Structure of a Cell
細胞是生物的基本單位,是由細胞牆、細胞質、基因體和核醣體組成的。細胞可以分為原核細胞和真核細胞。
原核細胞 (Prokaryotic cells) 是指單細胞生物,例如細菌與古細菌,他們沒有真正的核心。細胞內沒有膜限定的器官,內部沒有被分割成許多不同的功能部分,是一個開放空間。基因體會位於開放空間的中心,通常會有一個圓形染色體(單一大環)。
真核細胞 (Eukaryotic cells) 是指真正的核心細胞,例如動物、植物、真菌或原生動物。真核細胞的內部會有膜限定的器官,並且會有許多不同的功能部分。基因體會被收納在核膜之內,並且會有一個或多個染色體。
Intro to cells
牆是"磚"砌成的,人是"細胞"組成的 (standard building block)
- 但細胞不像磚塊無趣,細胞的可能性非常多
- 有各種形狀、各種功能
- 還能到處移動
- 各種細胞會扮演各種不同角色,幫助我們成長、生存
- epithelial cell 負責保護身體的表面,例如皮膚或器官
- bone cell 負責建構骨骼支撐身體
- cells of immune system 對抗細菌
- blood cells 在身體裡四處運送養分及氧氣,並移除 carbon dioxide
- Cell 不只人類擁有,其他動物、植物、甚至細菌都有
- 雖然會有很大不同,但都會有一些相同的地方

Scale of cells
雖然我們知道 atom, protein, virus, cell, ... 都是小到肉眼看不到的東西,但他們還是有大小之分 !
- Water molecules : ~0.275 nm (約 10 億分之 1 公尺)
- Hemoglobin (protein) : 5 nm (約 10 億分之 5 公尺)
- HIV (virus) : 120 nm
- Red blood cell : 6 to 8 μm (micrometer, 約 100 萬分之 7 公尺)
- 含有 280 million 個 hemoglobin !
Cell theory
其實到 1600s 根本沒有人知道 cell 的存在
- 因為細胞實在太小了,沒有很強力的 microscopes 能夠看到細胞
- 附帶一提,最適合觀測細胞的是 light microscope
- 而最適合觀測到細胞內部架構的是 transmission electron microscope
直到第一個人看到,並且在他的書中命名為 cell
- Robert Hooke 這位英國科學家是第一個用他的 microscope 看到細胞這個 microscopic structures
- 他將看到的一切和命名都寫在他的 Micrographia 書中
- 他看到的細胞是 dead cork tissue
- 因為外型非常像寺院中僧侣所居住的小房間 (cells of a monastery)
- 所以就取名為 cell
但 Hooke 所看到的只是一個死掉的細胞
- 第一個看到活著的細胞的是一個荷蘭貿易家 Anton van Leeuwenhoek
- 他在 1670s 改善了 Hooke 的 microscopes
- 建立出更強大的 microscopes
- 這些加強的 microscopes 可以看到一些 single-celled organisms
- 例如 bacteria, sperm cells
- 他將這些 cell 稱作 animalcules
儘管如此,還是沒有人相信 cell 是組成動物、植物、細菌最基礎的 building block,直到 160 年後 ...
- 植物學家 Matthias Schleiden 和動物學家 Theodor Schwann
- 兩人在 1830s 提出了跨世紀的突破理論
- 也就是所有植物和動物的所有部位,都是由 cell 組合而成
- 以及 cells 是可以被其他 cells 所生產出來的
接著德國科學家 Rudolf Virchow 盜用了別人的點子,也就是
- 波蘭科學家 Robert Remak 基於上面兩位所提出的第三個理論
- 所有的 cells 都是從其他 cells 而來 !!!
- 這在今日聽起來也是非常匪夷所思的理論
這三點總結起來就是 modern cell theory
- All living things are composed of one or more cells.
- The cell is the basic unit of life.
- New cells arise from pre-existing cells.
Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
人體是一個細胞的家,總共有 100 trillion 的細胞在人體中
- 人體其實就是一個 ecosystem
- 包含了 prokaryotic, eukaryotic cells
- 所有的細胞就是分成了這兩類
- Prokaryotic (pro- : before, kary- : nucleus)
- 目前只有 single-celled organisms (Bacteria, Archaea) 被分類在此
- Eukaryotic (eu- : true)
- Animals, plants, fungi, protists 是該分類
- 而他們又是由很多的 eukaryotic cells 組成
- Prokaryotic (pro- : before, kary- : nucleus)
Cell 的大小範圍在 0.1 到 100 μm
- 其中 prokaryotic cells 在 0.1 到 5 micrometers (μm)
- 而 eukaryotic cells 在 10 到 100 micrometers (μm)
- 為什麼不能更小 ?
- 因為細胞必須要放得下需要的元件
- 為什麼不能更大 ?
- 因為細胞越大越難和外界交換足夠的養分來供給
- 可以從 surface-area-to-volume ratio 看得出來
Prokaryotic cells
不同的細胞主要還是有四種重要的元件
- plasma membrane
- 幫助細胞分開內部和外部環境的接觸
- cytoplasm (細胞質)
- 包含像果凍的 cytosol,還有一些 cellular structures
- 通常在 nucleus 和 membrane 之間
- DNA
- 是該細胞的 genetic material
- Ribosomes
- 是一個 molecular machines 用於合成 proteins
上面講的是和 eukaryotes 共同的地方,再來講點相異的地方
- Prokaryote 指的是簡單的 single-celled 生物
- 沒有 nucleus 和 membrane-bound 的 organelles
- 內部沒有被切成多個功能的部分,是一個開放空間
- prokaryotic DNA 會在開放空間的最中間 (nucleoid)
