Central Dogma
Central dogma 是一個概念,指 DNA 透過轉錄、翻譯的步驟將 genetic information 轉換為蛋白質的過程。轉錄是指 DNA sequence 會被"轉錄"成相似的 RNA sequence,翻譯則是指 mRNA 被"翻譯"成對應的 amino acids "語言",以此建構 polypeptide。此外,codon 和 amino acid 之間的對應關係叫做 genetic code,可以用完整的 genetic code table 來表示,並有 start codon 以及 stop codon 來標註開始與結束的位置。
Central dogma and the genetic code
Intro to gene expression
DNA 是生物的 genetic material,但實際上 DNA 到底是怎麼樣來影響特徵的 ?
Genes specify functional products
- DNA 可以細分成好多個 functional units 叫做 genes
- Genes 提供 instruction 來製作 functional product
- 通常 functional product 是 protein
- 例如 flower color gene 幫助 (提供指令) 製作控制花朵顏色的 protein
- Genes 提供 instruction 來製作 functional product
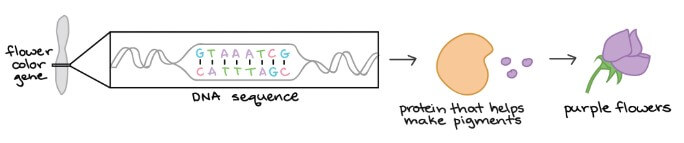
- 這些 protein 通常都是 polypeptides
- Polypeptide 的意思是 chain of amino acids
- 有的 protein 只有單個 polypeptide
- 有的 protein 有多個 polypeptides
- 幫助製作 polypeptides 的 gene 叫做 protein-coding genes
有的 gene 則幫助製作 functional RNA molecules (tRNA, rRNA, ...)
Gene expression
DNA 將透過 gene 的指令,用兩個步驟來建構 polypeptide:
- Transcription
- DNA sequence 會被"轉錄"成相似的 RNA sequence
- 在 eukaryotes 中 RNA 會被處理成 messenger RNA (mRNA)
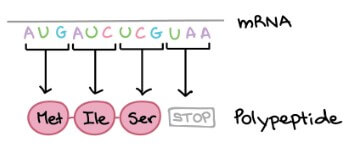
- Translation
- mRNA 被"翻譯"成對應的 amino acids "語言"
- 這個 amino acids sequence 就是 polypeptide
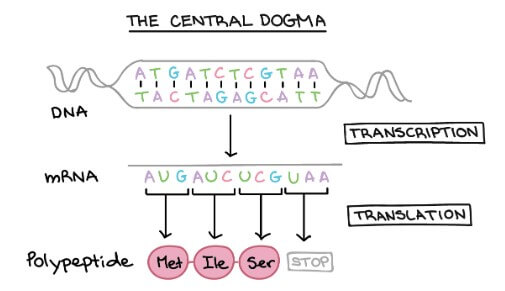
整個從 DNA 變成 functional product 的過程叫做 gene expression
- 上面看到的 Gene expression 有兩種
- expression of protein-coding gene
- DNA → RNA (mRNA) → protein
- 又稱為 central dogma
- expression of non-protein-coding gene
- DNA → RNA (functional RNA)
- expression of protein-coding gene
Transcription
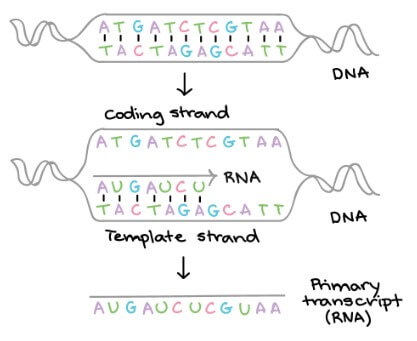
- 被作為 template 的 strand 叫做 non-coding strand
- 沒事的另一個 strand 叫做 coding strand
RNA polymerase 將參考 non-coding strand 打造出對應的 primary transcript
- Primary transcript 會和 coding strand 擁有一模一樣的資訊
- 但 base thymine (T) 會變成 base uracil (U)
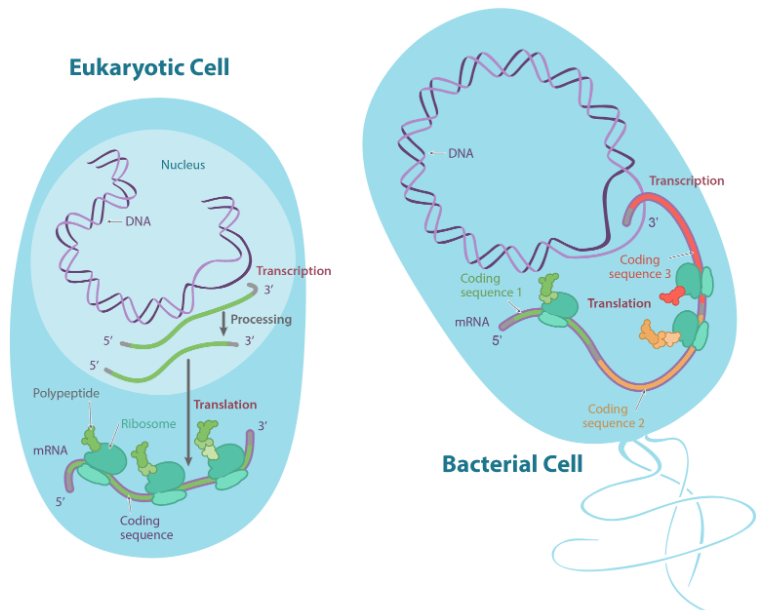
Transcription 在 bacteria 和 eukaryotes 有很多不同處
- 在細菌中的 primary transcript
- 會直接作為 mRNA (DNA 和 ribosomes 的媒介)
- p.s. ribosomes 在 cytosol 負責製作 protein
- Transcription 和 translation 都在 cytosol 中進行
