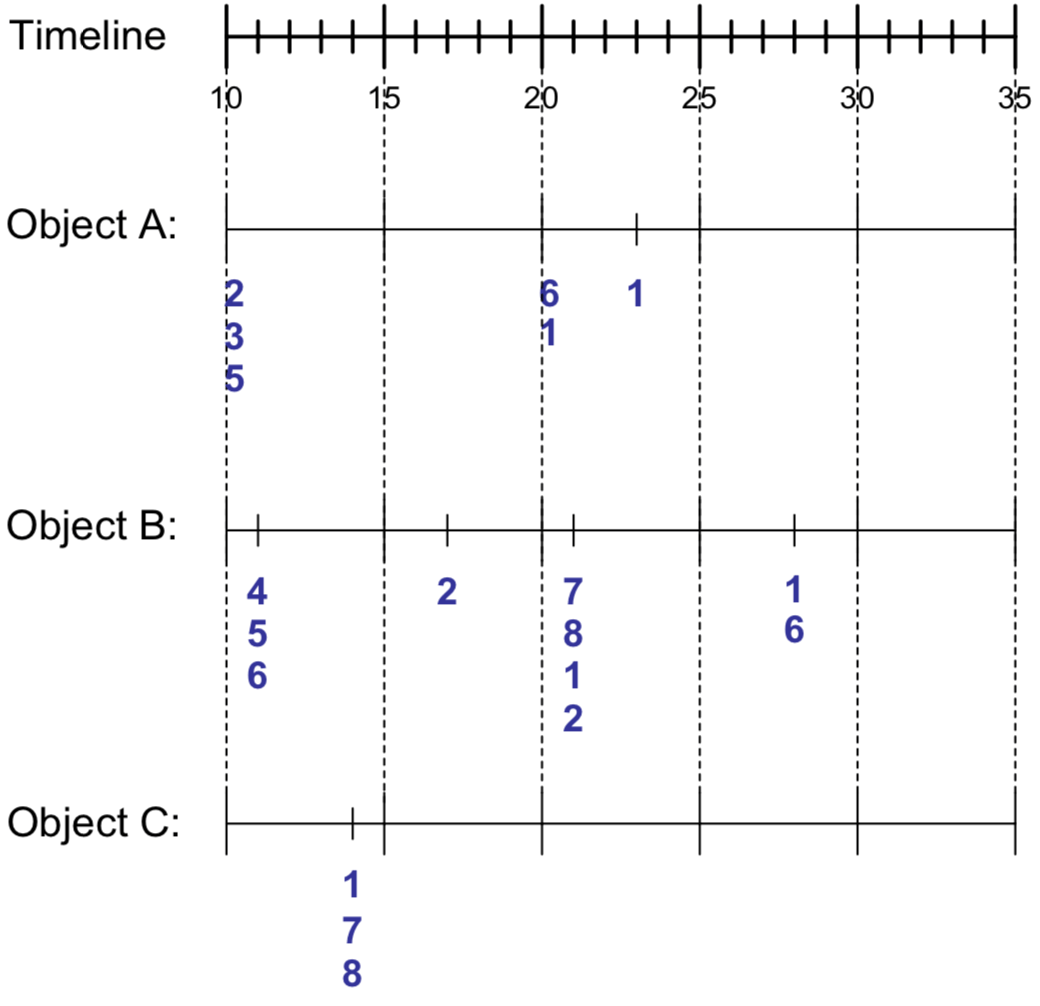
| Object | Timestamp | Events |
|---|---|---|
| A | 10 | 2,3,5 |
| A | 20 | 6,1 |
| A | 23 | 1 |
| B | 11 | 4,5,6 |
| B | 17 | 2 |
| B | 21 | 7,8,1,2 |
| B | 28 | 1,6 |
| C | 14 | 1,8,7 |
Definition
| 名詞 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| Sequence | 我們的時間軸,時間軸上有許多 elements |
| Element | 即 transaction,一個 transaction 有許多 events |
| Event | 每個 events 代表一個 item |
| Length of sequence | 用 表達 sequence 上的 elements 有幾個。k-sequence 代表該 sequence 上共有 k 個 events |
舉例來說,下圖是一個 8-sequence with length 5 的 sequence data:
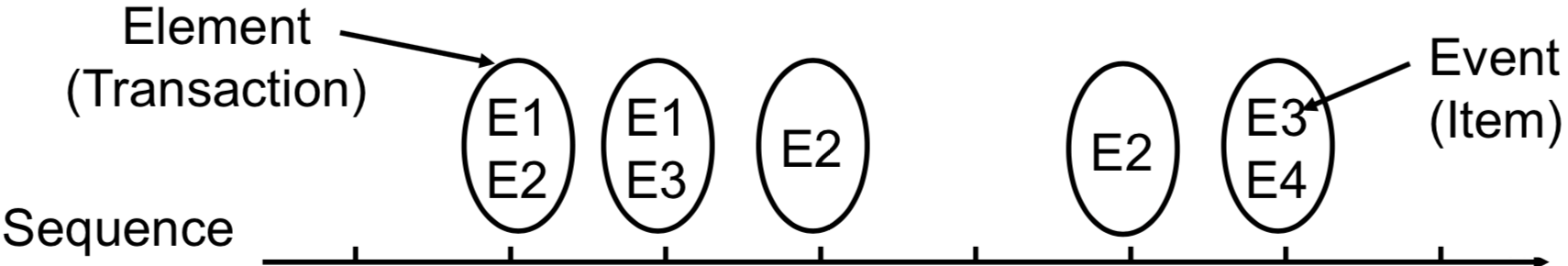
還有許多的例子
- web sequence
<{Homepage} {Electronics} {Cameras} {Shopping Cart} ... > - library checkout books
