Water, Acids, Bases
Water, Acids, Bases 的關係是一個複雜的系統,可以藉由水開始了解。水是一種 polar molecule,有分正負電荷,可以和電荷相關的 molecule 互相吸引,例如鹽 (NaCl)。而 acids 和 bases 是一種離子物質,可以和水作用,acids 具有細菌分解的能力,而 bases 則是可以和酸還原的能力,可以用來調整 pH 值。這些離子會和水分子產生一個三維的水包圍結構,改變水的特性,例如溶解度、抗壓力等等。
Water
- 大多動物甚至細菌都是由水組成
- 水能夠溶解非常多的 polar 和 charged molecules
- 水有 cohesion (和自己結合) 還有 adhesion (和其他分子結合) 的特性
- 水有 high heat capacity, heat of vaporization, ice (less dense than liquid) 等特性
- 水能有這麼多特性都跟他 polarity 和 hydrogen bonds 有關
Polarity of water molecules
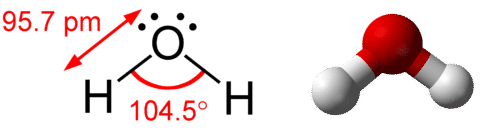
- Water molecule 有兩個 hydrogen atom 和一個 oxygen atom
- 因為 oxygen 有較高 electronegativity, 讓他偏向 hog 兩個 electrons
- 所以 oxygen end 有 partial negative charge
- 而兩個 hydrogen end 有 partial positive charge
- Water molecule 形狀呈下圖樣式,像一個 tetrahedron
Hydrogen bonding of water molecules
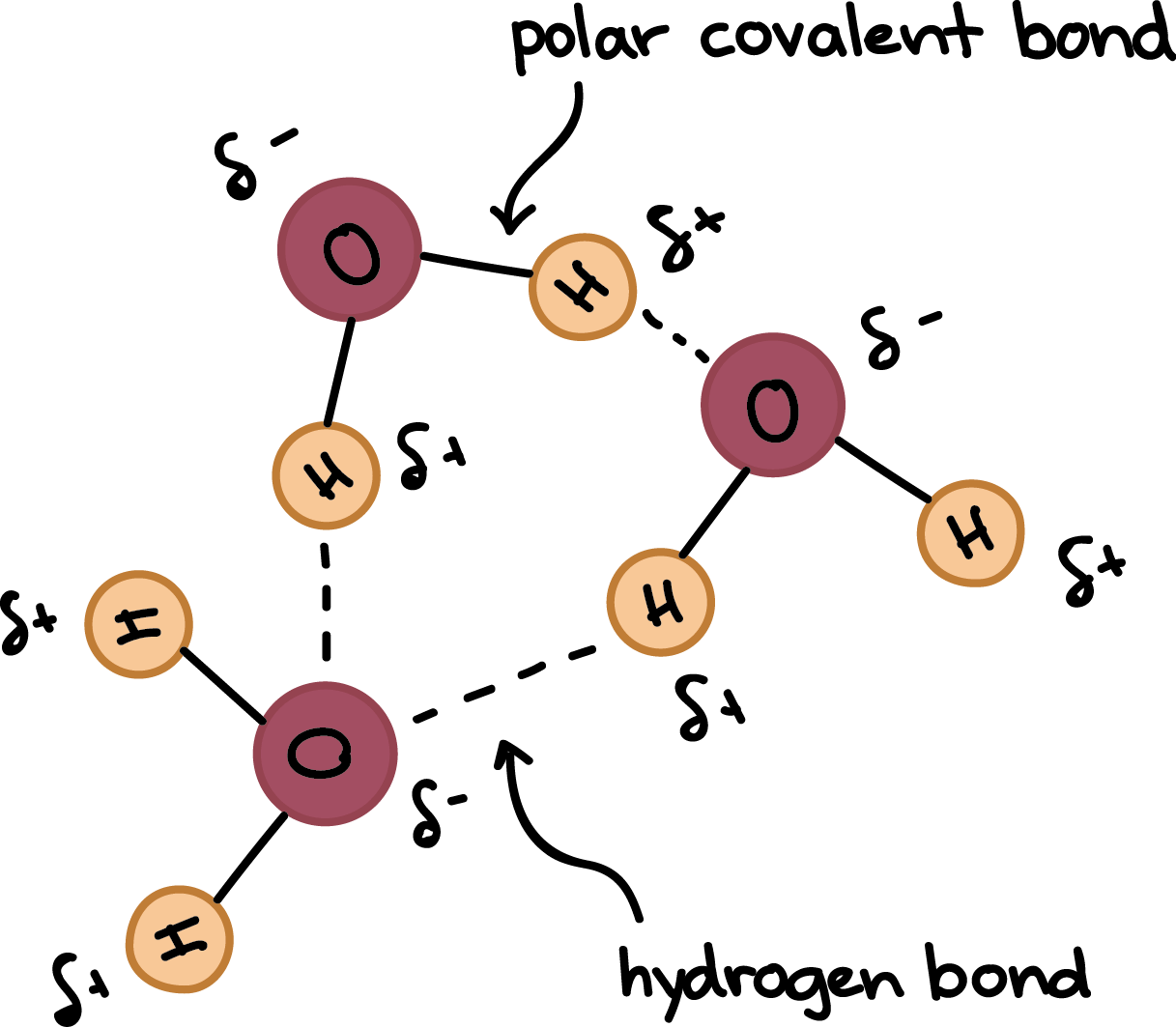
- 多虧 polarity,水分子之間非常喜歡互相吸引
- 微負極的 hydrogen 去和隔壁老王微正極 oxygen 相互吸引
- 這些吸引關係就是較弱 (weak) 的 hydrogen bonds
- 水分子還會和其他 polar molecules 相互吸引並變成 ion
- 有些 polar 物質容易和水作用並溶解於水的稱他們 hydrophilic
- 例如食鹽 (NaCl)
