Multi-view Geometry
本文介紹了三維圖學中的 Structure from Motion (SfM) 和 SIFT 等方法,以及如何將 camera calibration、Perspective-n-point (PnP),以及 Unknown Structure Initialization 等方法應用在多視圖技術上。
SLAM 在控制中使用了許多 SfM 相關技術,包括提取特徵點、求取 camera calibration、Perspective-n-point (PnP),以及 Unknown Structure Initialization 等。SfM 幫助機器人提取以往視覺資訊推算出空間位置,從而可以協助 SLAM 更精準地判斷機器人的位置。
Structure from Motion (SfM)
圖學的 SfM 和 SLAM 十分相似,只是 SLAM 是 realtime 版本的 SfM。SfM 透過多個圖像來復原 camera motion 和 scene structure。
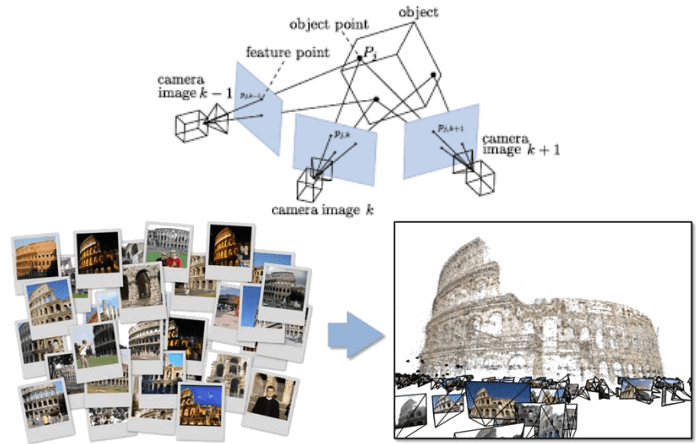
而 SfM 流程可以大致列為

- 找 feature points (SIFT: NN 以外最好)
- 預測 points 對應到真實 3D 場景會變怎樣 (geometry)
- 優化預測 (bundle adjustment)
- 找出 rotation 或 translation 是否合理
SIFT
以下介紹 SIFT 如何萃取 feature points