- 通常包含了 circular chromosome (single large loop)
- 下圖是一個 rod-shaped bacterium 剖面
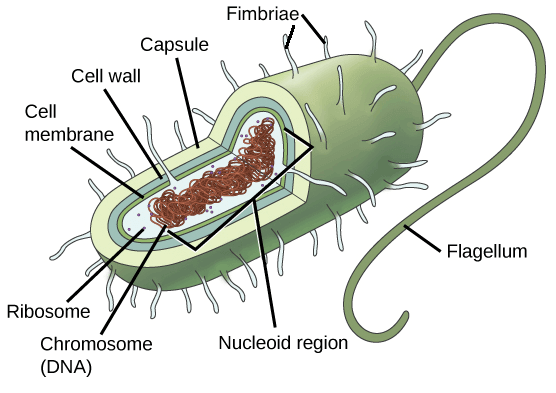
- 一般的 bacteria 含有這些構造 :
- 用 peptidoglycan (肽聚醣) 組成的 rigid cell wall
- Cell wall 保護細胞、維持形狀、避免 dehydration
- 有的還有用 carbohydrates 組成最外層的 capsule
- Capsule 幫助細胞跟當下環境表面接觸
- 一些外部構造幫助移動細胞,甚至交換 genetic material
- Flagella 像 rotary motors 一樣幫助 bacteria 移動
- 另外還有跟頭髮很像的 fimbriae 用來跟 host cell 或其他表面接觸
- 有的 bacteria 還有各種不同的桿狀架構 pili
- 有些幫助 bacteria 之間傳遞 DNA molecules
- 有些也幫助 bacteria 移動
- 用 peptidoglycan (肽聚醣) 組成的 rigid cell wall
Eukaryotic cells
如果把 prokaryotic cells 譬喻為比較窄的單人房,那麼 eukaryotic cells 就是合租公寓了吧
- 就像大房子一樣,有浴室、廚房、臥室、客廳一樣
- Eukaryotic cells 會含有各種不同功能的 compartments
- Compartments 被層層的 membrane 分隔開來
- 所以每個 compartment 都有獨自的 conditions 進行自己的工作
以下舉幾個常見的 compartments
- Lysosomes (溶酶體) 是細胞的回收中心
- 必須要保持正常的 acidic pH 才能 dispose 細胞垃圾
- Peroxisomes (過氧化體) 負責處理一些 chemical reaction
- 例如 oxidation reactions 和生產 hydrogen peroxide
- 這兩件事都有可能傷及細胞,所以 compartment 起到很好的保護
就是因為 eukaryotic cell 可以維持多種環境在一個細胞的能力,而 prokaryotes 不行
- 所以 eukaryotic cells 可以比 prokaryotic cells 還能成長好幾倍
Eukaryotic cells 還比 prokaryotic cells 多了幾種重要特徵
- Membrane-bound nucleus
- 在細胞中央被 membrane 包住的洞,是 genetic material 的家
- Number of membrane-bound organelles,各種浮在 cytosol 上的 compartments
- Multiple linear chromosomes
- 對應到 prokaryote 中的 single circular chromosome
Plasma membrane and cytoplasm
- Cell 非常簡單來說就是 bag of goo
- Plasma membrane 就是 bag
- Cytoplasm 就是 goo
- 但 cell 其實非常精緻,所以 bag 和 goo 也非常複雜
- Membrane 是包含 lipids 和 proteins 的雙層架構,負責任何東西進出 cell
- Cytoplasm 不只包含 cytosol,更包含 organelles, structural proteins (skeleton of the cell)
Plasma membrane
- Membrane 所含的 lipids 是 phospholipids
- phospholipid 由 hydrophilic 的 phosphate head 和兩個 hydrophobic 的 fatty acid tails 組成
- hydrophilic head 朝外,hydrophobic tails 朝內,自然形成雙層架構
- 這個 energetically faborable 的雙層架構又稱為 phospholipid bilayer
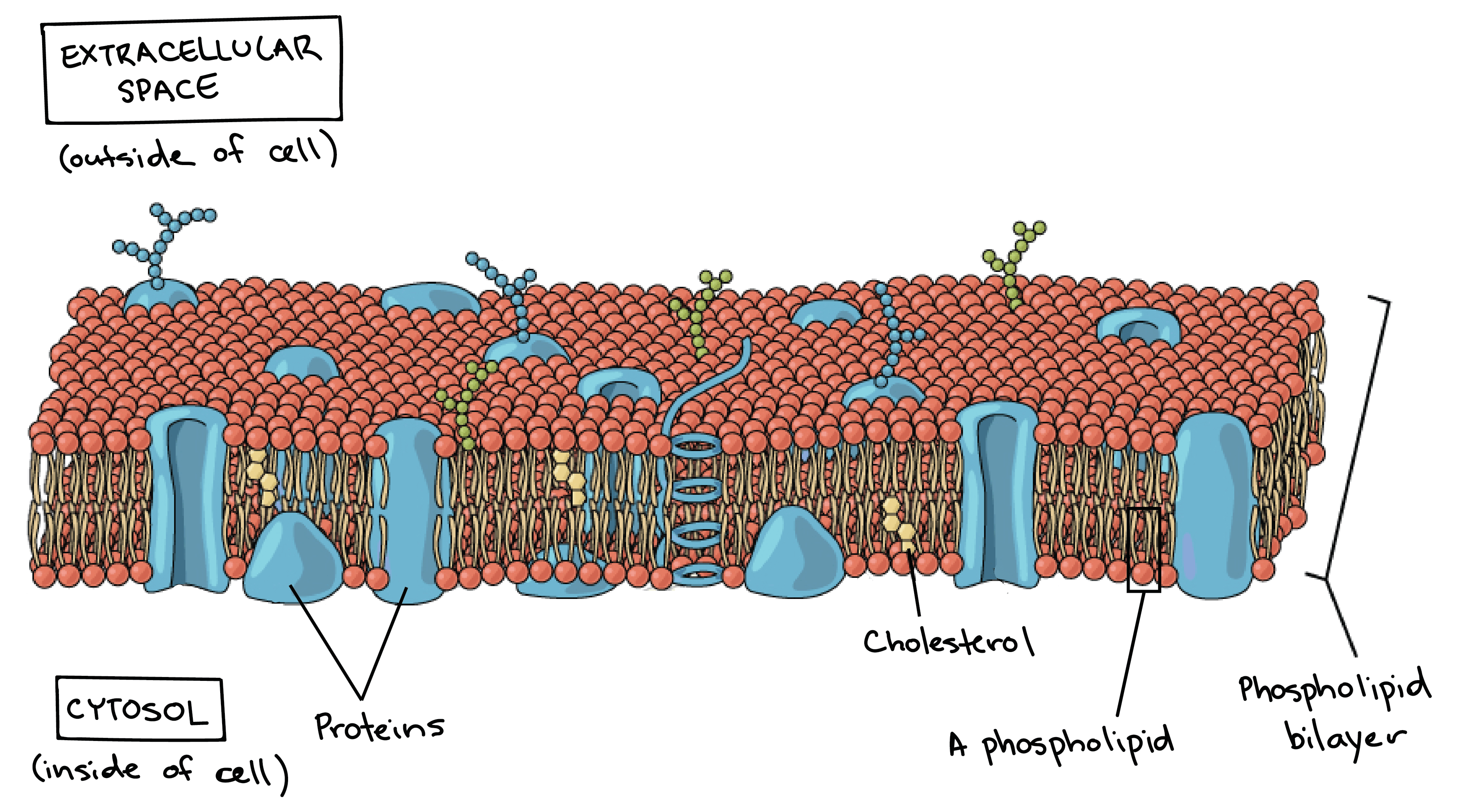
- Protein 會傳過整個 membrane,作為 channels 或 signal receptors 的角色
- 有的 lipids 如 cholesterol 則是控制了 membrane 的 fluidity
Plasma membrane 是 cell 內部和外部的邊界,控制一些 molecules 的通過
- 所以 sugars, water, ions, amino acids 都需要通過 plasma membrane 才能到達 cell 內部
- 簡單的 nonpolar molecules (e.g., oxygen) 可以直接從 phospholipid 部分通過
- 較大的 polar, hydrophilic molecules (e.g., amino acids) 必須從 protein channel 通過
Plasma membrane 的 surface area 會限制 cell 和周遭環境物質交換的上限
- 某些特別需要物質交換的 cell 的 membrane surface area 就會較大
- 例如為了吸收養分的 cells 會折成 fingerlike projection 形狀
- 這些稱為 microvilli (singular: microvillus)
- Microvilli 分布在小腸表面,從食物中吸收養分
- 因為增加表面積的關係,讓 microvilli 幫助小腸最大化的得到養分
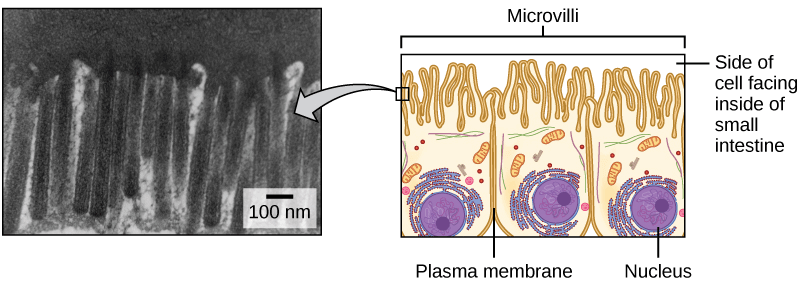
Cytoplasm
Cytoplasm 在 eukaryotes 和 prokaryotes 中有些微的不同
- 在 eukaryotes 指的是 nucleus 和 membrane 間的所有東西
- 在 prokaryotes 因為沒有 nucleus,所以指的是在 membrane 裡所有的東西
兩者共同有的是 cytosol
- Gel-like 的 cytosol 是 cytoplasm 主要物件
- 組成物是 water-based solution (含有 ions, small molecules, macromolecules)
- 為什麼 cytosol 主要是水組成,但為何會是 Jello-like 的呢
- cytosol 包含大量的 macromolecules (e.g., proteins) 還有 small organic molecules 懸浮其中
- 有 glucose, sugars, polysaccharides, amino acids, nucleic acids, fatty acids, ...