- 會直接作為 mRNA (DNA 和 ribosomes 的媒介)

- 在 eukaryotes 的 primary transcript
- 需要一些步驟才能變成 mRNA
- 在過程中 RNA 末端會有保護,且會被一點點消去 (splicing)
- Transcription 在 nucleus 進行
- mRNA 需要輸出到 cytosol 才能找到 ribosome 進行 translation
Translation
有了 mRNA 就可以翻譯成 polypeptide 了,這個步驟叫做 translation
- mRNA 中的 nucleotides 會以三個一組 (codon) 來讀取
- 總共有 61 個 codons 來做出 amino acids
- 其中一個是 start codon
- 指定從哪裡開始 translation
- 起點是 amino acid methionine
- 其中三個是 stop codons
- 提示 polypeptide 的終點
- 這三個不算在 61+3 裡面,因為不是用來 coding protein
Codons 和 amino acids 的關係叫做 genetic code
Translation 在 ribosomes 裡面進行,釋出 polypeptides
- Ribosome 會和 mRNA 結合,找出 start codon
- 然後開始往下讀取 mRNA (一次讀取一個 codon)
- 產生對應 mRNA codons 的 amino acid sequence
但負責找出 codon 對應的 amino acid 的不是 ribosome 而是 transfer RNAs (tRNAs)
- tRNA 的一邊有 3 個 nucleotides
- 用來找對應的 codon 是否有對應的 base-pair
- tRNA 另一邊則載著 amino acid
- 這個就是對應 codon 的 amino acid
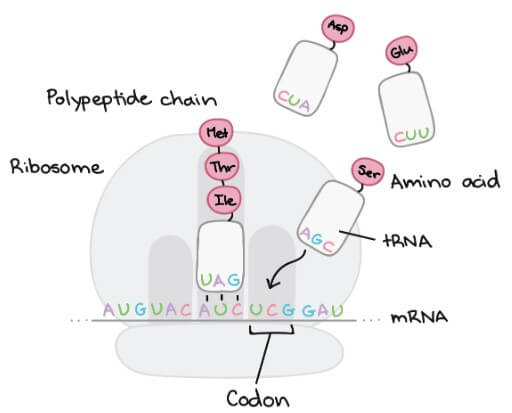
細胞中漂浮著很多 tRNAs,直到找到對應的 codon 並交付 amino acid 給他
- tRNA 在 ribosome 找到對應的 codon
- amino acid 會被加入到 polypeptide chain 的末端
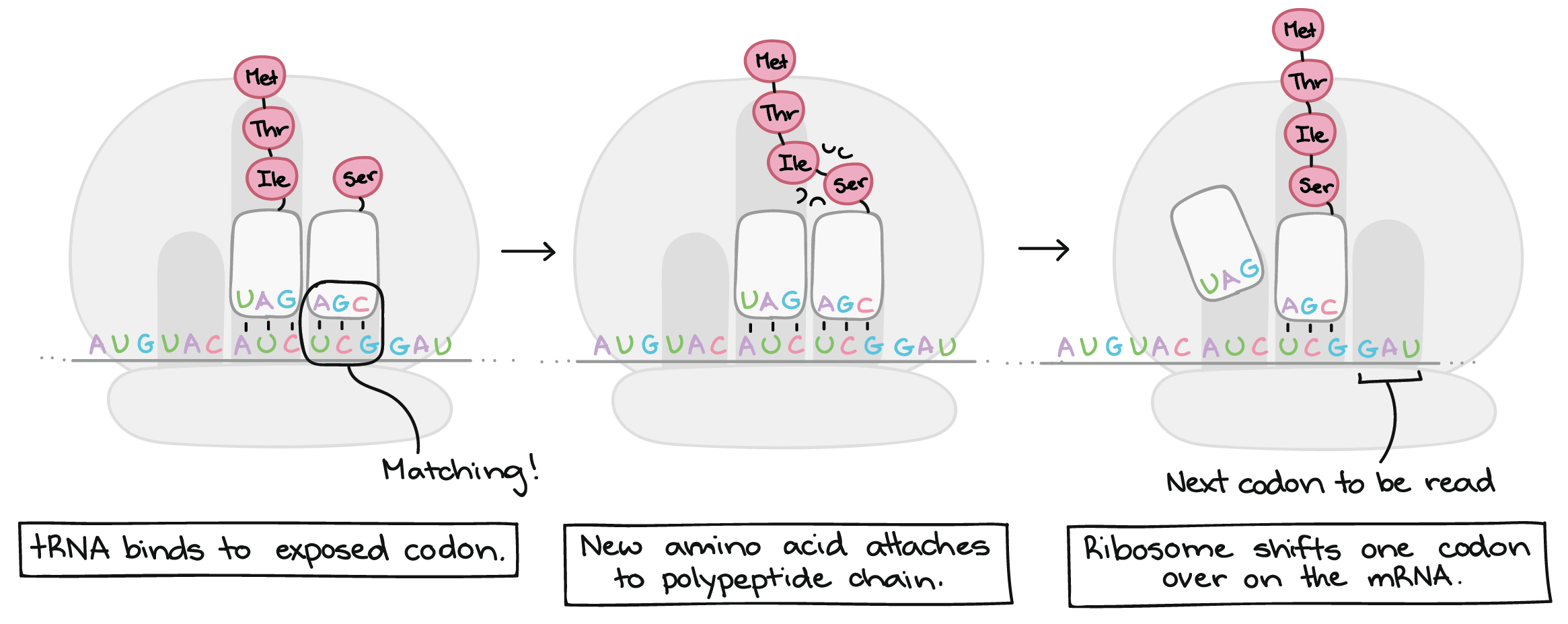
這些步驟會一直重複,直到 ribosome 讀到 stop codon 然後釋出 polypeptide
The genetic code
Codons
Codon 是三個 nucleotides 一組的產物,以下是 codons 的幾個特徵:
- 大部分的 codons 都對應一個 amino acid
- 3 個 "stop" codons 定義 protein 的終點
- 1 個 "start" codon (AUG) 定義 protein 的起點
- 這個 codon 對應的是 amino acid methionine
mRNA 分成一個個 codons,由 5' 讀到 3',產出的 amino acid 則從 N-terminus (methionine) 輸出到 C-terminus
- N-terminus 有 amino group exposed
- C-terminus 有 carboxyl group exposed

The genetic code table
Codons 和輸出的 amino acids,兩者之間的關係 (genetic code) 可以用完整的 genetic code table 表示
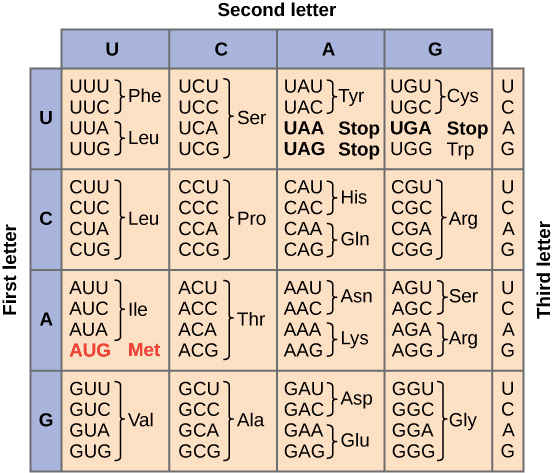
- 左邊是 codon 的第一個 base
- 上方是 codon 的第二個 base
- 右邊是 codon 的第三個 base
有的 amino acids 可以對應多種 codons,例如從表中可看出 leucine 對應了 6 種 codons 組合。
Genetic code table 有個重要的特點,就是幾乎可以對應所有物種合成 protein 的 RNA 組合
Reading frame
mRNA 到 protein 還有一個重要的概念是 reading frame
- 要怎麼在長長一段的 RNA sequence 找出正確的 codon 順序
- 不同的看法就有不同的 reading frame
- 例如下圖同個 mRNA 可以被看成三種完全不同的 polypeptide sequence
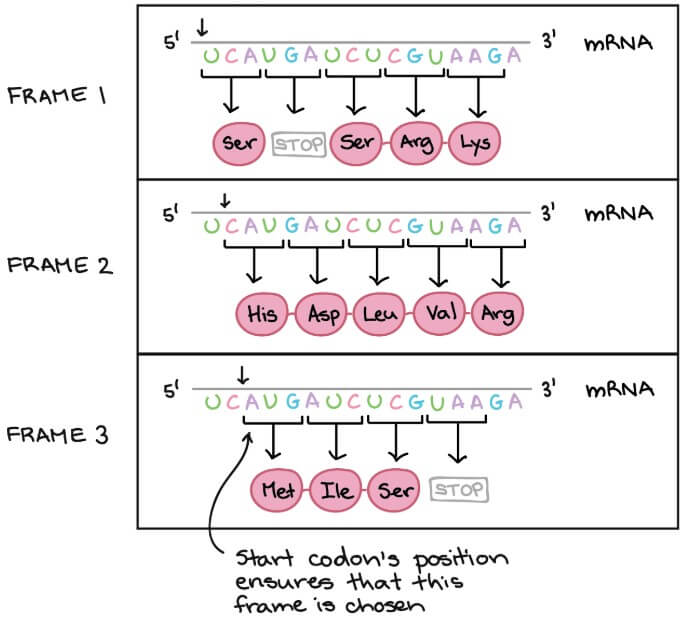
- 哪一個 frame 才是正確的 ?