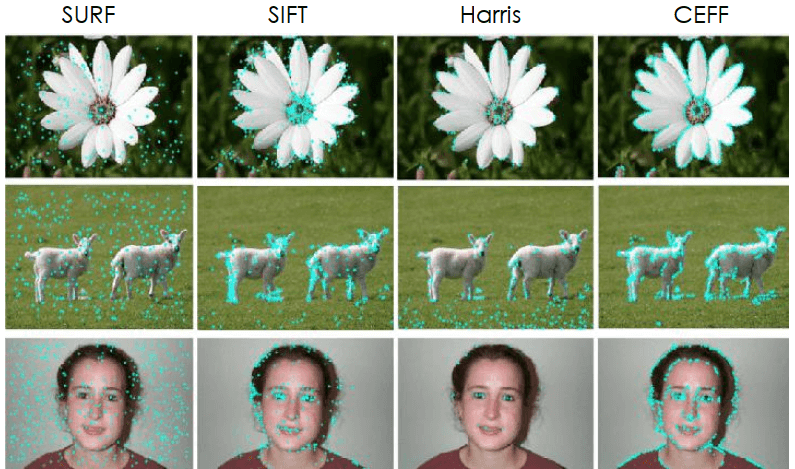
SIFT idea 是將圖像的內容轉換成 local feature coordinates,這些座標不受到 translation, rotation, scale 或其他 imaging parameters 的影響而改變。
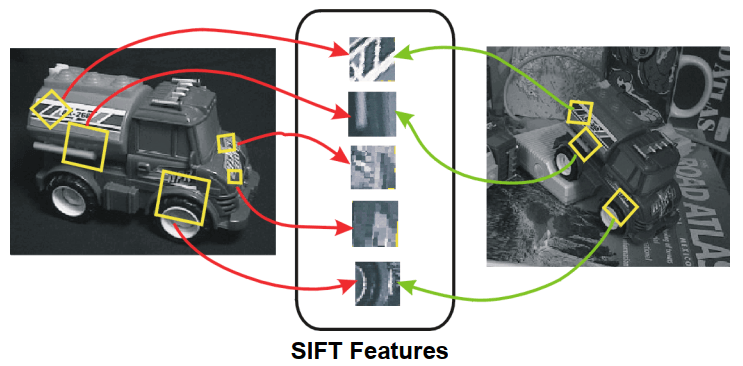
SIFT 應用有 Object recognition (matching),找兩張圖 matching 地點。Image Stitching,找多張圖 overlap 的部分並拼接,以及 Photosynth,找多張圖的共同點並拼接成 3D 圖。
SIFT Process
1. Scale-space extrema detection
搜索多種比例和圖像位置,找出圖片變化較大的點,做法是使用 Gaussian pyramid
2. Keypoint localization
利用模型以確定位置和比例,根據穩定性來選擇 keypoints,在產生的 pyramid 找極值。
- 跟鄰居比較
- 用 taylor 找出更精確的預測
- check 是否為平坦區域或 edge 並 reject

3. Orientation assignment
計算每個 keypoints 的最佳方向,以就是為 keypoint 找出描述 (任意方向都是在描述同一點)
4. Keypoint descriptor