<{Fellowship of the Ring} {The Two Towers} {Return of the King}>
Subsequence
如果序列 A 的每個元素的事件都是另一個序列 B 對應的元素的子集,那麼序列 A 就是 B 的子序列 (subsequence)。
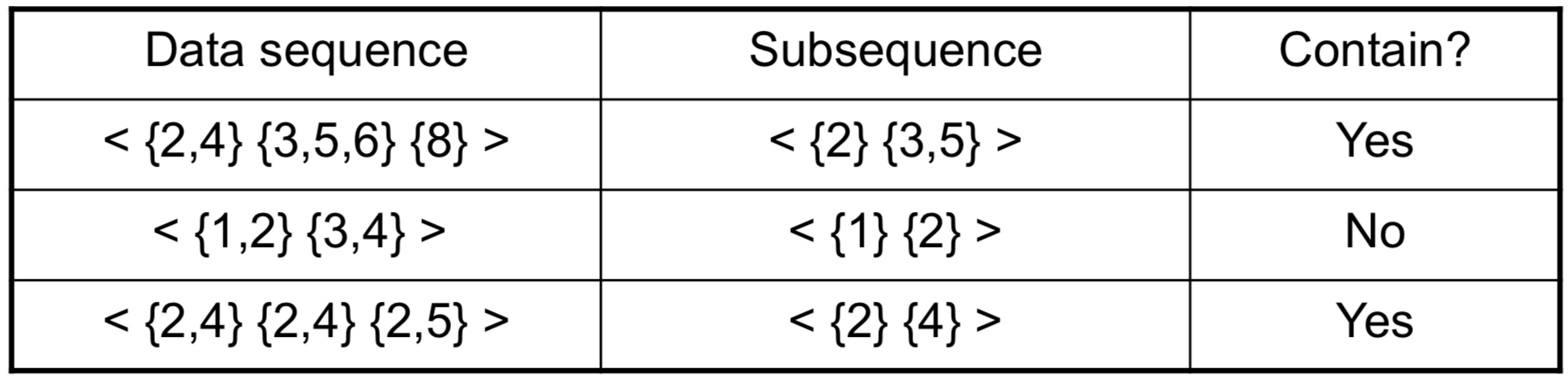
一個 subsequence 的 support 等於 data sequences 包含該 subsequence 的比例。求 Sequential pattern 等於是求 Frequent subsequence,也就是 support minsup 的 subsequence。
Sequential Pattern Mining
Sequential Pattern Mining 就是從一群 sequences 中找出所有的 frequent subsequences。
我們這邊使用 <a(bc)dc> 來表示有四個 elements 分別為 a, bc, d, c。而他是 <a(abc)(ac)d(cf)> 的 subsequence:
<a( bc) d c>
<a(abc)(ac)d(cf)>
現在我們要從這個 sequence database 找出 sequential pattern
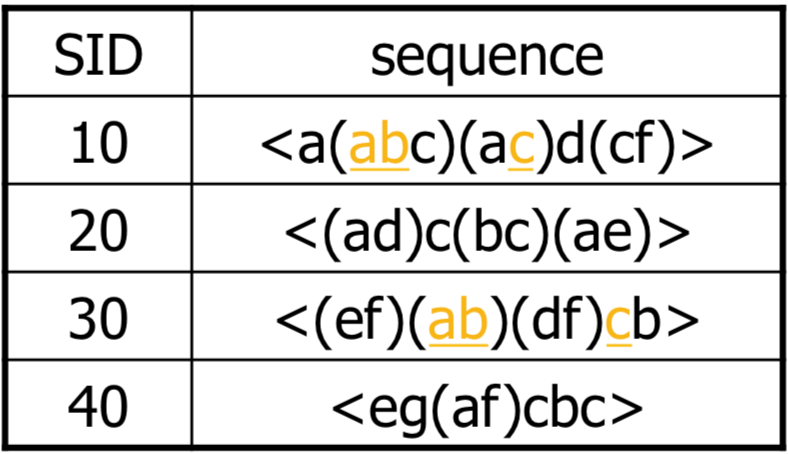
假設 minsup = 2,那我們可以找到 <(ab)c> 是一個 sequential pattern,因為 (ab) 跟 c 都有出現過兩次。