- Ions of sodium, potassium, calcium, ...
- 很多的 metabolic reaction (e.g., protein synthesis) 也都是在 cytosol 進行
在 eukaryotes 有特別的一些東西在 cytosol 當中
- Membrane-bound organelles
- cytoskeleton (network of fibers)
- give the cell shape
- organize cellular components
Nucleus and ribosomes
汽車、房子、模型,都需要藍圖,人體也有藍圖,不只給了建造的重點,更給了所有建造的步驟
- 這麼重要的資訊一定存在很保密的地方
- 這正是 eukaryotic cells 所做的事
- 將 genetic material 存放在 membrane-enclosed 的 nucleus 當中
- 這正是 eukaryotic cells 所做的事
Eukaryotes 甚至不會讓重要資訊離開 nucleus 中
- Eukaryotic DNA 透過 transcribe (copy) 至 RNA molecules 再離開 nucleus
- RNA 接著再 cytosol 與 ribosomes 相遇,創造出 proteins
Nucleus
- Nucleus (plural: nuclei) 就是 genetic materia (DNA) 的家
- 可以生成 ribosomes
- 收集 proteins
- chromatin (纏繞 protein 的 DNA) 儲存在 nucleoplasm (gel-like)
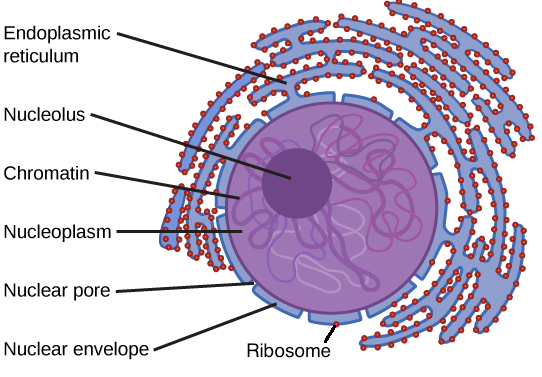
- 包住 nucleoplasm 的是 nuclear envelope
- Envelope 包含 2 層的 membrane (outer & inner)
- Membrane 又再包含 2 層的 phospholipids bilayer (tails inward)
- Envelope 的 2 層 membrane 的中間有一個小空間
- 小空間將會連接到 endoplasmic reticulum (membranous organelle)
- Envelope 包含 2 層的 membrane (outer & inner)
再來是控制物質進去的部分
- Nuclear pores 將 envelope 些微張開,控制物質進出 nucleus
- 控制進出的開關稱為 nuclear pore complex
若用顯微鏡可以看到一點黑點在中心
- Nucleolus 產生新的 ribosomes
- 一些 chromosomes 含有 DNA 片段能夠 encode ribosomal RNA
- 這類 RNA 和 protein 結合成為 ribosome
- 在 nucleolus 中,新的 ribosomal RNA 和 proteins 合成出 ribosome 的 subunits
- 這些 subunits 就會穿過 nuclear pores 移動到 cytoplasm 開始他們的工作
有些 cell 可以多達 6 個 nucleoli (e.g., mouse cell),而 prokaryotes 沒有半個 nucleus,需要在 cytosol 中製造 ribosomes
Chromosomes and DNA
了解 nucleus 後,我們來深入了解他內部的 DNA
- DNA 主要由 1 至多個 chromosomes 組成
- 一個 chromosome 是非常長的 string 或 DNA loop
- 一個 chromosome 可以承載非常多 genes
- 在 prokaryotes 中 DNA 通常是單個 circular chromosome (a loop)
- 在 eukaryotes 中則是 linear structures (strings)
- 每個 eukaryotes 都有特定數量的 chromosomes 在 cells 的 nucleus 當中
- 例如人類細胞有 46 個 chromosomes
- 果蠅的細胞只有 8 個 chromosomes
- 每個 eukaryotes 都有特定數量的 chromosomes 在 cells 的 nucleus 當中
Chromosomes 只有在細胞進行 division 時才可以很好的觀測到
- 所以細胞在生長和維護的階段時
- Chromosomes 會變成 unwound, jumbled bunch threads
- 此時 enzyme 就可以介入將 DNA 編譯成 RNA 來利用
不論是 loose 還是 compact 的 chromosomes 都會和 structural proteins 結合在一起
- 例如下圖的 DNA 和 histone (protein) 結合在一起
- 這些跟 DNA 相關的 proteins 幫助 DNA 進入 nucleus
- 他們也扮演讓 genes 啟動或不啟動的角色
- 這種 DNA 和 proteins 組合的複雜結構叫作 chromatin

- 一個人類細胞的 DNA 通常有 2 m
- 一個 nucleus 的半徑大約只有 0.006 mm
所以要把整個 DNA 塞進 nucleus 相當於將 40 km 的直線塞到一顆網球裡 !!
Ribosomes
接下來是用來產生 protein 的重要角色 ribosomes
- Ribosome 由 RNA 和 proteins 組成
- 含有兩個分開的 RNA-protein complexes (small, large subunits)
- 大的在小的上面,中間夾著 RNA template (mRNA)
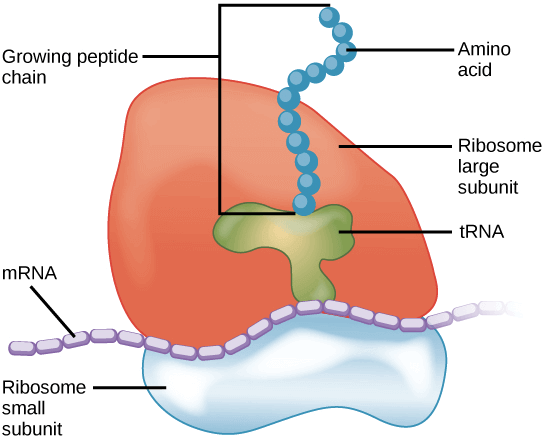
在 eukaryotes 中, ribosomes 是怎麼樣從 nucleus 獲得製造 protein 的指令呢 ?