用現有 feature 做出一致性的 feature descriptor,在選定的 scale, rotation 上利用 local image gradients,來描述 keypoints。一種做法是 Lowe's keypoint descriptor。
Camera Calibration
為了更了解 RANSAC 做法要先講到 camera calibration。 Camera calibration 就是求出 intrinsics 和 extrinsics 所有參數,而 world coordinate (x, y, z) 投影到 camera coordinate (u, v) 可以寫成公式:

- A 矩陣為 intrinsics matrix
- [R t] 矩陣為 extrinsics matrix
Pinhole Camera Projection Model
我們可以利用 image coordinate 和 world coordinate 的對應,來找出沒有做任何 rotation, translation 的 intrinsic, extrinsic matrix。其中的 extrinsic 等於 rotation (3-d identity matrix) 加上 translation。

為了解決 offset ,我們要加入 做為 principle point 和原點的 offset
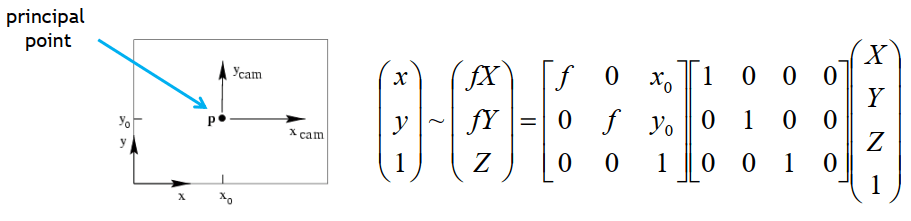
為了解決 distortion,我們要加入 a, s 來進行校正
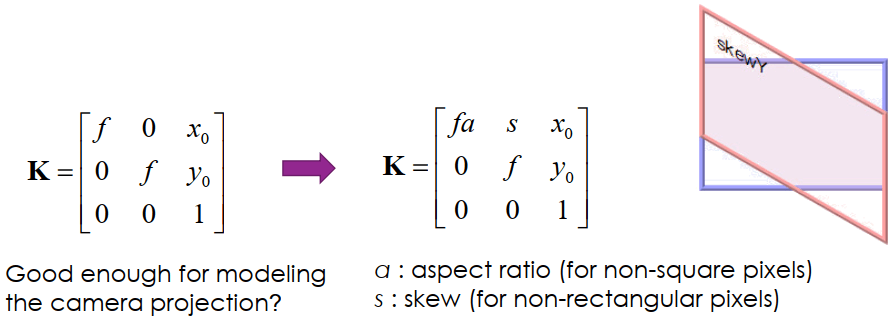