Definition of Sequential Pattern Mining
Given :
1. a database of sequences
2. a minsup
Task :
1. find all subsequences with support >= minsup
Extracting sequential patterns method
首先,直覺上可以用 candidates + apriori 的方法來找出 subsequences。這類的方法有: Apriori* (Apriori All, Apriori Some)、Apriori-based SP algorithm (GSP)。但有一些問題:
- 會產生過多的 candidate sequences
- database scans 次數過多
- 要找的 sequential patterns 長度越大越困難
Sequential Pattern Mining Algorithm
- 首先將 data 進行 sorting
- 計算 large itemset 也就是 support 值
- 進行 transformation (Replacement)
- sequence phase
- maximal phase
Example
進行 sorting 後產生以下資料

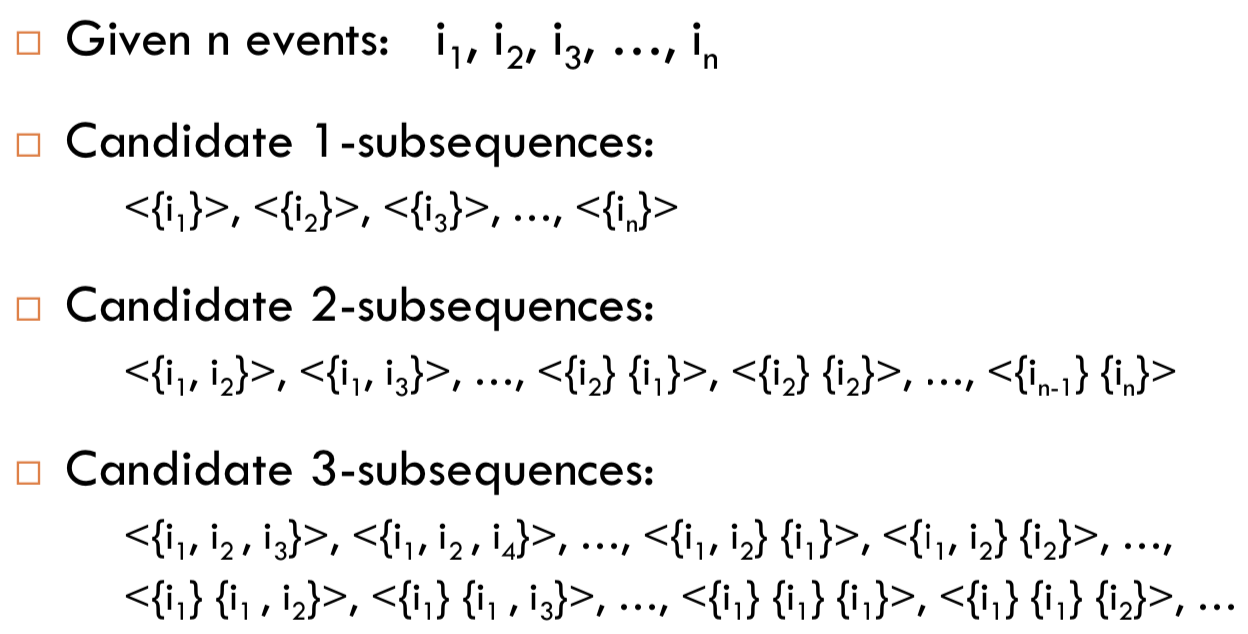
找出滿足 support 的 large itemset,並給他們定義一個新 id
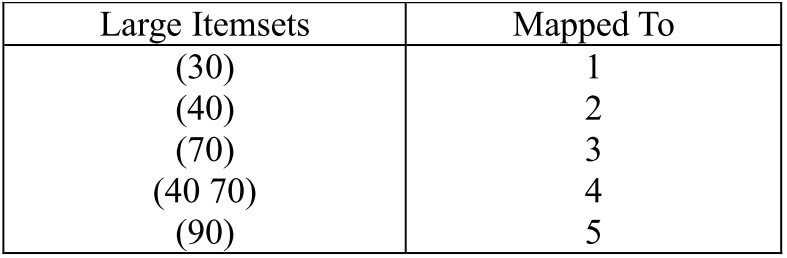