- Nucleus 中一部分的 DNA (genes) 被轉錄 (transcribed) 成 messenger RNAs (mRNAs)
- mRNAs 從 nucleus 來到 ribosome 並告訴他基因給予製造 protein 的訊息
- 例如用什麼特別的 amino acids 序列
- 這一連串的動作叫作 translation
- 另外在 prokaryotes 因為沒有 nucleus,所以直接在 cytoplasm 轉錄成 mRNAs 然後直接給 ribosomes
在 eukaryotes 的 ribosomes 可以出現在各種地方
- 例如漂浮在 cytoplasm
- 或是 bound (attach) 在 endoplasmic reticulum 和 nuclear envelope 的外部
- Nucleus 那張圖的紅點就是 bound ribosomes
- ribosomes 和 endoplasmic reticulum 結合在一起會成為 rough endoplasmic reticulum
因為 protein synthesis 是細胞中非常基本且重要的功能,幾乎所有 cell 都有 ribosomes (甚至 bacteria)
- 而某些特別需要產生 proteins 的細胞會有非常大量的 ribosomes
- 例如 pancreas (胰臟) 為了產生大量 digestive enzymes
- 所以 pancreatic cells 擁有異常多數量的 ribosomes
Tour of eukaryotic cell
The endomembrane system
想像你是 pancreatic cell 要讓自己的 digestive enzymes 離開自己到小腸幫助消化。這件事需要整個 endomembrane system 的幫忙!
- Endomembrane system (endo-: "within")
- 指的是 eukaryotic cell 中一群 membranes 和 organelles
- 這些東西幫忙修正、打包、運輸 lipids 和 proteins
- 例如 nuclear envelope, lysosomes 還有 endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus
- Plasma membrane 雖說不算在 cell 內,但也是 system 的一員
- 幫助前面所說的 pancreatic enzymes 等 secreted proteins 排出細胞
- 另外 mitochondria (粒線體), chloroplasts (葉綠體), peroxisomes (過氧化體) 不屬於 system
The endoplasmic reticulum
- ER 扮演非常重要的角色,修改 proteins 和合成 lipids
- ER 包含由 membranous tubules 和 flattened sacs 組成的網路
- 這些 disc 和 tubule 都是中空的,然後裡面的空間稱為 lumen
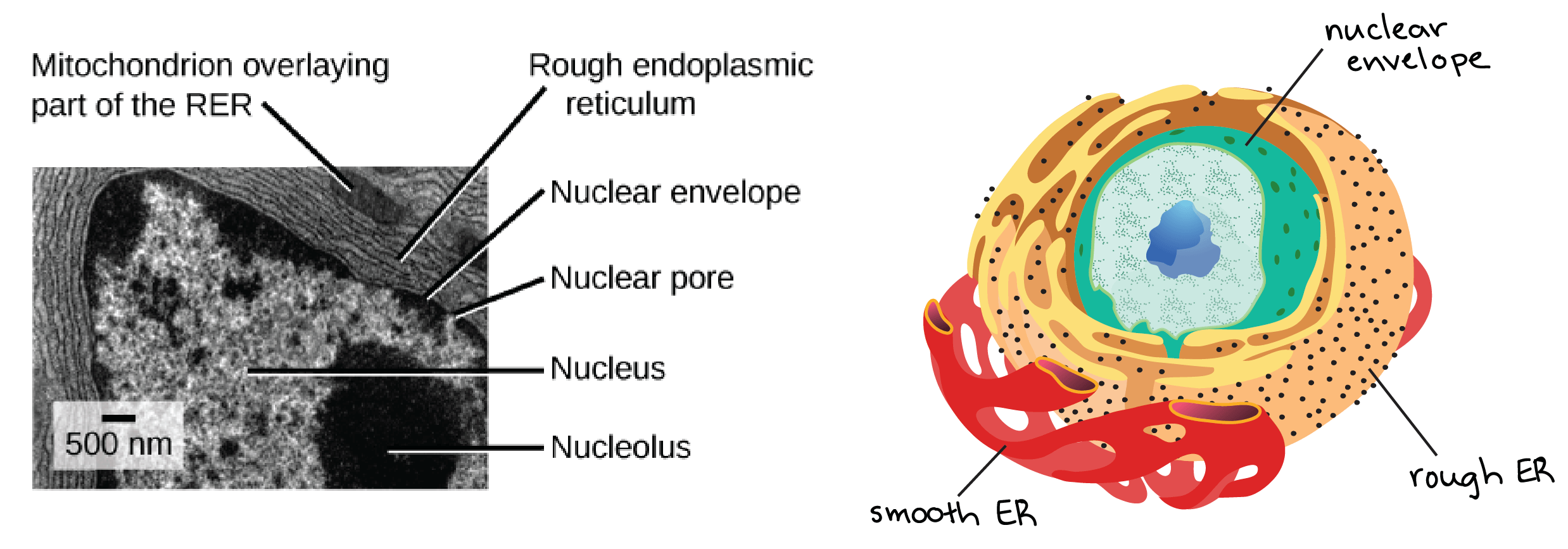
Rough ER
前段的 ER 因為一堆 ribosomes 附在上面,所以稱為 rough endoplasmic reticulum
- Ribosomes 生產的 protein chains 會被送進 lumen
- 一些完全送進去並漂浮在 ER
- 一些固定在 ER 的 membrane 上
- 在 ER 中,proteins 會被 fold 或被修改 (e.g., addition of carbohydrate side chains)
- 被改變的 proteins 就會到其他 membranes 報到
- e.g., membrane of ER, other organelles, secreted from the cell
- 沒有待在 ER 的 proteins 將會被打包成 vesicles 送至 Golgi apparatus
- 被改變的 proteins 就會到其他 membranes 報到
- Rough ER 還可以製造 phospholipids 供其他 membranes 使用
- 一樣是使用 vesicle form 傳送
一些 cell 的工作主要為 secrete protein 就會有大量的 rough ER (e.g., liver cell)
Smooth ER
接續 rough ER 的就是 smooth endoplasmic reticulum