- 這要看 start codon 在哪裡
- 因為 translation 永遠是從 start codon 開始,每三個為一組讀取
- 所以上圖的 frame 3 才是正確的
另外 mutation 的發生 (insert, delete nucleotides) 會改變 reading frame
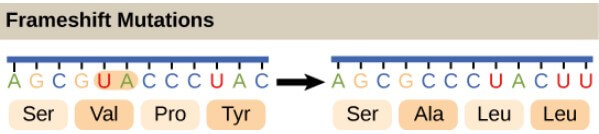
- Frameshift mutation
- 上圖的 UA 就因為 mutation 而被刪除
- 造成後方的 RNA 也被讀取錯誤
- 最終產生錯誤的 protein
One gene, one enzyme
Mendel 雖然找到遺傳現象,但他沒發現他口中的遺傳因子 (gene),跟其他重要的 functional molecules (e.g., protein) 有所關聯。
- 第一個找出 gene 和 protein 有所關係的是 Archibald Garrod (英國醫學家)
- Garrod 觀察病人全家都有的 metabolic diseases 叫做 alkaptonuria
- Alkaptonuria 會讓病人的尿變黑
- 原因是他們無法分解 alkapton 這個 molecule
- Garrod 觀察病人全家都有的 metabolic diseases 叫做 alkaptonuria
Garrod 認為這和 Mendel 提出的 recessive pattern of inheritance 有關
- Garrod 將這個現象定義成 "inborn error of metabolism"
- 而且發現其他疾病也有相同現象
- 因為發現 gene 和控制 metabolic reactions 相關的 enzymes 有關
- 所以可以說是 "the father of chemical genetics"
Beadle and Tatum: Connecting genes to enzymes
Garrod 的想法沒得到重視,直到 1940s 兩位科學家 George Beadle 和 Edward Tatum 進行實驗
- Beadle 和 Tatum 使用 bread mold 作為實驗主角
- bread mold 又稱 Neurospora crassa
- Neurospora 有快速又方便的 life cycle
- Neurospora 可以生存在 minimal 或 complete medium 當中
- Minimal medium 只有 sugar, salts, biotin (vitamin)
- Complete medium 則有豐富的養分讓細胞成長
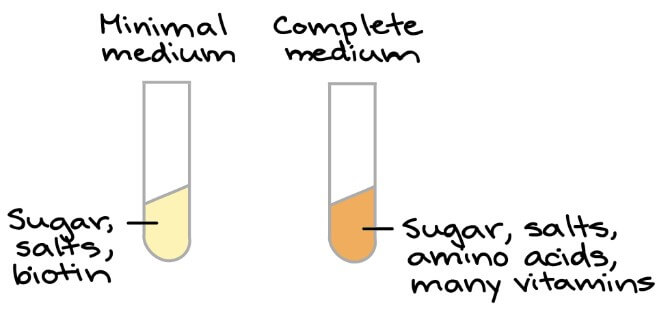
Neurospora 細胞可以在簡單的 minimal medium 存活,是實驗成功的關鍵 !