在 Transformation Phase,我們刪除原本資料不滿足 support 的 item。將滿足的資料能攤開的攤開,然後設定新 id
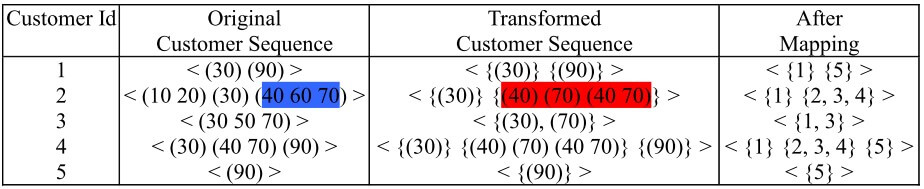
在 Sequence Phase,將 after mapping 的 items 攤開成 Maximal Large Sequence (Apriori-like)
<1 2 3> : support = 2
<1 2 4> : support = 2
Generate <1 2 3 4>
最後 Maximal Sequence,找出 sequence 沒有包含在其他 sequence 即為 maximal sequence。
e.g.
<(3) (4 5) (8)> is contained by <(7) (3 8) (9) (4 5 6) (8)>
<(3) (5)> is not contained by <(3 5)>
Episode Mining
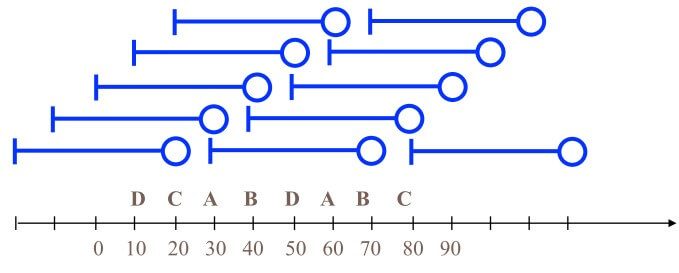
- Episode : A partially ordered collection of events occurring together
- 以 sliding window 方式來抓出 sequence
- discover all frequent episodes from a given class(ex. all parallel or all serial) of episodes
FreeSpan