- smooth ER 上幾乎沒有 ribosomes,而主要的功能為
- 合成 carbohydrates, lipids, steroid hormones
- 對藥物或毒物進行解毒
- 儲存 calcium ions (sarcoplasmic reticulum in muscle cell)
rough ER 中也有一些 "smooth" patches 用來作為 vesicles 的出口,這些稱為 transitional ER
The Golgi apparatus
從 ER 出來的 vesicles 在抵達終點之前還要再通過 Golgi apparatus
- Vesicle 中的 lipids, proteins 需要被 sorted, packaged, tagged 到正確的格式,這些動作就是在 golgi apparatus 中進行
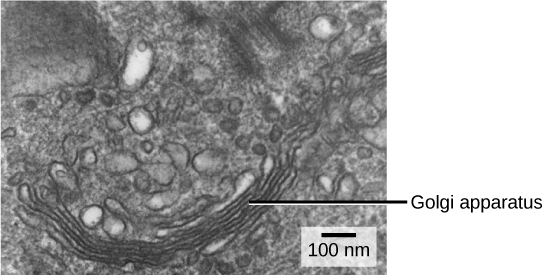
- Golgi apparatus 有兩面,負責接收 vesicle 的為 cis face
- vesicle 和 cis face 結合,將內容物都丟進 Golgi apparatus 的 lumen 當中
- 另一面則為 trans face
- proteins, lipids 在 Golgi apparatus 中被改造完成
- 加入或移除 sugar 或加入 phosphate groups 當作 tags
- 改造過的 proteins 將進行排序然後再次打包成 vesicle 從 trans face 送出
- proteins, lipids 在 Golgi apparatus 中被改造完成

從 Golgi 出來的 vesicles 終於可以用了
- 有的送至 cell 內部的地方使用
- 例如 lysosome, vacuole
- 有的則到外圍和 plasma membrane 結合
- 將一些 secreted proteins 釋放到 cell 外作用
一些需要 secrete 大量 proteins 的 cell 會有很多 Golgi stacks
- 分泌 digestive enzymes 的 salivary gland cells
- 分泌 antibodies 的 immune system
植物的 Golgi apparatus 也會製造 polysaccharides 用於 cell wall
Lysosomes
Lysosome 包含 digestive enzymes 作為 animal cell 的回收場
- Lysosome 將不要的分子架構拆解重新使用
- 上面說的,一些離開 Golgi 的 vesicles 會來到 lysosome
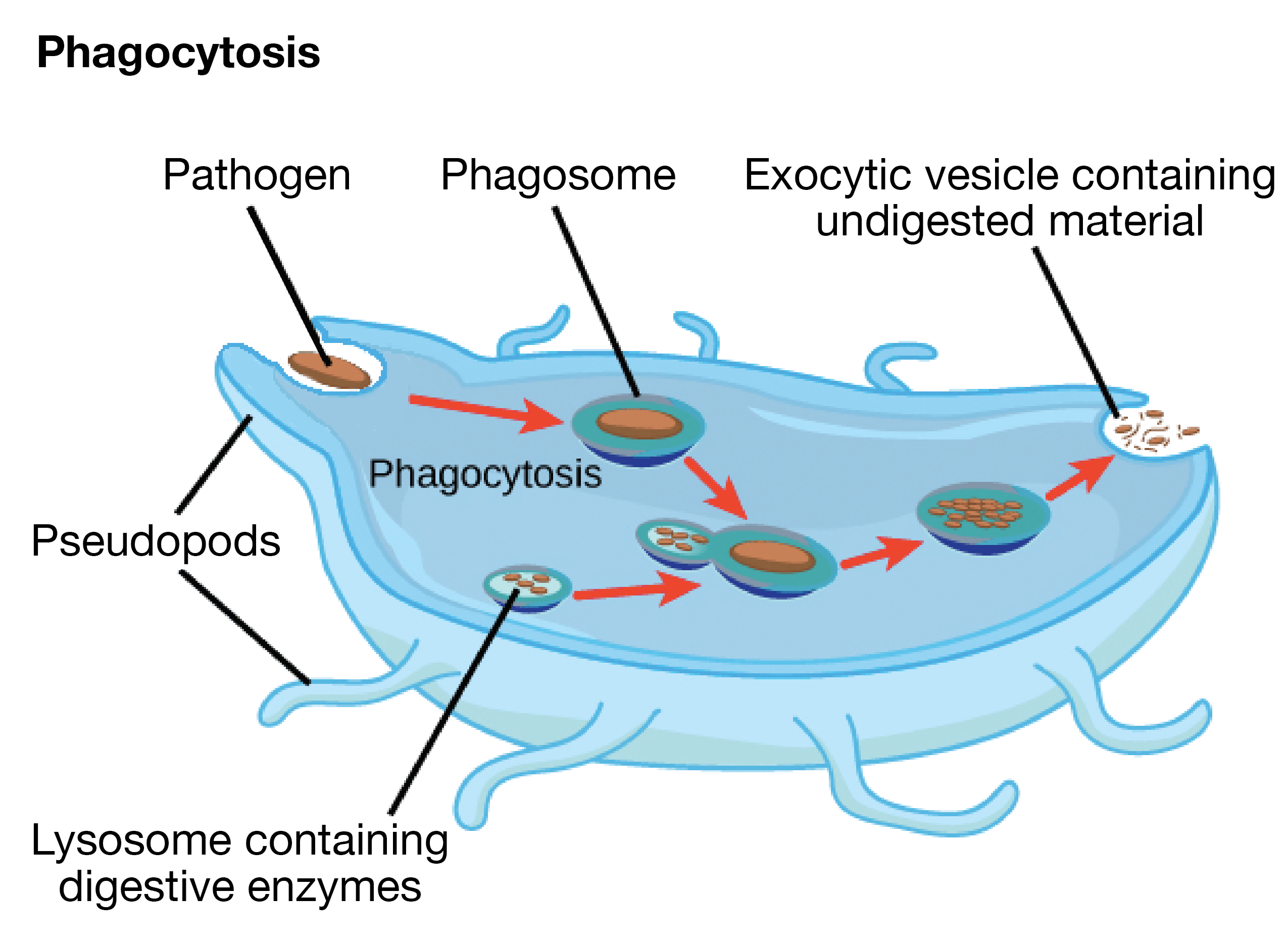
Lysosome 還能夠分解外部進入 cell 的垃圾
- 例如人類免疫系統的 macrophages (某種 white blood cell)
- 會進行 phagocytosis (吞噬作用)
- 一段在 macrophages 的 membrane 會內陷 (invaginates)
- 接著如下圖一樣吞噬 pathogen
Peroxisome
這邊額外討論一下非 endomembrane system 的 peroxisome
- Peroxisomes 和 lysosomes
- 一樣負責分解並中和細胞中的 molecules
- 並且兩者的形狀都很像
但 peroxisome 有獨特的一些特性
- Peroxisome 的 enzymes 通常會涉及 oxidation reactions
- 也就是產出 hydrogen peroxide by-product
- 這些 enzymes 負責分解的是 fatty acids 和 amino acids
- 另外也會解毒進到身體中的毒素
- 例如 liver cell 的 peroxisomes 能夠解毒 alcohol
Vacuoles
植物多了一個跟 lysosome 很像的 organelle 稱為 vacuoles
- Vacuole 儲存水和廢物,隔離危險的物質
- 其中的 enzymes 一樣能分解廢物 (macromolecules, cellular components)
- 能進行 water balance
- 儲存一些 toxins, pigments 等 compound
Mitochondria and chloroplasts
假設你吃了花椰菜,你要怎麼從他得到能量來運動,花椰菜又為什麼會有能量 ?