Hypothesis
- 若 gene 真的和 biochemical enzymes 有關
- 那麼 gene 一定會被外界因素改變 (mutation)
- 從而將特定的 enzymes "消滅"掉
- 讓細胞無法在 "minimal" medium 生存
也就是 Neurospora 可以在 complete medium 生存,但無法在 minimal medium 生存
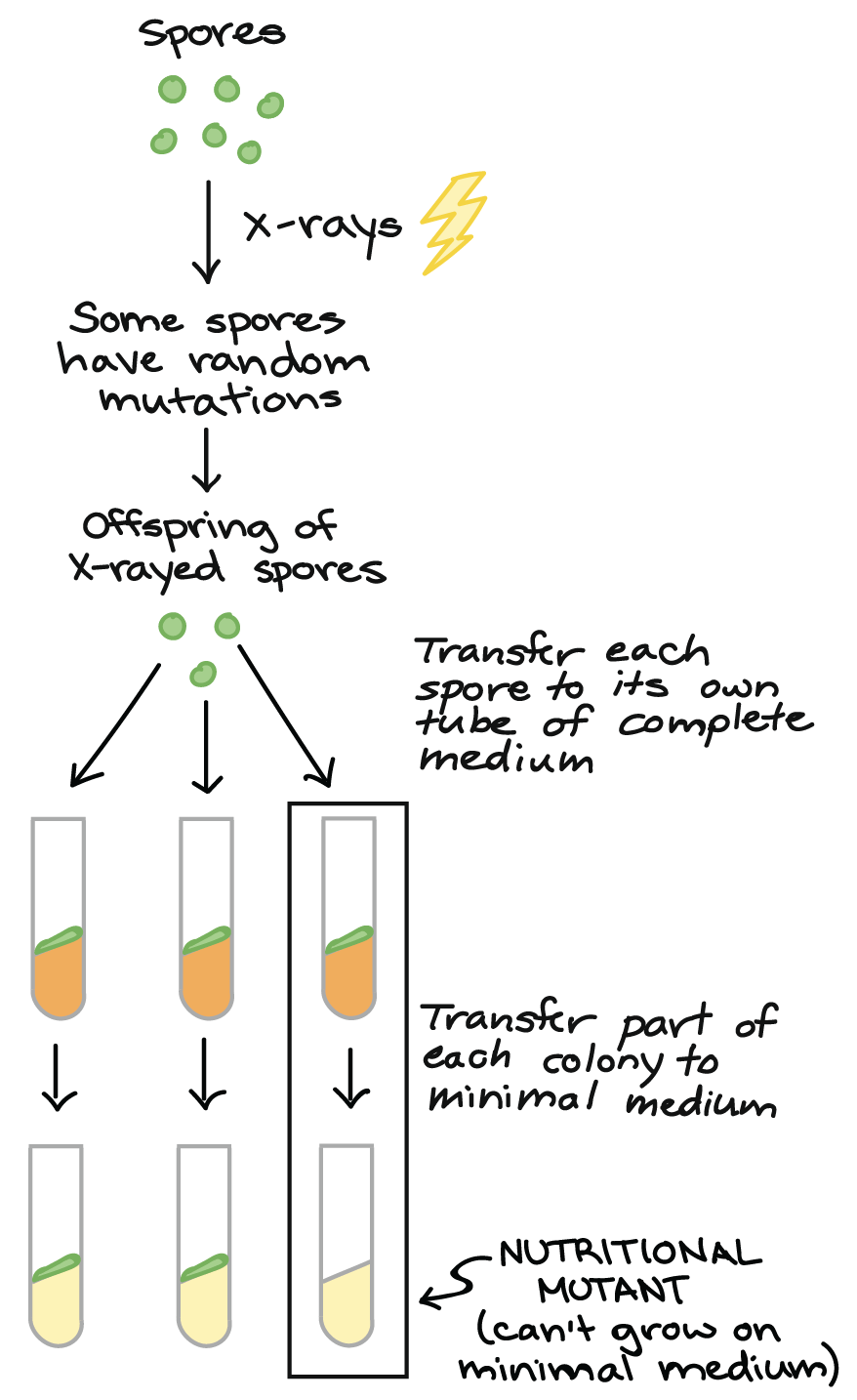
- Beadle 和 Tatum 將 Neurospora spores 暴露在輻射中
- 再來將它們的子代放到 complete medium 中
- 當子代繁衍成一群 (colonies) 時,取出一些丟入 minimal medium 中
結果出爐 !
- 有的 colonies 能夠存活在 minimal medium
- 有的 colonies 無法存活在 minimal medium
- 這些 colonies 就是 nutritional mutants
- Nutritional mutants 的 gene 被破壞,無法產生存活必要的 molecule
- 而他們可以存活在 complete medium
- 因為 complete medium 提供了他們無法製造的養分
Pinpointing the broken pathway
Beadle 和 Tatum 進行了第二階段的實驗,為了是找出真正無法被生產的 protein
- 首先將 mutant 裝入 minimal medium (但還加入特別的東西)
- 一種加入完整的 amino acids (20 種融合)
- 如果該杯的 mutant 可以存活 (但 vitamin 那杯無法存活)
- 代表 mutant 一定是無法生成 amino acids
- 一種加入完整的 vitamins
- 如果該杯的 mutant 可以存活 (但 amino acids 那杯無法存活)
- 代表 mutant 一定是無法生成 vitamin
- 一種加入完整的 amino acids (20 種融合)
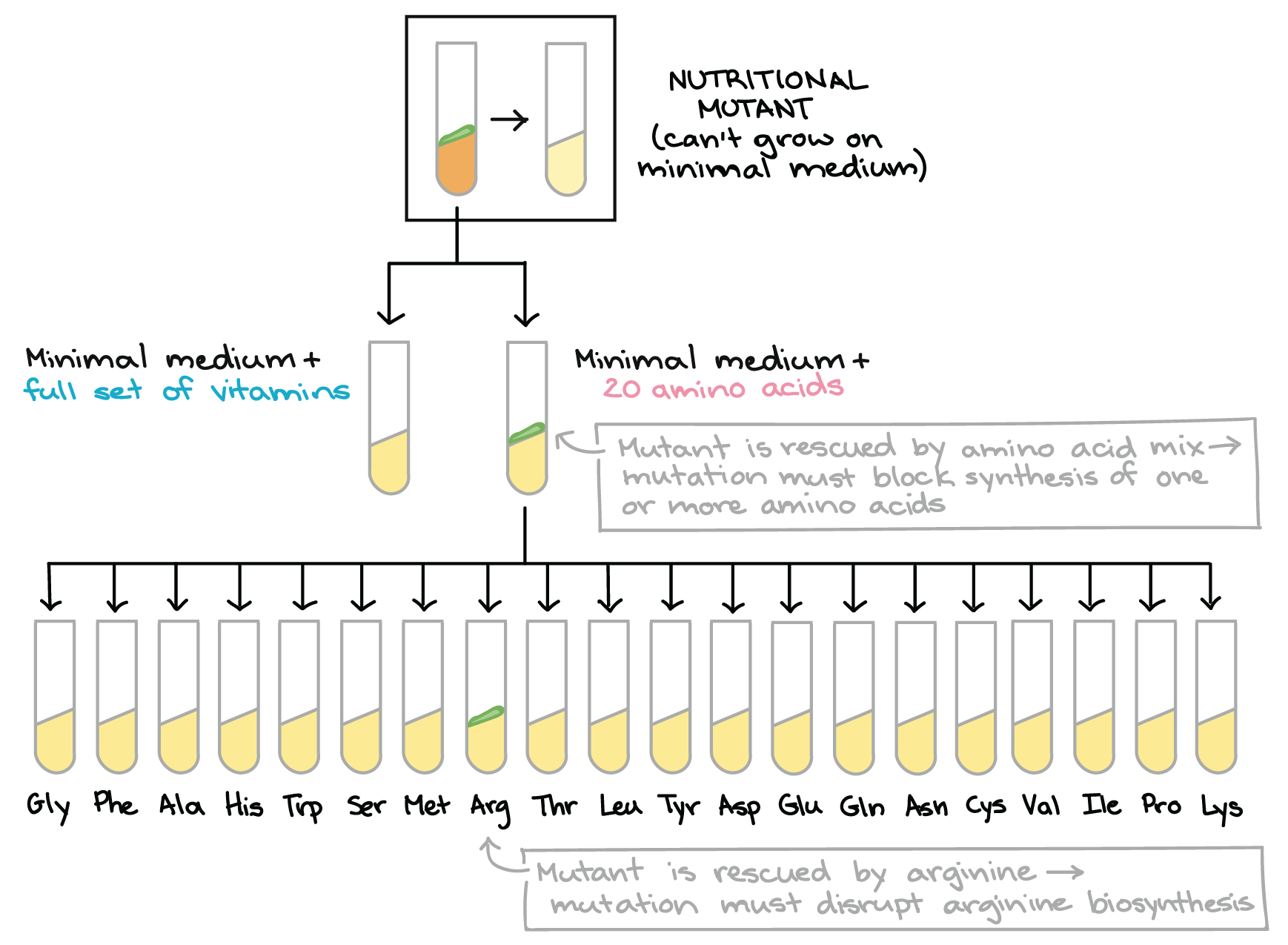
- 當確定是生成 amino acids 的 gene 被破壞後
- 就可以進入第二輪的測試
- 將 20 種 amino acids 的 medium 都測試一遍
- 若 mutant 只存活在某一杯 amino acid medium
- 就代表該杯就是 mutant 無法生成的 amino acid
- 就可以進入第二輪的測試
這個做法讓 Beadle 和 Tatum 找到了 nutritional mutants 和 amino acid, vitamin 的關係
"One gene-one enzyme" today
Beadle 和 Tatum 的這個發現稱為 "one gene-one enzyme" 假設,但也在之後被進行了多次的更新
- Some genes encode proteins that are not enzymes.