- Frequent pattern-projected Sequential pattern mining
- 將 sequence database 投影成較小的 projected database
- grow subsequence fragments in each projected database
- Divide-and-conquer
Example
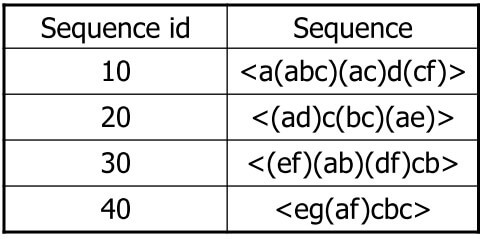
- a 皆出現在這四筆所以 a : 4
- 以此類推求出所有 support > 2 的 item 並排序
f_list = a:4, b:4, c:4, d:3, e:3, f:3
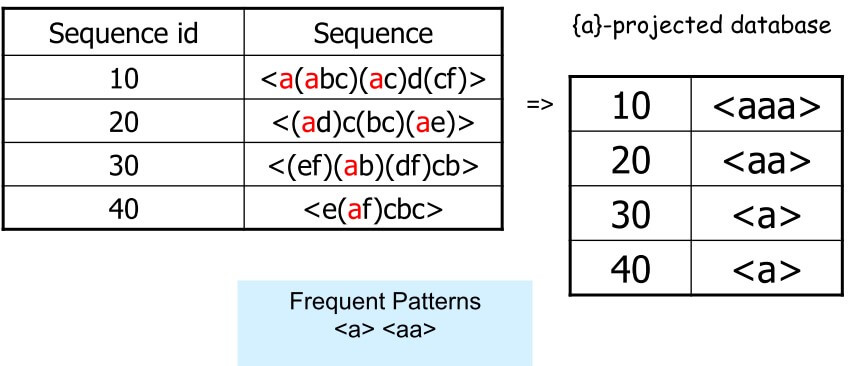
- 先對 a 投影
- aaa 只出現 1 次所以不拿
- aa 出現 2 次
- a 出現 4 次
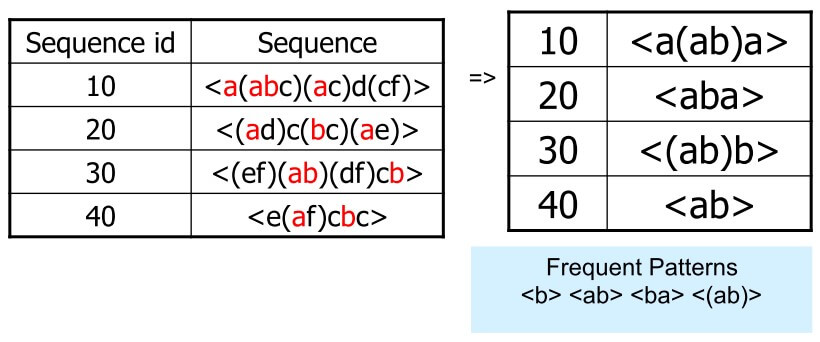
- 以 a 為底,接著對 b 投影
- 可以抓出 b 出現 4 次
- ab 出現 4 次
- (ab) 出現 2 次
- 要注意 ab 和 (ab) 是不同的
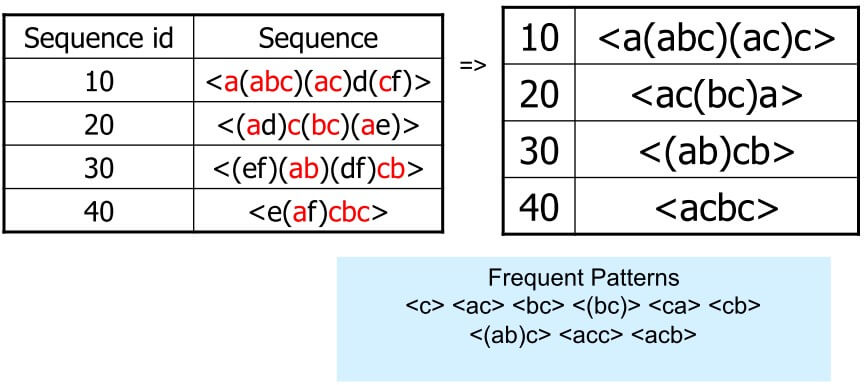
- 以 a, b 為底,接著對 c 投影
PrefixSpan
- Prefix-projected Sequential pattern mining
- 一樣是 Projection-based
- less projections and quickly shrinking sequences