這必須要牽扯到兩個重要的 organelles : mitochondria 和 chloroplasts
- Chloroplasts 只存在於植物細胞中,將得到的陽光能量轉化成 sugars (透過 photosynthesis)
- 這些 sugars (fuel molecules) 存在 plant's tissues
- Mitochondria 是細胞中的"發電所",將 fuel molecules 分解,然後幫助人類吸收養分 (透過 cellular respiration)
Endosymbiotic theory (共生體學說)
這兩個 organelles 的起源被認為是在古代和一些細菌共生而成
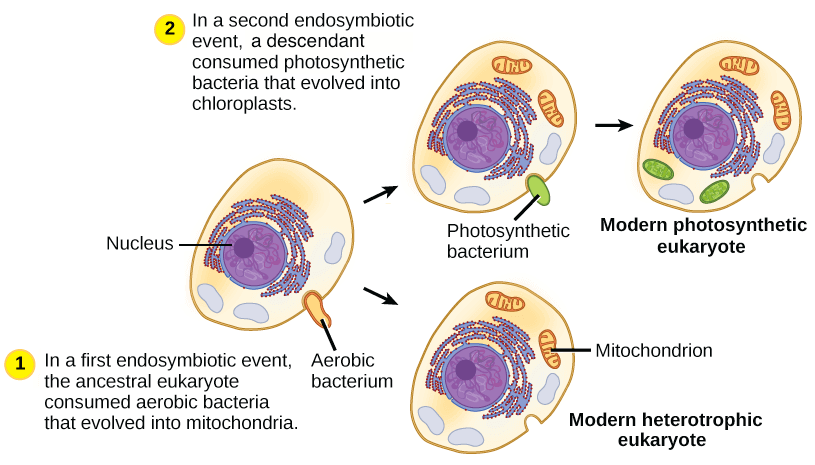
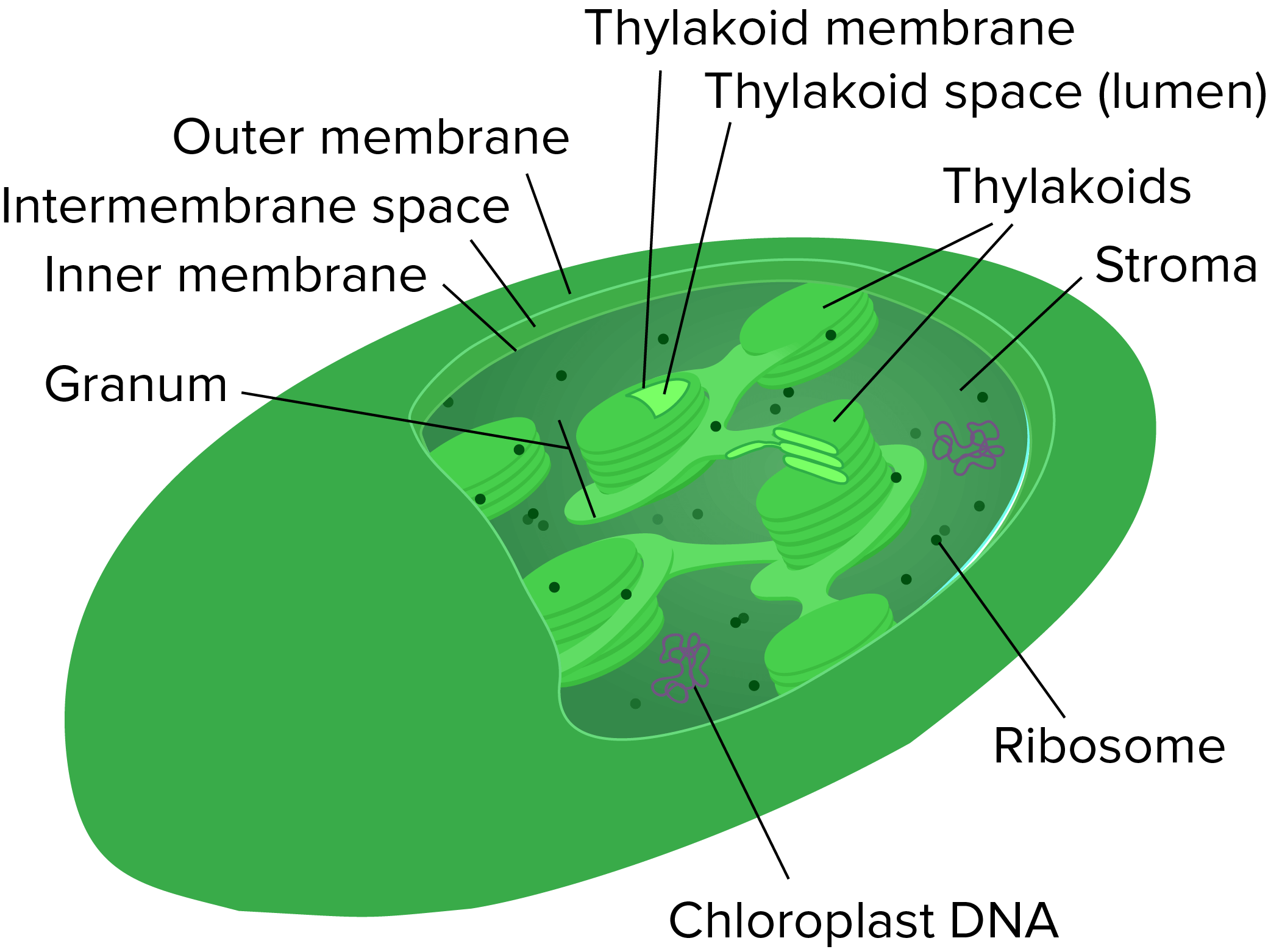
Chloroplasts
- Chloroplasts (葉綠體) 可以在 cytosol 中被找到
- 是 disc-shaped 的 organelles
- membrane 包含 outer 和 inner,中間夾著 intermembrane space
- 裡面包含了 thylakoids (類囊體,含有 membrane 的膠囊)
- thylakoid 的 membrane 包含可以捕獲光的複合物
- 這些複合物包含了 chlorophyll (葉綠素,讓植物變綠色的顏料)
- thylakoid 是中空的,裡面的空間稱為 thylakoid space (lumen)
- thylakoid 的 membrane 包含可以捕獲光的複合物
- 這些 thylakoids 疊成了 grana (singular: granum)
- 漂浮在周圍的液體為 stroma
Mitochondria
- Mitochondria (singular: mitochondrion) 的工作是穩定輸出 ATP
- 利用 fuel (e.g., sugar) 產生 ATP 的行為稱為 cellular respiration
- 而這些過程發生在 mitochondria 當中
Mitochondria 一樣漂浮在 cytosol 中
- Mitochondria 是 oval-shaped 的 organelles
- 有兩個 membranes
- 一個是把整個 mitochondrion 包覆住的 membrane (outer)
- 一個是在內層把 cristae 包覆住的 membrane (inner)
- Cristae 指的是為了增加表面面積的突起物
- Cristae 原本被想像為 broad, wavy folds
- 但現在被認為應該是 long carven 的形狀
- 有兩個 membranes

- 兩個 membranes 之間是 intermembrane space
- Inner membrane 中被分隔的 compartment 稱為 mitochondrial matrix
- Matrix 中包含 DNA 和 ribosomes
- multi-compartment 架構方便進行 cellular respiration
- 讓不同的 "room" 能夠有不同的 concentration of molecules
雖然 mitochondria 都可以在動物和植物多數的細胞被找到,但還是會依照能量需求有所不同
- Muscle cells 需要非常多的能量,所以 cell 中的 mitochondria 非常多
- Red blood cells 只專注於運送氧氣,所以 cell 中沒有任何的 mitochondria
Cytoskeleton
細胞就像人體的器官一樣,需要各種 skeleton 支撐
- 支撐細胞的 skeleton 稱為 cytoskeleton
- 不只支撐 plasma membrane 賦予整個細胞形狀
- 更負責正確的布置各種 organelles 的位置
- 提供 vesicles 移動路徑
- 多數的 cytoskeleton 也幫助細胞移動
在 eukaryotes 中有三種 protein fibers 存在於 cytoskeleton:
- microfilaments
