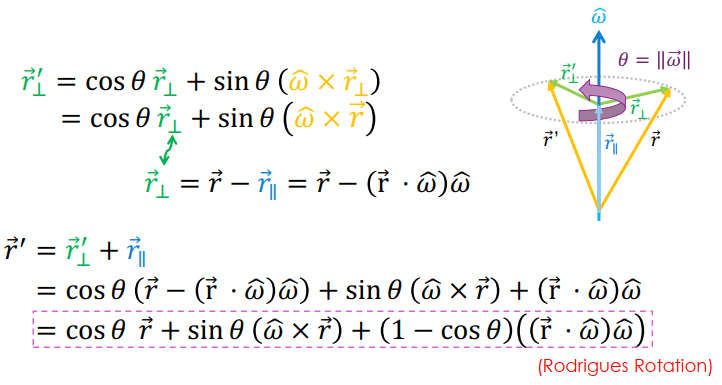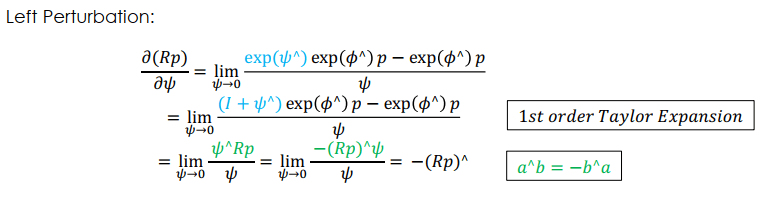Lie group and Lie algebra 本文介紹了 Lie Group 和 Lie Algebra,他們可以用來解決 3D 時的最佳化問題,特別是計算 Rotation Matrix。Lie Group 是把所有合法的 Rotation Matrix 集合起來稱為 Special Orthogonal Group (SO),以及如果想描述 Translation 時就要加入 t 來組成 Special Euclidean group (SE)。而 Lie Algebra 由 Φ \Phi Φ
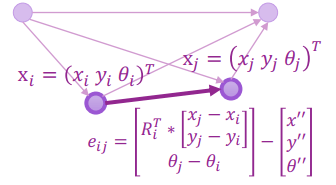
還記得我們要求 Graph Optimization for 2D Pose 的時候,需要計算 rotation 嗎 ? 這個 Rotation 在 2D 時可以用 θ \theta θ
Graph Optimization for 2D Error 在 3D 時我們只可以在 manifold space 解決 rotation matrix 的最佳化。而 rotation 有很多種表達方式:
Rotation matrix Euler Angles Axis-angle Quaternion Etc. Manifold Space 用 Axis-angle 舉例,定義旋轉軸 ω \omega ω θ = ∥ ω ⃗ ∥ \theta = \lVert \vec{\omega}\rVert θ = ∥ ω ∥ r ′ r' r ′ r r r ω \omega ω θ \theta θ ω \omega ω
Axis-angle 把所有合法的 rotation matrix 集合起來稱為 Special Orthogonal Group (SO),其中 R 要是 orthogonal 且 det = 1。例如當 R 在三維空間時為 SO(3):
S O ( 3 ) = { R ∈ R 3 × 3 ∣ R R T = I , det ( R ) = 1 } SO(3) = \left\{ \mathbf{R}\in \mathbb{R}^{3\times3} \mid \mathbf{RR^T = I}, \det(\mathbf{R}) = 1 \right\} SO ( 3 ) = { R ∈ R 3 × 3 ∣ R R T = I , det ( R ) = 1 } 當你不只描述 rotation 還想描述 translation 時就要加入 t,因為連續的轉換太麻煩,用更簡潔的方式 T 來表達整個 transformation:
[ a ′ 1 ] = [ R t 0 T 1 ] [ a 1 ] = d e f T [ a 1 ] \begin{aligned} \begin{bmatrix} \mathbf{a}' \\1 \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} \mathbf{R} & \mathbf{t} \\ 0^T & 1\end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix} \mathbf{a}\\ 1\end{bmatrix} \overset{\mathrm{def}}{=} \mathbf{T}\begin{bmatrix} \mathbf{a} \\ 1\end{bmatrix} \end{aligned} [ a ′ 1 ] = [ R 0 T t 1 ] [ a 1 ] = def T [ a 1 ] 合法的 T 一樣可以組成 group,稱為 Special Euclidean group (SE),必須滿足 R 在 SO 且 t 為合法向量,例如當 T 在三維空間時為 SE(3):