Transformation Matrix Estimation by Reprojection
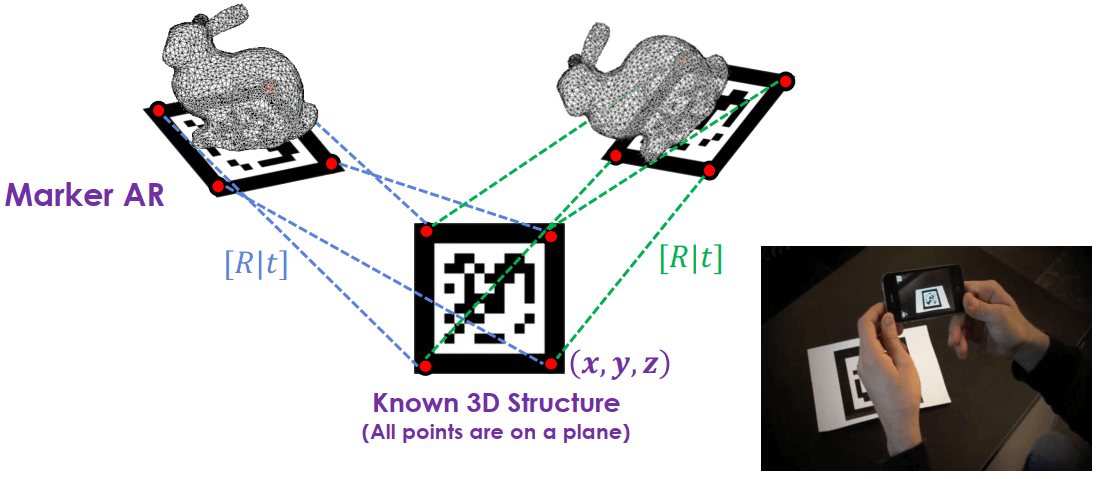
一組 x, y, z 可以和 u 或 v 分別產生兩個對應的方程式,所以假設 extrinsic 有 8 個要解,只需要 4 組對應點。如果原本需要六組 point pair 才能解出 C = A|AT,現在只需要三組就能解出。這種解法稱為 Perspective-n-Point (PnP)。

傳統是利用 AR marker 來解
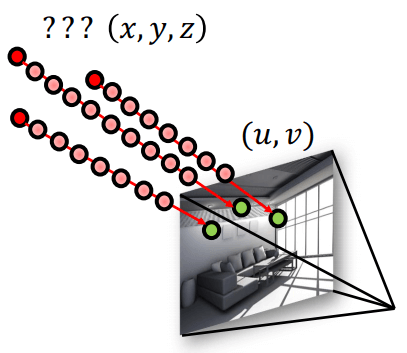
但現實中沒有 AR marker,也不知道 x, y, z 是如何對應 u, v 的
我們假設有一連串 frame (),寫成 KMP = intrinsic extrinsic 3d coordinate
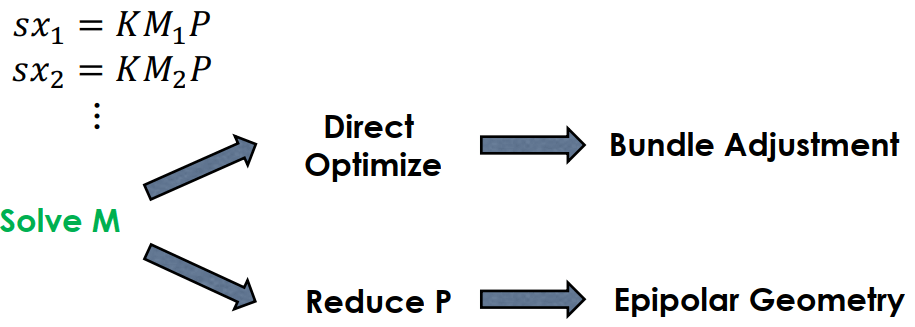
可以看到這個做法就像是 bundle adjustment,其中 intrinsics K 是給定的,要求的是 extrinsics M。其中 s (scale) 要猜測,除非用 marker 有固定比例尺。
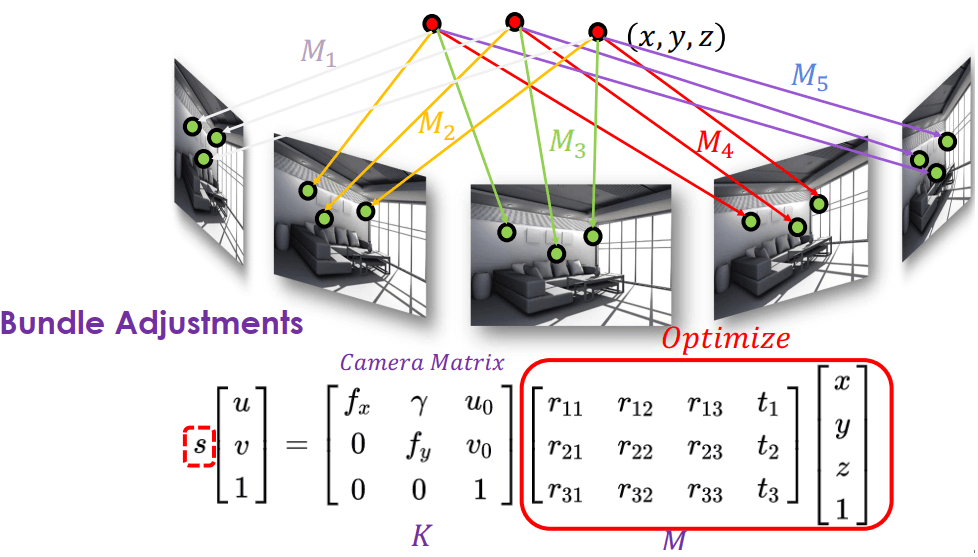
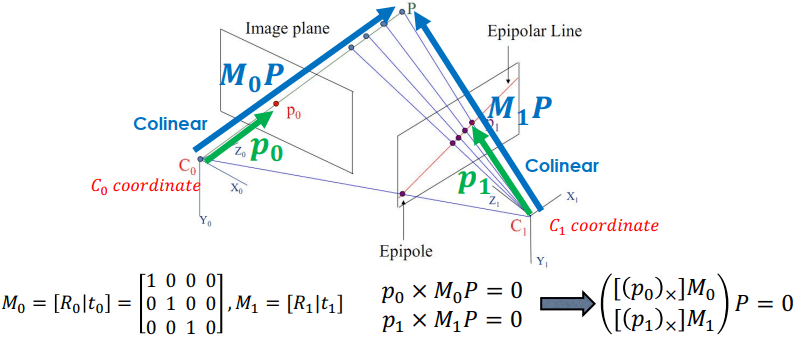
Unknown Structure Initialization
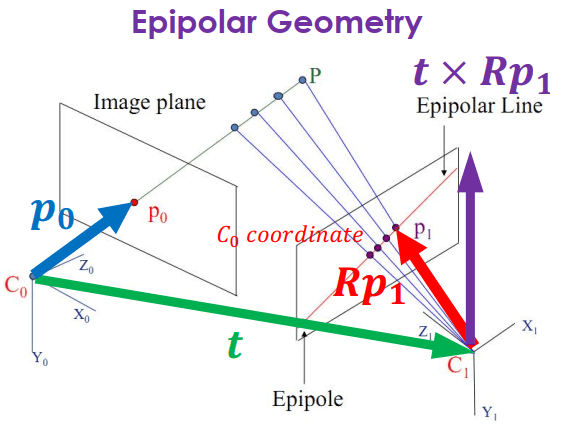