- PrefixSpan 有三個核心,分別是 prefix, postfix, projection
- 假設有一 sequence 為
<a(abc)(ac)d(cf)> - Prefix
<a>, <aa>, <a(ab)>, <a(abc)> ...- 一定要從每一個 item 的頭開始
- 所以
<ab>, <a(bc)>這些都不算在 prefix
- Postfix
- 對於
<aa>來說他的 postfix 為<(_bc)(ac)d(cf)>
- 對於
<bd>來說他的 postfix 為<(cf)>
- 對於
- Projection
- projection 讓我們可以 groupby
<bd>的 projection 是<bd(cf)>
- 假設有一 sequence 為
Example
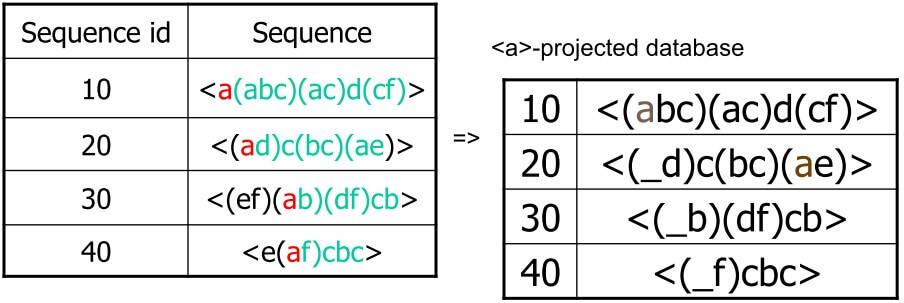
- 先對 a 投影,就可以找出所有有 prefix a 的 length 2 sequence
<aa>:2 <ab>:4 <(ab)>:2 <ac>:4 <ad>:2 <af>:2- 接著就可以對這 6 個 subsets 遞迴投影
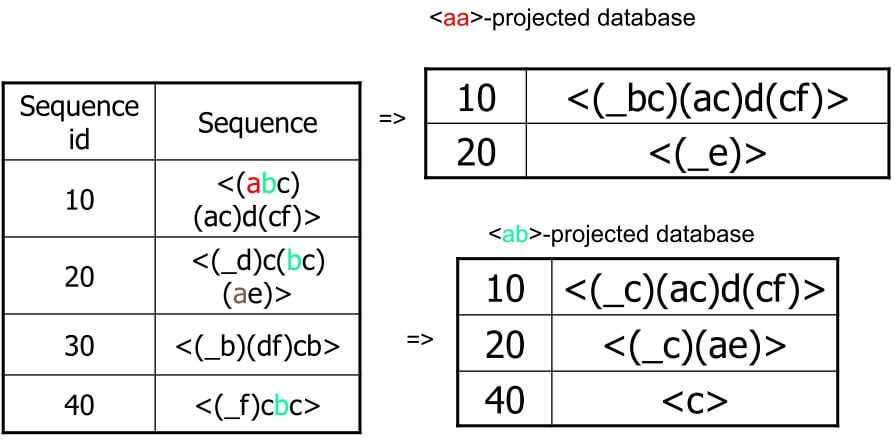
- 例如對
<aa>投影,有兩筆可以繼續遞迴 - 對
<ab>投影,有三筆可以繼續遞迴 - 同時也可以刪去不滿足 support 的 item
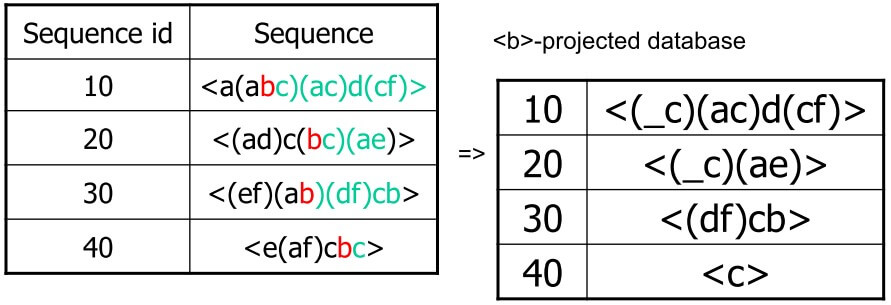
- 將 a 及其 subsets 進行一輪後
- 接著就可以對 b 及他的 subsets 投影