SLAM Front-end
SLAM FrontEnd 主要負責採樣和優化,本文介紹 SLAM FrontEnd 的基本概念,例如辨識影像資料,定義目標函數,以及 ORB SLAM 的結構。ORB SLAM 主要可以分成三大部分,Tracking,Local Mapping 和 Loop Closing。Tracking 負責接收影像資料,並且將影像資料轉換成地圖資料,Local Mapping 負責將地圖資料優化,Loop Closing 負責檢查是否有環路,並且將環路優化。
SLAM Overview
SLAM 是一種定位和地圖構建技術,它利用連續的測量來估計運動 (Pose Tracking),多次測量來優化對地圖的誤差 (Local optimization),以及檢查是否形成環路來穩定整個 SLAM 架構 (Loop Closure Detection)。

Information from Image Data
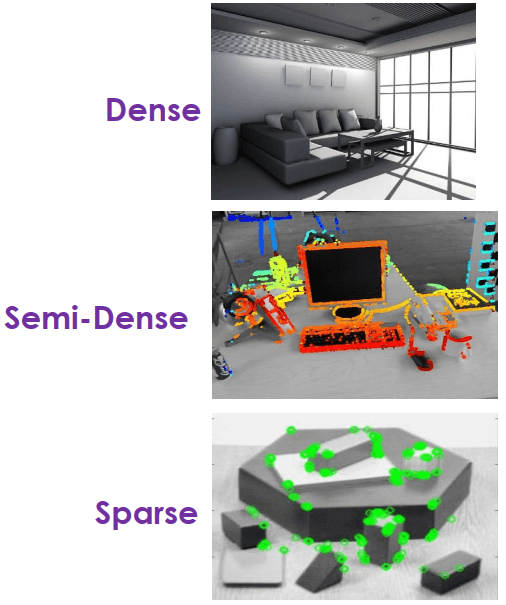
一種 SLAM 定義方式是由抓點方式定義,因為 ICP 時要抓點,所以有幾種方法可以抓點:
- Dense: 接收全點
- Demi-Dense: 接收較重要的點
- Sparse: 接收較少的點

Objective Function
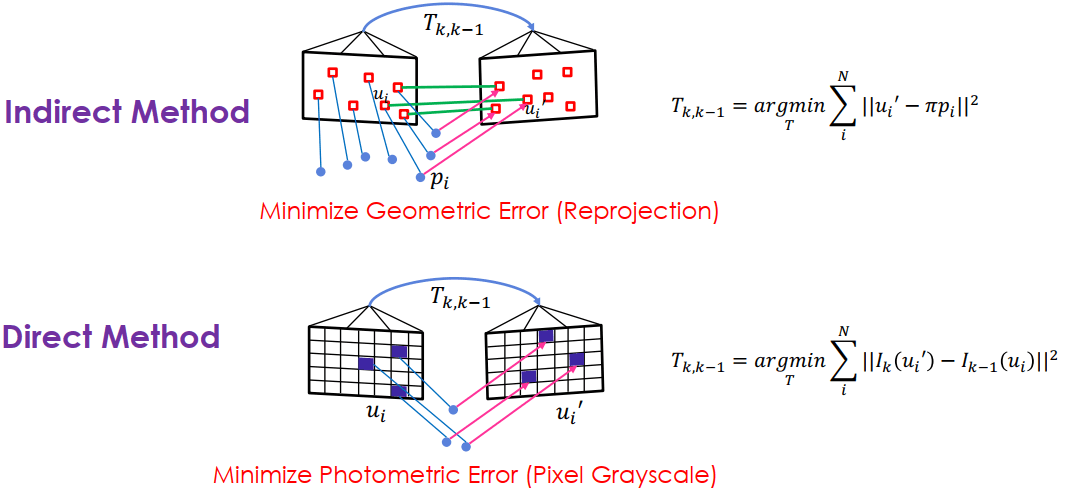
另一種 SLAM 定義方式為 objective function,有兩種方法可以比較:
- Direct: 畫面點都已定義好,所以可以直接比較
- Indirect: 跟對應點的投影結果比較,越像越好
History of Visual SLAM
我們可以把 Feature-based Visual SLAM 分成兩大學問,一個是 Computer Vision,另一個是 System Pipeline。
- Computer Vision (measurement)
- Feature Points Matching
- Perspective-n-Points
- Bundle Adjustment
- Epipolar Geometry
- System Pipeline (optimization)
- Map storage
- Graph Optimization
- Loop Closure Detection