兩個 camera 中心對到點 P,會產生 () 這個三角形平面 (epipolar plane)
- 可看成 到 的 translation
- 可看成對 做 rotation ()
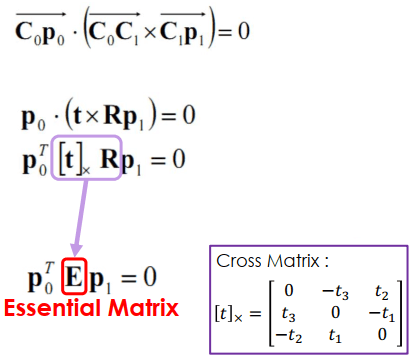
我們就可以列出多組已知 來求 E,用多組對應來解 E,可以寫成 Ax = 0 來求解。

另外,找對應點時不用全部 SIFT points 都找,可用 epipolar line 找,從 投影來的 這幾個點會連成一直線,稱為 epipolar line。透過 epipolar line 可以得到兩個畫面對同一點所產生的投影關係方程。
Essential Matrix Decomposition
得到 E 就可以用 SVD 來拆解回 t 跟 R
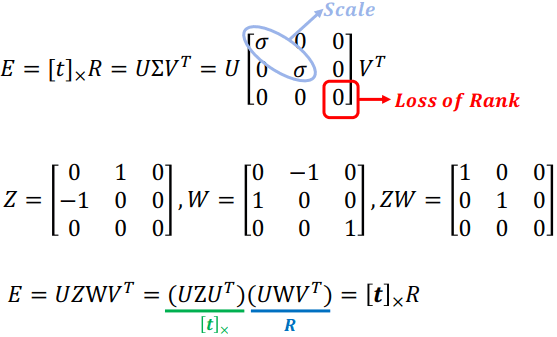
因為矩陣拆解可能有正負影響得到多種結果,意思是 p 點到底坐落在 A, B 相機的前方還是後方 (所以有四種可能),所以必須要都在 A, B 前方的那一個解才行
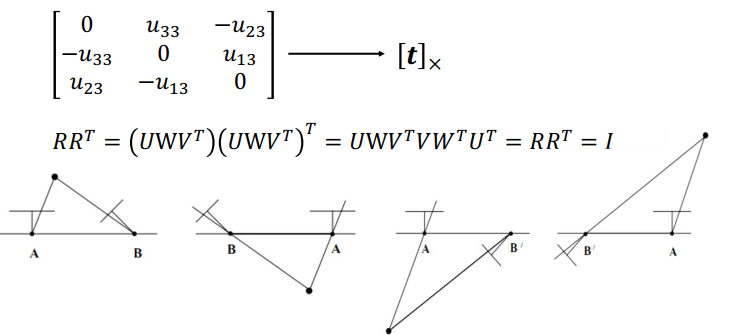
3D Structure Recovering (Triangulation)
有了 t, R 接著要來猜 p 的 3D structure P
Basic Initialization and Tracking
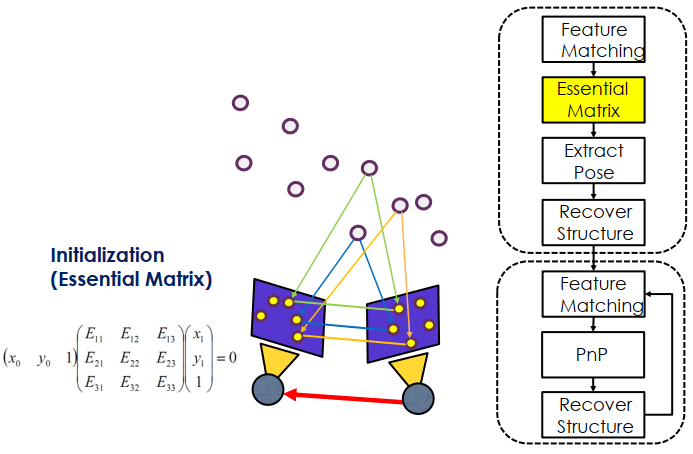
整個 SfM 用於 SLAM 的流程大致上如下