S E ( 3 ) = { T = [ R t 0 T 1 ] ∈ R 4 × 4 ∣ R ∈ S O ( 3 ) , t ∈ R 3 } \begin{aligned} SE(3) = \left\{ T = \begin{bmatrix} \mathbf{R} & \mathbf{t} \\ 0^T & 1\end{bmatrix} \in \mathbb{R}^{4\times 4} \mid \mathbf{R} \in SO(3), t\in \mathbb{R}^3 \right\} \end{aligned} SE ( 3 ) = { T = [ R 0 T t 1 ] ∈ R 4 × 4 ∣ R ∈ SO ( 3 ) , t ∈ R 3 } Group 的基本定義,必須滿足以下四點:
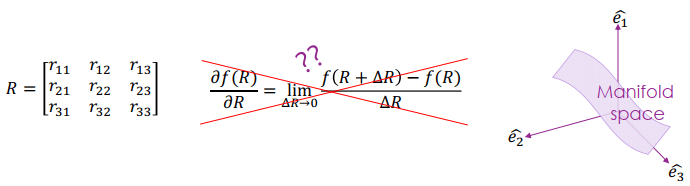
closure: 進行 binary operation 還在同空間 identity inverse associativity (結合律) 因為用簡單的三維矩陣來表達 rotation matrix,加法不滿足 group 的定義,無法進行導數,所以必須尋找替代方案
Interpolating Rotation Matrices Lie Group 裡的每個元素都是連續的,要解決 manifold space 的最佳化,就要了解 lie group 和 mapping 對應的 lie algebra。現在有一個任意的 rotation matrix 滿足 orthogonal (R R T = I \mathbf{RR^T = I} R R T = I R ( t ) \mathbf{R(t)} R ( t ) R ( t ) R ( t ) T = I \mathbf{R(t)R(t)^T = I} R ( t ) R ( t ) T = I 反對稱矩陣 。
∧ \wedge ∧ ∨ \vee ∨ a ∧ = A = [ 0 − a 3 a 2 a 3 0 − a 1 − a 2 a 1 0 ] , A ∨ = a = [ a 1 a 2 a 3 ] \begin{aligned} \mathbf{a}^{\wedge} = \mathbf{A} = \begin{bmatrix} 0 & -a_3 & a_2 \\ a_3 & 0 & -a_1 \\ -a_2 & a_1 & 0\end{bmatrix}, \quad \mathbf{A}^{\vee} = \mathbf{a} = \begin{bmatrix} a_1 \\ a_2 \\ a_3\end{bmatrix} \end{aligned} a ∧ = A = ⎣ ⎡ 0 a 3 − a 2 − a 3 0 a 1 a 2 − a 1 0 ⎦ ⎤ , A ∨ = a = ⎣ ⎡ a 1 a 2 a 3 ⎦ ⎤ 對 t 做導數,得到的反對稱矩陣記為 Φ ( t ) \Phi(t) Φ ( t ) R ˙ ( t ) R ( t ) T = Φ ( t ) ∧ \dot{\mathbf{R}}(t) \mathbf{R}(t)^{\mathrm{T}}=\Phi(t)^{\wedge} R ˙ ( t ) R ( t ) T = Φ ( t ) ∧ ϕ ( t ) \phi(t) ϕ ( t ) R ( t ) \mathbf{R(t)} R ( t )
R ˙ ( t ) = ϕ ( t ) ∧ R ( t ) = [ 0 − ϕ 3 ϕ 2 ϕ 3 0 − ϕ 1 − ϕ 2 ϕ 1 0 ] R ( t ) \begin{aligned} \dot{\mathbf{R}}(t)=\boldsymbol{\phi}(t)^{\wedge} \mathbf{R}(t)=\left[\begin{array}{ccc} 0 & -\phi_{3} & \phi_{2} \\ \phi_{3} & 0 & -\phi_{1} \\ -\phi_{2} & \phi_{1} & 0 \end{array}\right] \mathbf{R}(t) \end{aligned} R ˙ ( t ) = ϕ ( t ) ∧ R ( t ) = ⎣ ⎡ 0 ϕ 3 − ϕ 2 − ϕ 3 0 ϕ 1 ϕ 2 − ϕ 1 0 ⎦ ⎤ R ( t ) 而 ϕ ( t 0 ) \phi(t_0) ϕ ( t 0 )