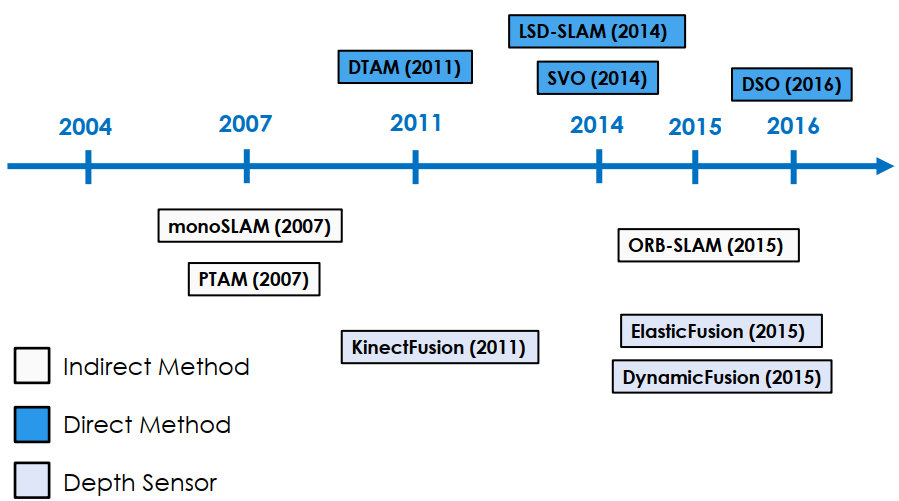
- ORB-SLAM (sparse + indirect)
- LSD-SLAM (semi-dense + direct)
- Kinect Fusion (depth sensor addition)
SLAM Direct Method
Indirect method 雖然能夠容忍環境的變化,但 matching 耗時,在特殊場景會找不到特徵點,且大量的特徵點可能不會被使用。而 direct method 雖然需要在光源需穩定 (亮度不變),相機移動小 (特徵點位置不會劇烈變化) 的情況才能實作,但計算較快速 (省略 matching)。
- 光流法: 直接找到像素點下個 frame 的位置 (不用 matching)
- 直接法: 直接找特徵點,其 transform 的 intensity 誤差盡量小 (最佳化問題)
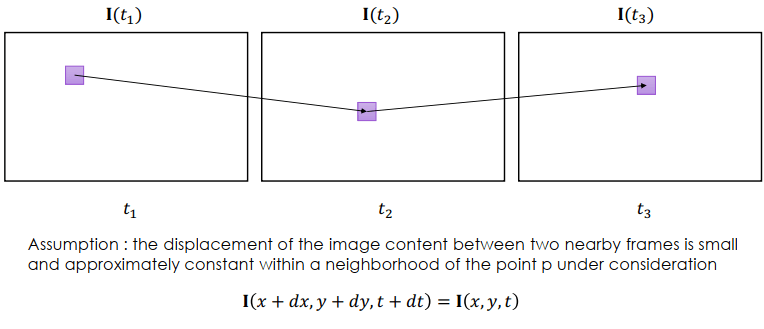
Optical flow
光流法必須滿足 intensity invariant,也就是 intensity 不變 (一階微分等於 I(x,y,t))。其中 Lucas–Kanade (L-K) Method 是光流法的一種算法,必須要滿足另一個條件 local consistency,也就是每個 pixel 的 optical flow displacement 必須一致。
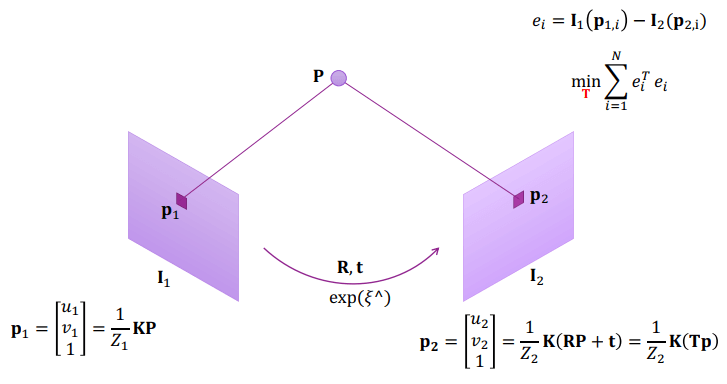
Direct Method
Direct Method 一樣要滿足 intensity invariant,他的想法是最小化轉換產生的 error term。
- p2 是轉換得來的
- 最小化 error term = e 對 T 的導數為 0
- 前提是 P 要已知,可以用 sensor 求
- 得到 J 就可以用高斯牛頓或 LM 計算最佳化
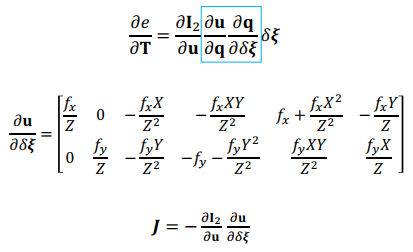
ORB SLAM
ORB-SLAM 主要可以分成三大部分,這三者是非同步處理的
- Tracking
- Local Mapping
- Loop Closing

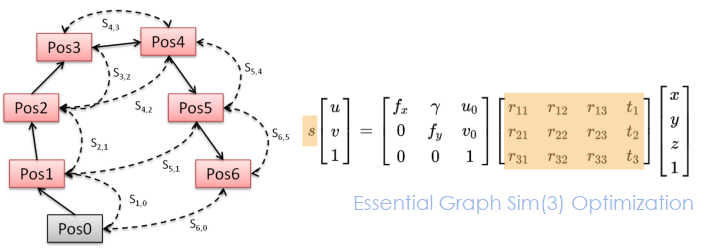
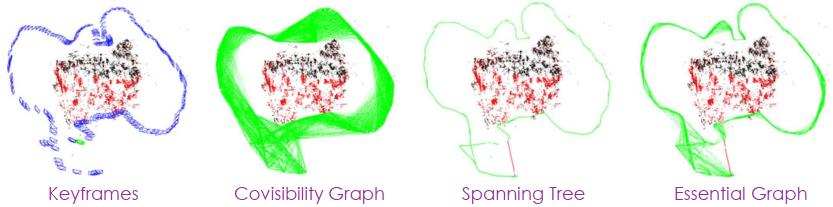