Initialization (Feature Matching)
首先從共同看到的點來求得 Essential Matrix (E)
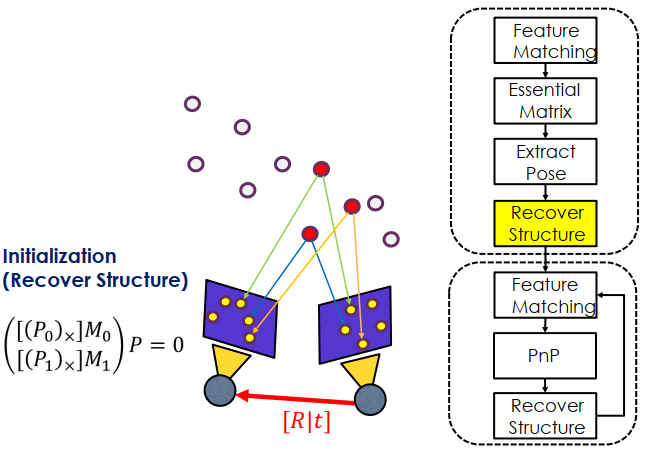
再來是 extract pose 的步驟,將 E 拆成 R 和 t

接著是從 R 和 t 來復原 P 的 3D structure (紅色點)
Tracking
新的 frame 進來,用 feature matching 找出 overlap 的部分
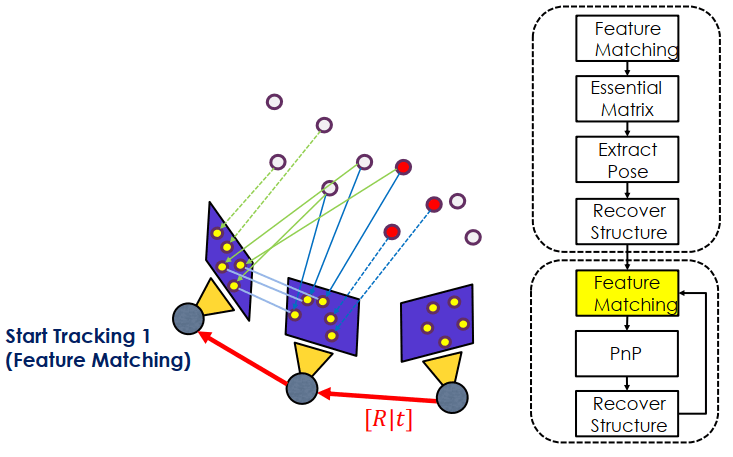
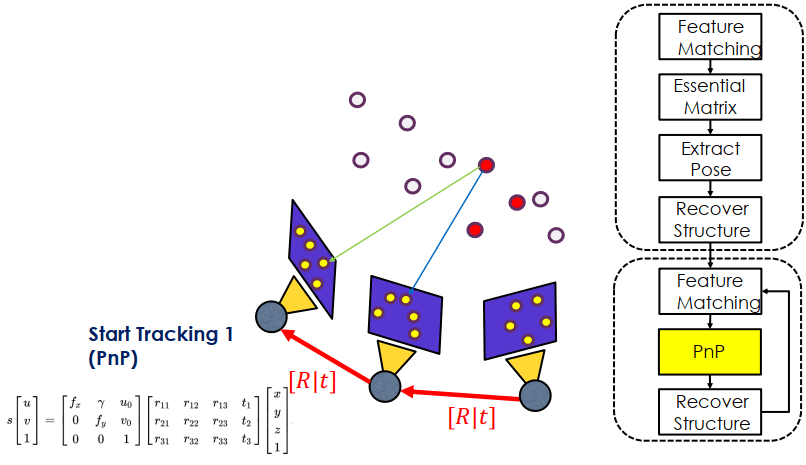
用 PnP 和 Recover 還原 P (紅色點) 的 3D structure
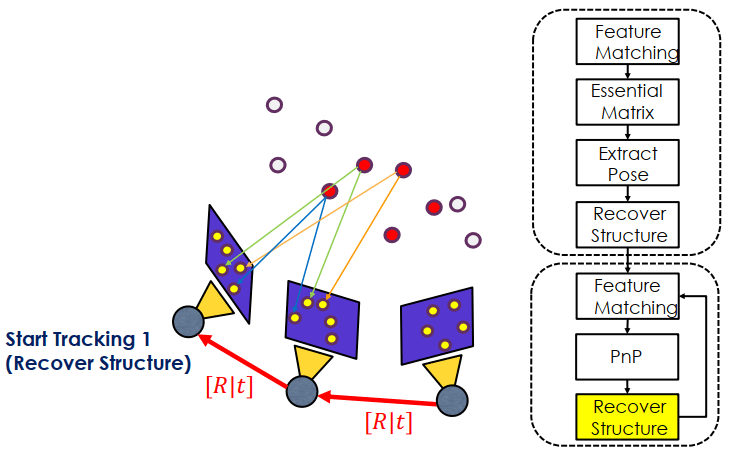
重復上述動作就是 tracking 的部份
Scaling Drift Problem
在進行 SfM 時,不只要猜 R, t 還要猜 scale (s),因為每個 frame 進來會改變 s,這個問題稱為 scaling drift problem,有一些方法可以校正 scale (這裡不討論)
Image Matching
因為要討論 SLAM 中最後一個 loop detection 所以要採用 image matching,一種方法是觀察 SIFT point pair 的 similarity,目標是找出 transformation T 可以解釋 similarity