ϕ ( t 0 ) = ϕ 0 R ˙ ( t ) = ϕ ( t ) ∧ R ( t ) = ϕ 0 ∧ R ( t ) \boldsymbol{\phi}\left(t_{0}\right)=\boldsymbol{\phi}_{0} \quad \dot{\mathbf{R}}(t)=\boldsymbol{\phi}(t)^{\wedge} \mathbf{R}(t)=\boldsymbol{\phi}_{0}^{\wedge} \mathbf{R}(t) ϕ ( t 0 ) = ϕ 0 R ˙ ( t ) = ϕ ( t ) ∧ R ( t ) = ϕ 0 ∧ R ( t )
因為知道怎麼求 R ( t ) \mathbf{R(t)} R ( t ) R ( t ) = exp ( ϕ 0 ∧ t ) \mathbf{R(t)} = \exp (\boldsymbol{\phi}^\wedge_0 t) R ( t ) = exp ( ϕ 0 ∧ t ) Φ \Phi Φ Φ \Phi Φ
Φ = ϕ ∧ = [ 0 − ϕ 3 ϕ 2 ϕ 3 0 − ϕ 1 − ϕ 2 ϕ 1 0 ] ∈ R 3 × 3 s d ( 3 ) = { ϕ ∈ R 3 , Φ = ϕ ∧ ∈ R 3 × 3 } \begin{aligned} &\Phi=\phi^{\wedge}=\left[\begin{array}{ccc} 0 & -\phi_{3} & \phi_{2} \\ \phi_{3} & 0 & -\phi_{1} \\ -\phi_{2} & \phi_{1} & 0 \end{array}\right] \in \mathbb{R}^{3 \times 3}\\ &\mathfrak{s} \mathfrak{d}(3)=\left\{\boldsymbol{\phi} \in \mathbb{R}^{3}, \boldsymbol{\Phi}=\boldsymbol{\phi}^{\wedge} \in \mathbb{R}^{3 \times 3}\right\} \end{aligned} Φ = ϕ ∧ = ⎣ ⎡ 0 ϕ 3 − ϕ 2 − ϕ 3 0 ϕ 1 ϕ 2 − ϕ 1 0 ⎦ ⎤ ∈ R 3 × 3 sd ( 3 ) = { ϕ ∈ R 3 , Φ = ϕ ∧ ∈ R 3 × 3 } Lie algebra 代表的就是 Lie group 的切線空間,也要滿足一些特性,其中的 binary operation 為 Lie bracket (外積可以是其中一種)
closure bilinearity alternativity jacobi identity 對 Lie algebra 中由 Φ \Phi Φ
exp ( A ) = ∑ n = 0 ∞ = 1 n ! A n \exp(A) = \sum_{n=0}^\infty = \frac{1}{n!}A^n exp ( A ) = n = 0 ∑ ∞ = n ! 1 A n 這個對 A 取 exp 就像在 Axis-Angle 的 Rodrigues Rotation 一樣在做 rotation 的描述
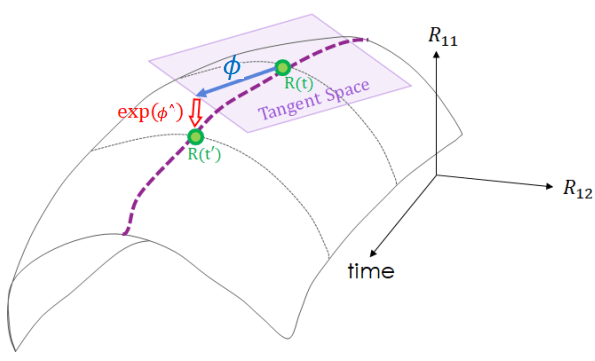
Lie Group vs. Lie Algebra Rotation matrix 是特殊的 lie group Rotation matrix 會有一個對應的 lie algebra (R 的切線空間) 可以用 exponential, logarithmic 來做 mapping Lie Group vs. Lie Algebra 上圖顯示 lie group, lie algebra 的對應關係 Lie group = manifold space 沿著時間 rotation 會不斷改變 在時間 t 可以找到切平面 ϕ \phi ϕ 用 ϕ \phi ϕ 因為對 lie algebra 求導太複雜,有比較簡單的做法稱為 perturbation model
Perturbation Model 最後可以得到更新 R 的方法
R new = exp ( ψ ∧ ) R init R_{\text{new}} = \exp(\psi^{\wedge}) R_{\text{init}} R new = exp ( ψ ∧ ) R init