- Gene 不只用來編碼 enzymes (protein)
- Gene 也用來編碼了其他 proteins
- Some genes encode a subunit of a protein, not a whole protein.
- Gene 編碼出來的 polypeptide 只是單串 amino acids
- 有很多 proteins 是由多個 genes 編碼的 polypeptides 組成
- Some genes don't encode polypeptides.
- Gene 不只編碼 proteins
- Gene 也編碼 functional RNA molecules
Transcription
Gene expression 的第一步,將 gene's DNA sequence 複製成 RNA copy (transcript)
- Bacteria 可以直接將 transcript 當作 mRNA
- Eukaryotes 則需要對 transcript 動些手腳才能變成 mRNA
負責 transcription 的是 RNA polymerase (enzyme)
- 將 double-stranded DNA 打開,並將其中一串 DNA 當作 template 來複製出 RNA
- 方向是從 5' 到 3'
- 被打開的 DNA 叫做 transcription bubble
人類等 eukaryotes 和細菌的 RNA polymerase 有所不同,和植物又不同
- 人類共有三種 RNA polymerase: I, II, III
- 每種負責不同種類的 genes
- 植物又比人類多了兩種 RNA polymerase: IV, V
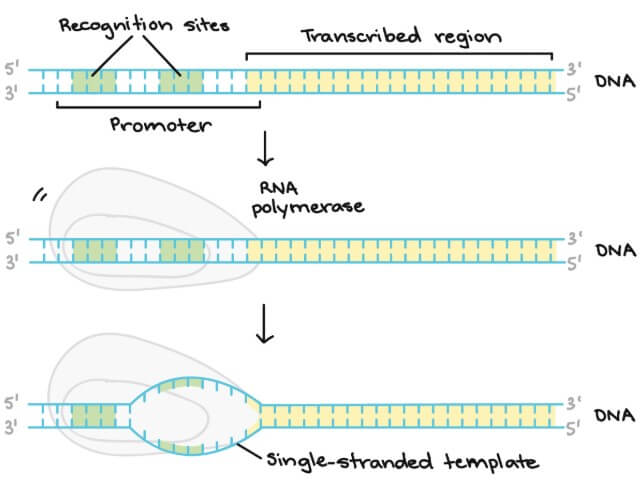
- 第一個被複寫成 RNA 的 DNA 地點稱為 initiation site
- Initiation site 又稱為 +1 site
- 在 +1 site 之前的都是負數,叫做 upstream
- 在 +1 site 之後的都是正數,叫做 downstream
Transcription 有三大步驟: initiation, elongation, termination
Initiation
- RNA polymerase 到 DNA 上找到 promoter (gene 的開始)
- 每個 gene 都有自己的 promoter
- RNA polymerase 和 promoter 結合後
- 會將 DNA 打開,把其中一條當作 template 來複寫
In bacteria
- 細菌的 promoter 有兩種 DNA sequence
- -10 elements
- -35 elements
- 取名來自它們在 +1 site 的前面 10 和 35 個 nucleotides 遠
- DNA 會在 -10 的地方被打開
- 因為充滿 As 和 Ts 所以較容易被打開 (2 hydrogen bonds only)

In human
- 細菌的 RNA polymerase 會直接接觸 promoter
- 但人類需要透過 basal transcription factors 先和 promoter 結合
- 提供 RNA polymerase 一個立足點
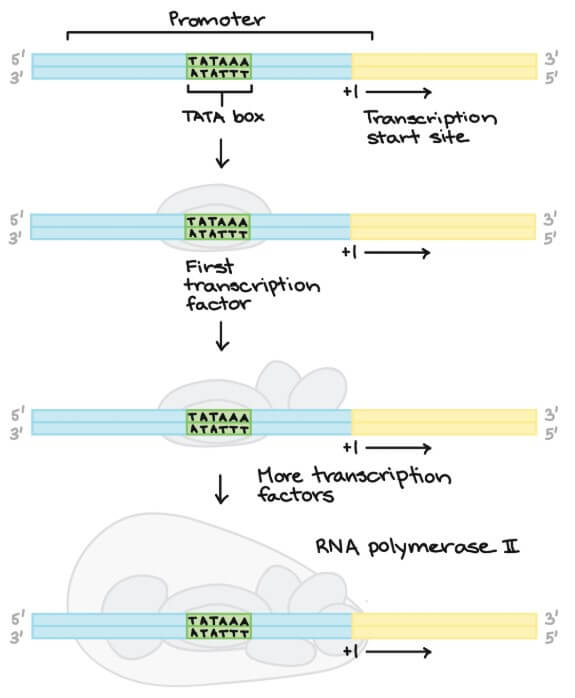
- 大多的 eukaryotic promoters 會有一個序列叫做 TATA box
- TATA box 的角色就像 -10 element 一樣
- 讓一堆 basal transcription factors 找到他並結合
- 最後吸引 RNA polymerase 來結合
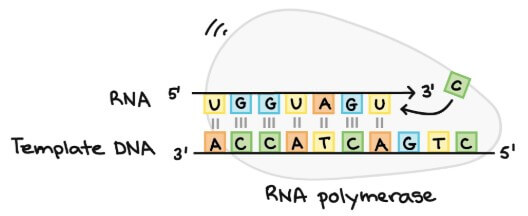
Elongation
- RNA polymerase 開始讀取 template strand (一次讀取一個 base)
- 讀取 DNA 的方向是 3' 到 5'
- 製作出一條對應的 RNA copy chain (由 5' 到 3')
- RNA copy chain (transcript) 會和 coding strand 有一模一樣的資訊
- 只是 uracil (U) 取代 thymine (T)

DNA 可以一次被很多 RNA polymerases 複寫
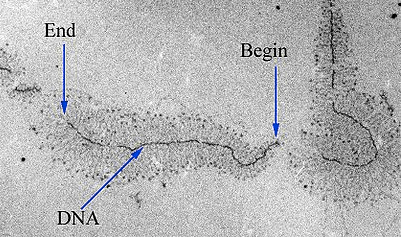
Termination
- DNA 中有一串序列叫做 terminator 會告訴 RNA 複寫完畢
- 當 RNA 複寫到 terminators
- 會讓 transcript 從 RNA polymerase 釋放出來
Termination 有兩大形式: Rho-dependent 和 Rho-independent