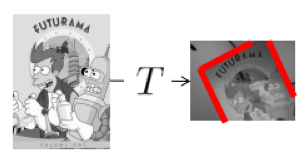
Find a transformation T that explains the movement of the matched features
transformation 可以表示成以下形式,有 6 個參數要解
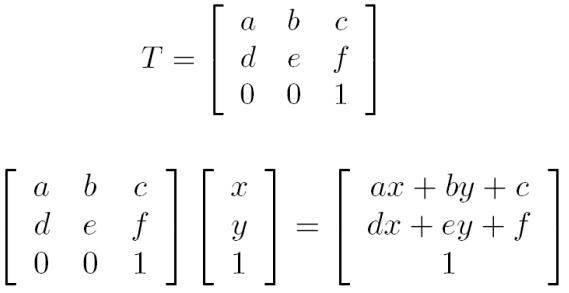
越多組 pair (三組以上) 可以越精準的猜出 transformation,但挑的點不好就會造成錯誤

一種除掉錯誤 outliers 的做法就是 RANSAC
RANSAC
RANdom SAmple Consensus (RANSAC),在一組數據點中找到一條最適合的線 (省略掉 outliers)
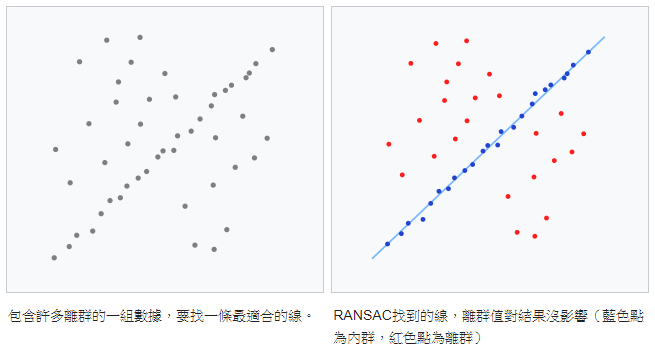
- Select two points at random
- Solve for the line (L) between these two points
- Count the number of inliers to the line L
- If L has the highest number of inliers so far, save it
- Repeat for N rounds, return the best L
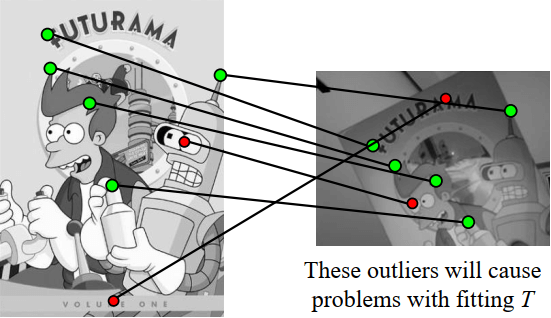
在實作上會把 match 失敗的定為 outliers 來移除掉,然後再重新計算 inliners