- intermediate filaments
- microtubules
Microfilaments
- Microfilaments 是三種 fiber 最窄的一個
- 他的半徑只有 7 nm
- 他是由很多 protein 的 monomer (actin) 所組成的 double helix
- 所以又稱為 actin filaments
- 他有 directionality 也就是兩邊的 end 不同
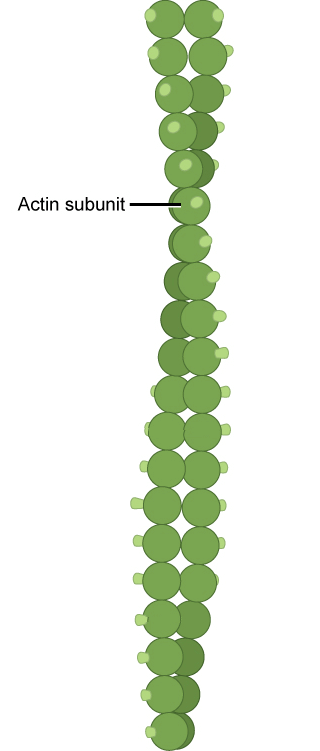
Microfilament 在細胞裡有幾個重要工作
- 幫助 myosin 這類 motor protein 移動的路徑
- 幫助 cell division
- 幫助 muscles contraction
- 能快速集中,幫助細胞移動 (例如免疫系統的白血球移動)
- 在 cytoplasm 周圍與 plasma membrane 連接,穩定細胞架構跟形狀
Intermediate filaments
- Intermediate filament 的半徑約為 8 到 10 nm
- 由多個 fibrous proteins 組成的 strands 組合而成

- Intermediate filaments 的種類非常多 (不同 protein 組成)
- 例如由 keratin 所組成的 intermediate filaments
- 常見在 hair, nails, skin
Intermediate filaments 不像 microfilaments 可以快速集中又散開
- Intermediate filament 通常是不變的
- 所以主要工作是維持細胞的張力
- 保持細胞的形狀和 nucleus 等 organelles 的位置
Microtubules
- Microtubules 是三類 fiber 中最大的一種
- 他的半徑能到 25 nm
- 主要由 tubulin proteins 組成一個空心吸管狀的管子
- 每個 tubulin proteins 又包含兩種 (alpha, beta- tubulin)
Microtubules 的特性和 microfilaments 大同小異
- 能夠快速集中的 dynamic structure (靠著 add, remove tubulin)
- 擁有 directionality
- microtubules 主要幫助細胞承受 compression force
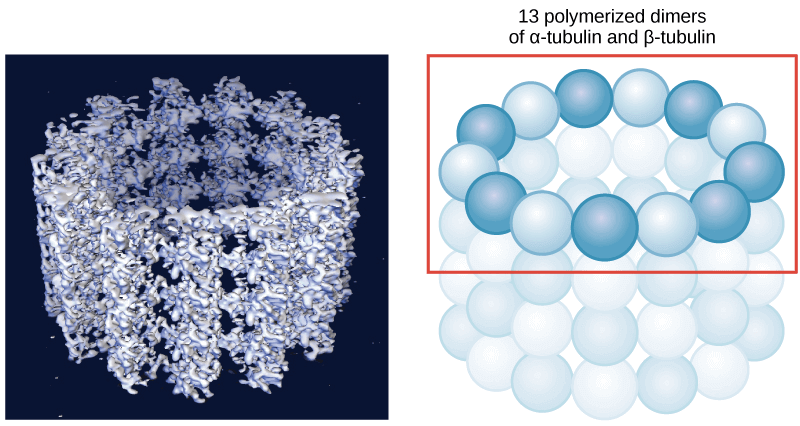
Microtubules 也扮演了非常多的角色
- 提供 kinesins, dyneins (motor proteins) 移動管道
- 移動細胞內的 visicles
- 在 cell division 期間組合成 spindle
- 負責將 chromosomes 分離
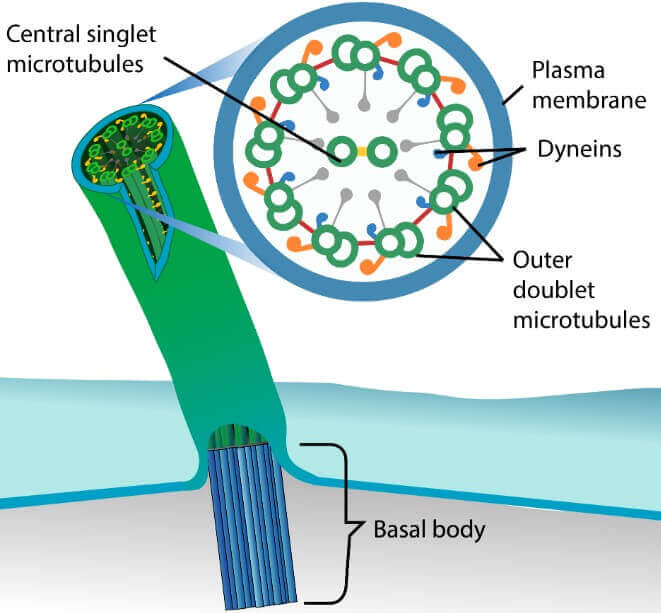
Flagella, cilia
Microtubules 還是組成 flagella 和 cilia 的重要元件
- Flagella 是很長的 hair-like structure
- 接在細胞後端,幫助整個細胞移動 (e.g., sperm)
- Cilia (singular: cilium) 也是幫助移動,但通常遍布細胞表面
- 例如上呼吸系統的細胞,他們的 cilia 幫助移動 dust, particles 到鼻孔
Flagella 和 cilia 的共同點有以下幾點
- 9 對 microtubules 排列成圓形
- 2 個 microtubules 則在中間
- 形成 9+2 的環
- 有 dyneins 這個 motor proteins 在 microtubules 移動
- 使得 flagella 和 cilia 跳動 (beating)
- 在兩者的底部有 basal body 存在
- basal body 一樣由 microtubules 組成,負責集合 cilium 或 flagellum
Extracellular structures and cell-cell junctions
我們花了很多時間在觀察 cell 的內部,但外部呢 ?