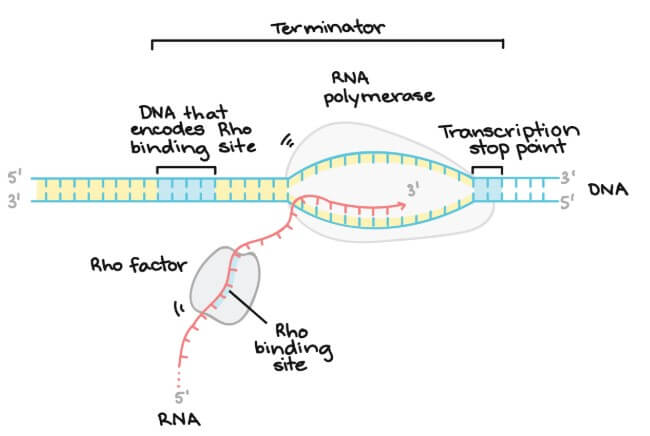
Rho-dependent termination
- 在 RNA 中會有一個 Rho factor (protein)
- 會往上爬到 RNA polymerase 的地方
- 將 RNA transcript 從 DNA template strand 拔出來
- DNA 中會有一個 transcription stop point
- 停止 RNA polymerase 幫助 Rho factor 趕上
- 會往上爬到 RNA polymerase 的地方
Rho-independent termination
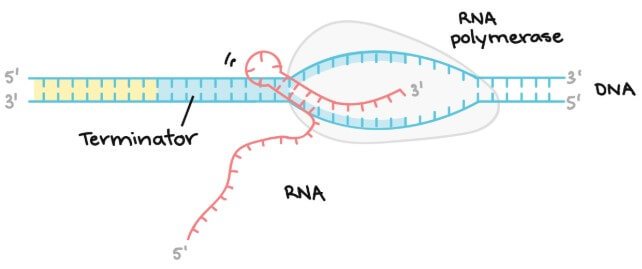
- DNA template 中有一個區域富含 Cs 和 Gs nucleotides
- RNA 複寫這段時,會變成摺疊變成髮夾狀
- RNA 髮夾會接續著 U nucleotides
- 因為 U 是和 DNA 的 A 吸引 (2 hydrogen bond)
- 所以容易被其他 enzyme 拉開
What happens to the RNA transcript?
- 在細菌中,完成複寫的 transcript 作為 mRNA
- 會快速和 ribosomes 進行下一個步驟 "translation"
- mRNA 和 ribosome 形成 polyribosome

而人類的 transcript 必須進行 RNA modification 變成 mRNA 先
Eukaryotic RNA modifications
RNA transcripts 在 bacteria 和 eukaryotes 有不同角色
- 在 bacteria 的 transcript 等於 mRNA
- 可以開始 translation
- 在 eukaryotes 的 transcript 等於 pre-mRNA
- 還需要程序才能變成 mRNA
5' cap and poly-A tail
程序一,在 pre-mRNA 的開頭 (cap) 和結尾 (tail) 加入保護機制,方便 mRNA 離開 nucleus
- 5' cap 會被加入到第一個 nucleotide
- Cap 是一個 modified guanine (G) nucleotide
- 保護 transcript 不被破壞
- 幫助 ribosome 方便和 mRNA 結合
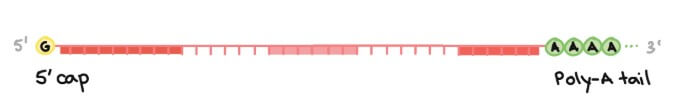
- 3' end 是多個 adenine (A) nucleotides 被加入到最後
- RNA 在 transcription 有一個序列叫做 polyadenylation signal
- Enzyme 會在這個序列將 RNA 切成兩半
- 其他 enzyme 會再將 100 至 200 個 adenine (A) 加入到切點的後方,形成 poly-A tail
- 讓 transcript 更穩固,幫助他更容易離開 nucleus
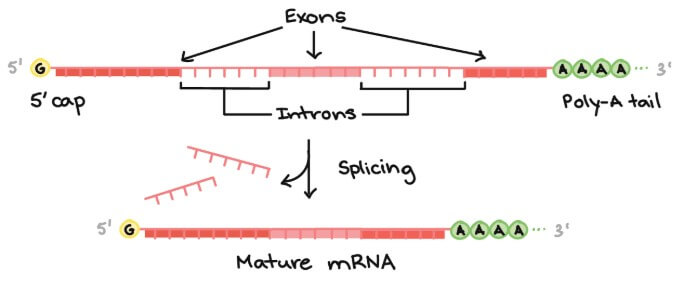
RNA splicing
程序二,RNA splicing 移除 pre-mRNA 不必要的地方,合併有用的地方
- 執行的是 spliceosome (protein-RNA complex)
- 發現並移除 introns (沒用的 pre-mRNA 部分)
- 接著發現並合併 exons (有用的 pre-mRNA 部分)

只有正確的 exons 組合才能真正合成 protein,多一點或少一點 introns 都會無法運作
Alternative splicing
Splicing 看起來很無意義,但他是為要 alternative splicing 而存在
- 一個相同的 gene 只要 splicing 切法不同
- 就可以產生多種 mRNA 的結果
- 製造出不一樣的 proteins
下圖時是一個 pre-mRNA 在保留各種 exons 時,產生不同的 protein 結果
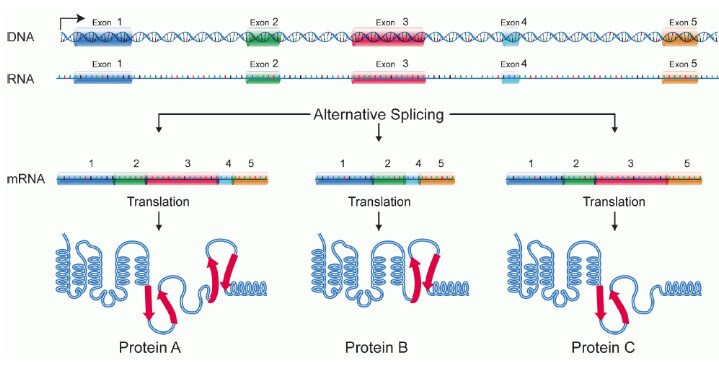
Transcription happens for individual genes
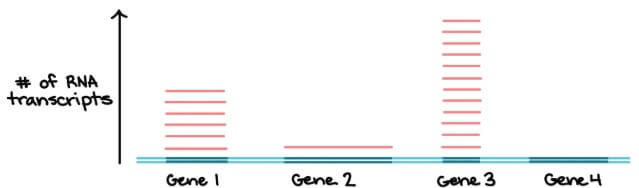
- 每個細胞會調節每個 gene 被 transcript 的時機
- 只有需要特定 products 的時候才會執行
- 例如下圖對 4 種 gene 的要求不同,執行 transcription 的次數也不同
Translation
你知道 antibiotics 是怎麼殺死細菌的嗎 ? 其實就是靠著中斷細菌的 translation !