Covisibility Graph & Essential Graph
在 ORB SLAM 中有幾種方法表示地圖,其中最常用的是 Covisibility Graph 和 Essential Graph。
- Covisibility Graph
- 每個 node 都是 keyframe,而 edges 的權重代表 keyframe 間共同分享的 points 數量
- Essential Graph
- Covisibility graph 做完 spanning tree 之後所產生
- 做法是只對有最多共同點的 keyframe 進行連接
- 最後再連接共同點大於 100 的 keyframe 得到新的 edges
- 最後就可以直接用 essential graph 進行最佳化
Tracking
使用 constant velocity motion model 來預測相機的 pose,根據上個 frame 和現在的 frame 來優化 pose。實作時先找附近的 keyframe (K1) 再從 K1 找到 K2 一起最佳化現在的 keyframe。

Mapping
找出潛在的 map points,然後再對他們進行優化:
- Keyframe Insertion 針對每個 unmatched ORB,在 covisibility graph 中尋找其他連接的 keyframe (Kc) 有沒有可以 match 的 points
- Map Point Creation 在 covisibility graph 的 connected keyframes 對 ORB 進行 triangulation
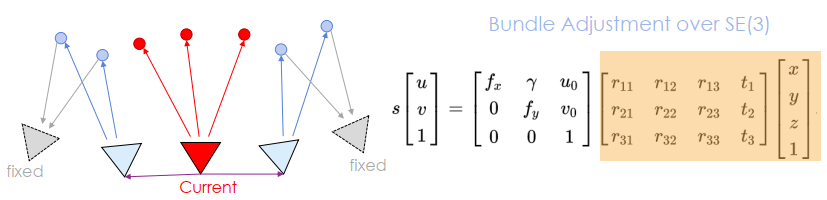
優化當前的 keyframe 和所有連接的 keyframes,以及這些 keyframes 看到的所有 map points。那些看的到 map points 但不跟 current keyframe 連接的 keyframes 會被包含在最佳化中,但是不會改變。
Loop Closing
時間拉長 error 會累積,所以需要 loop closing 穩定整個 ORB-SLAM。融合重複的地圖點,將 edges 插入 covisibility graph 並傳播 scale 的資訊,修正鄰近 keyframes 的 pose,最後進行 global pose graph 最佳化。