The extracellular matrix and cell wall
植物細胞有堅固的 cell wall 而動物細胞則和周圍的細胞互相形成 meshwork (extracellular matrix)
Extracellular matrix of animal cells
- 有的 animal cell 釋放一些物質 (protein collagen,膠原蛋白) 到細胞外部的空間
- 釋放的 collagen 會和 carbohydrates 組合形成複雜的 meshwork
- 這些外部的 long fibers 又叫做 collagen fibrils
這些 collagen proteins 非常重要,讓 tissues 的架構能夠穩固
- 在 extracellular matrix 中
- Collagen fibers 會和 proteoglycans (carbohydrate-bearing) 交織在一起
- extracellular matrix 會直接透過 integrins connector 和最近的 cell 連接
- integrins 被嵌在 plasma membrane 上面
- integrins 上有 fibronectin 作為外部 protein 和 integrins 的橋樑
- integrins 在內部會和 cytoskeleton 連接起來

Integrins 幫助細胞架在 extracellular matrix 上面,進一步的說,integrins 幫助細胞感知外部環境,並做出適當的訊號跟反應
The cell wall
植物沒有 collagen 可以維持細胞間的組織,但有 cell walls 維持細胞的架構和形狀
- Fungi, protists, most prokaryotes 幾乎都有 cell walls
- Cell wall 是由 cell 所排出的 molecules (cellulose,纖維素) 所組成
- Cellulose 是 glucose units 所組成的 polysaccharide
- cellulose 集合再形成 microfibrils 的 fibers

- 除了 cellulose 外,還有許多 polysaccharides 常見於 cell wall
- 例如 hemicellulose, pectin
- 最上層的 middle lamella 則負責 cell walls 之間的穩定
Cell-cell junctions
在蓋房子時,房間之間到底要怎麼處理呢 ? 細胞之間也有這個問題 !
- 要直接開一個通道直接連接鄰居嗎
- 要加強細胞之間的關係,強化整個 layer 嗎
- 還是建立 tight seal 避免水通過整個 tissue
Junctions 就是為了解決這些事情的專家,而且有很多種 junctions
Plasmodesmata
植物的 cell walls 之間會有特殊的 junctions 叫做 plasmodesmata (singular: plasmodesma)

- Cytoplasm 的物質可以透過這個洞互相交換
- 一些較小的 molecules 可以順利的透過 passive diffusion 通過這個管道
- 一些較大的 (e.g., proteins),plasmodesmata 可能會選擇性的撐大管道來讓他們通過
Gap junctions
Gap junctions 是動物版的 plasmodesmata,讓細胞可以交換 water, ions, 還有一些物質。但其實和 plasmodesmata 有些差異
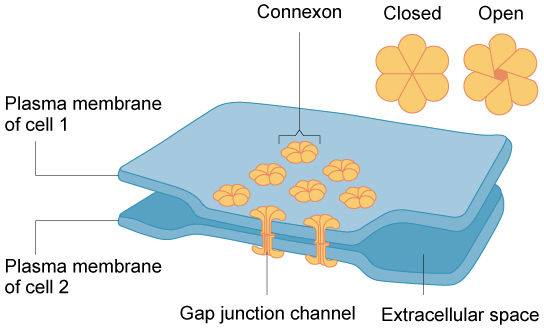
- 在脊椎動物中,六個 membrane proteins (connexins) 組合成一個 connexon
- connexons 為甜甜圈形狀的架構
- connexons 會連接兩個相鄰的 animal cells
- 在無脊椎動物中,也會有類似的 gap junctions,但用的 proteins 叫做 innexins
Gap junctions 主要應用在 cardiac muscle
- Heart muscle cells 之間應用 gap junctions 來傳遞 ions,起到讓 cell 之間同時收縮的效果
Tight junctions
Tight junctions 不提供 cytoplasmic connections,而是提供 watertight seal
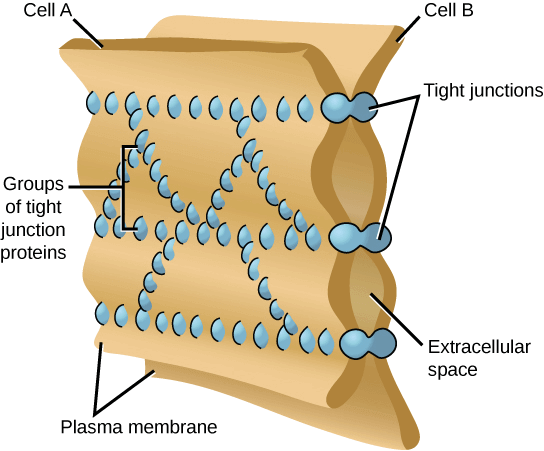
- Cells 之間透過 tight junction proteins group (claudins) 緊密湊在一起
- Groups 之間排成 strands 形成 branching network
- Tight junctions 目的是防止水分從 cells 間流失
- 讓 cells 整層形成無法穿透的屏障 (e.g., cells those lining an organ)
- 例如膀胱的 epithelial cells 透過 tight junctions 防止尿液洩漏
Desmosomes
一些動物細胞間還會有 desmosomes 幫助連接 epithelial cells 不被扯斷
- Desmosomes 通常由複雜的 proteins 組成 (e.g., Cadherins)
- Cadherins 出現在 membrane 中,將兩個 cells 的 membranes 連結起來
- Cadherins 透過 cytoplasmic plaque (下圖紅色部分) 一路連接到內部的 intermediate filaments
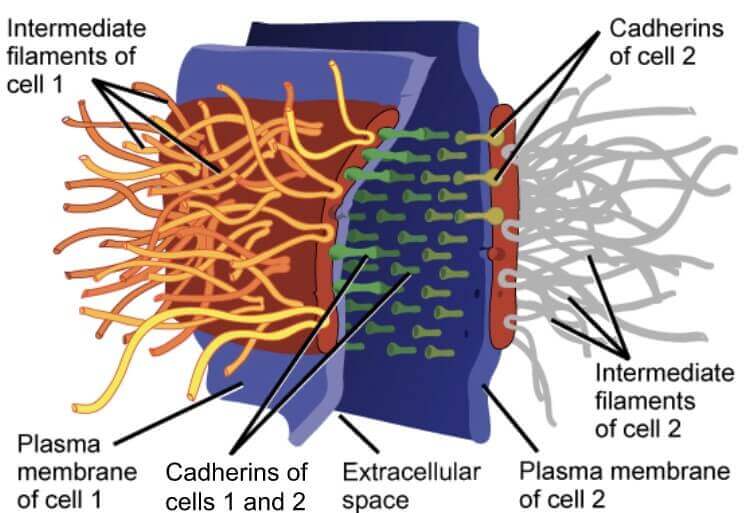
Desmosomes 讓器官、組織等 (cardiac muscle, skin),能夠拉伸並且保持 unbroken 的樣子