Translation molecules
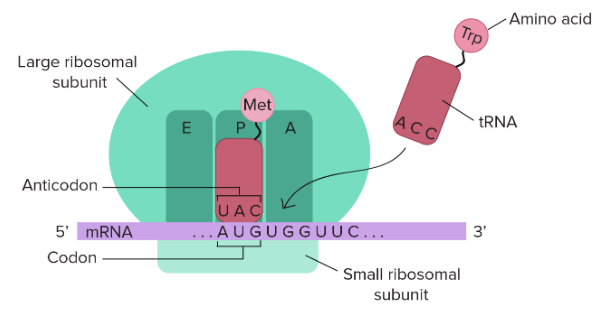
要將 mRNA 正確 "read" 然後製作出 polypeptide 需要兩大 molecules: tRNAs 和 ribosomes
Transfer RNAs (tRNAs)
tRNAs 是 mRNAs codons 和最終 amino acids 的橋樑
- tRNAs 有兩側
- 一側有一串 nucleotides 叫做 anticodon
- Anticodon 會和對應的 mRNA codons 組合
- 一側載著 codon 對應的 amino acids
- 一側有一串 nucleotides 叫做 anticodon
tRNAs 的種類很多,每種都會讀取一或多個 codons 然後給他正確的 amino acids
The 3D structure of a tRNA
- 雖然上面的 tRNA 是長方形的,但實際上 tRNA 是 L 形的
- 這是因為 nucleotides 之間形成 base pairs
- 讓 tRNA 之間產生 double-standed 的 regions 還有 loops
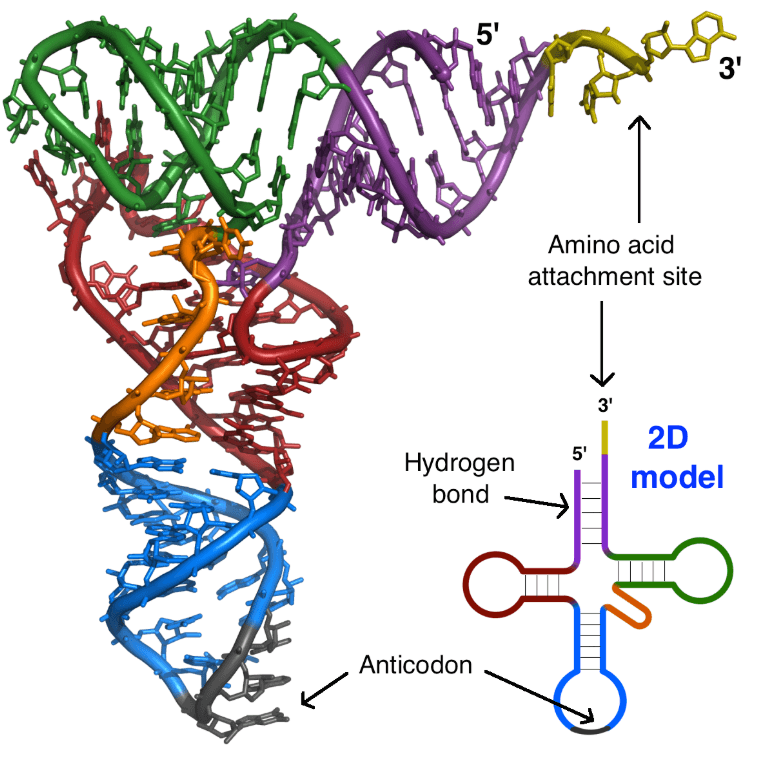
其中的一邊是 anticodon,另一邊則是 amino acids
Loading a tRNA with an amino acid
- Amino acids 是透過一種 enzyme 來和正確的 tRNA 組合的
- 這個 enzyme 叫做 aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases
- 每一種 amino acid 都有不同的 synthetase enzyme
- 組合中需要耗費一個 ATP
- 有的 enzyme 具有 proofreading site 防止錯誤

Ribosomes
Ribosomes 是建造出 polypeptides 的地方
- Ribosome 由 protein 和 RNA (ribosomal RNA, rRNA) 組成
- Ribosome 有兩個 subunits
- 大的和小的,一起將 mRNA 像漢堡一樣夾住
- Ribosome 的架構中分別有三個區域 (A, P, E) 讓 tRNA 經過
- Ribosome 也會扮演 enzyme 的角色,催化 amino acids 串聯起來
Stages of translation
Translation 一樣可以分成三大部分: initiation, elongation, termination
Initiation
- Ribosome 集中包覆在 mRNA 周圍
- 第一個 tRNA 來到現場
- 這個 tRNA 帶著 methionine (對應 start codon: AUG)
- 第一個 tRNA 來到現場
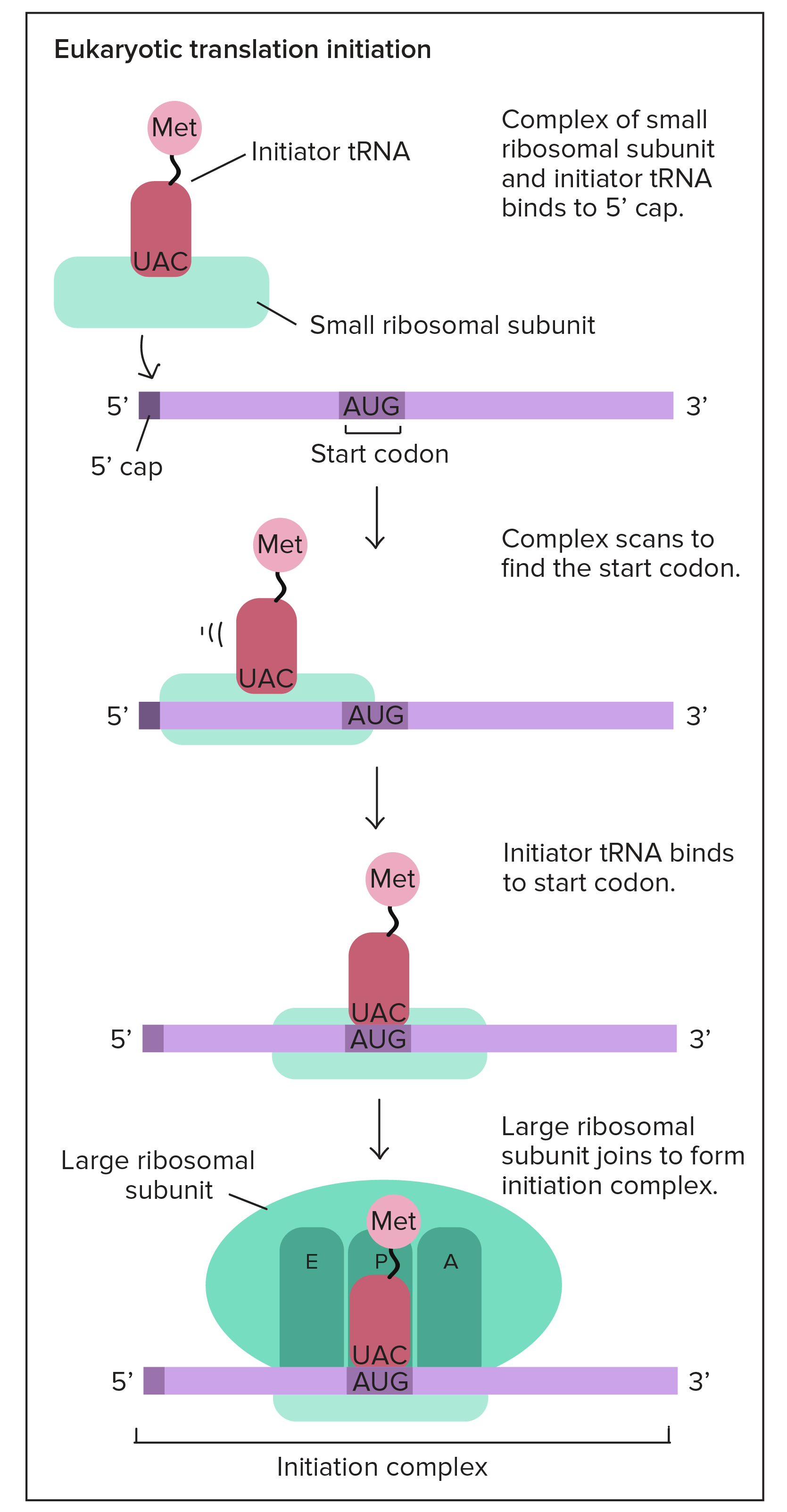
整個 setup (ribosome + mRNA + Met-tRNA) 稱作 initiation complex,準備開始 translation
Initiation 的整個詳細步驟如下 (in eukaryotes):
- 帶著 methionine 的 tRNA 依附在 small ribosomal subunit
- 他們一起結合到 mRNA 的 5' GTP cap
- 接著往 3' 方向走
- 停在 start codon
在細菌中的 initiation 有些不同
- Small ribosomal subunit 會直接到達 Shine-Dalgarno sequences
- 這是因為細菌的 genes 通常都是一整組 (operons) 一起 transcribe 的
- 所以一個 mRNA 有不同的段落給不同的 genes
- Shine-Dalgarno 方便讓 ribosome 快速找到位置
Elongation
在 initiation complex 形成之後,Amino acid chain 要開始變得 longer
- 每次 mRNA 一次讀取一個 codon
- 對應的 tRNA 就會來結合
- tRNA 運送的 amino acids 將和現有的 amino acid chain (polypeptide) 串起來 (chemical reaction)
- mRNA 移動,讓下一個 codon 能夠被讀取
- 整個過程 tRNA 會在 A, P, E sites 移動
- A: Aminoacyl
- P: Polypeptide forming
- E: ready to Exit
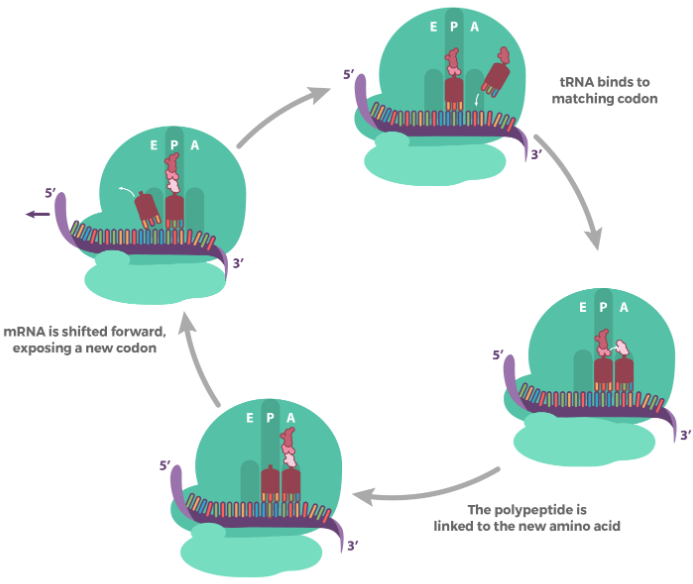
- 一開始 Met-tRNA 落在 P site
- 新的 codon 在 A site 準備被讀取
- 這時 tRNA 帶著新的 amino acid 來到 A site
- 消耗 energy 和 codon 結合
- P site 的 polypeptide 和 A site 的 amino acid 結合
- 以 peptide bond 的形式結合
- P site 的 polypeptide 轉移到 A site
- P site 來的是 N-terminus
- A site 的是 C-terminus
- mRNA 被 ribosome 往後拉一個 codon
- 在 P site 的 tRNA 來到 E site 準備離開
- 一個循環結束
Elongation 最長可以到 33000 個 loops (形成肌肉中的 titin)
Termination
- 當 stop codon (UAG, UAA, UGA) 進入到 ribosome (A site) 的時候
- polypeptide chain 將會被釋放
- polypeptide 會折疊成 3D 形狀
- 到細胞中下一個工作的地點
- 或跟其他 polypeptide 組合
- polypeptide chain 將會被釋放
Stop codons 會被 release factors (protein) 認出
- Release factor 存在於 P site
- 會擾亂形成 peptide bonds 的 enzymes
- 透過加入水分子到 amino acid chain 的最後
- 拆斷 chain 和 tRNA 以此釋放 protein
整個 translation 的工具 (ribosomal subunits) 會分開,然後可以重複使用