- 而 nonpolar 物質不會和水作用且不易溶解的稱他們 hydrophobic
- 例如己烷 (hexane)
- 有些 polar 物質容易和水作用並溶解於水的稱他們 hydrophilic
Solvent properties of water
- Solvent 指的是某些物質 (e.g., 水) 能將其他物質溶解
- 而能被溶解的物質就稱 solute
- 能夠良好將 solvent, solute 一起混合的現象稱 solution
- 大部分的 life chemistry 皆為 aqueous solutions
- 水因為 polarity, hydrogen bonds 的關係,是非常好的 solvent
- 有時又被稱為 "universal solvent"
- 這樣講有點不對,因為水比較偏向溶解 ions, polar molecules
- 不易溶解 nonpolar molecules
備註
- 複習 : Polar 指的是 neutral, uncharged
- 但 asynmmetric internal distribution of charge
- 有 partially positive, negative regions
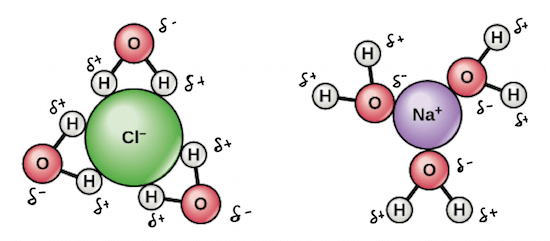
- 從上圖看到,水的 O 帶負電 H 帶正電的 polarity
- 讓水有辦法和 polar molecules, ions (NaCl) 進行 electrostatic interactions
- 可以看到正電 Na 被負電 O 圍繞,負電 Cl 則被正電 H 圍繞
- 當非常多的水分子和 solute 作用於 aqueous solution 時
- 水和物質間的圍繞,會產生一種叫 hydration shell 的 3D sphere
- 該 shell 會讓 particles 均勻的分解到水中
- 所以一些 nonpolar (e.g., oil) 就不會和水產生 hydration shell
- 也就不會溶解於水中
Cohesion and adhesion
- Cohesive, Adhesive forces 對於非常多 water-based process 的 biology 十分重要
- 例如水往樹上跑 (capillary action)
- 昆蟲在水面行走 (surface tension)
Cohesion of water
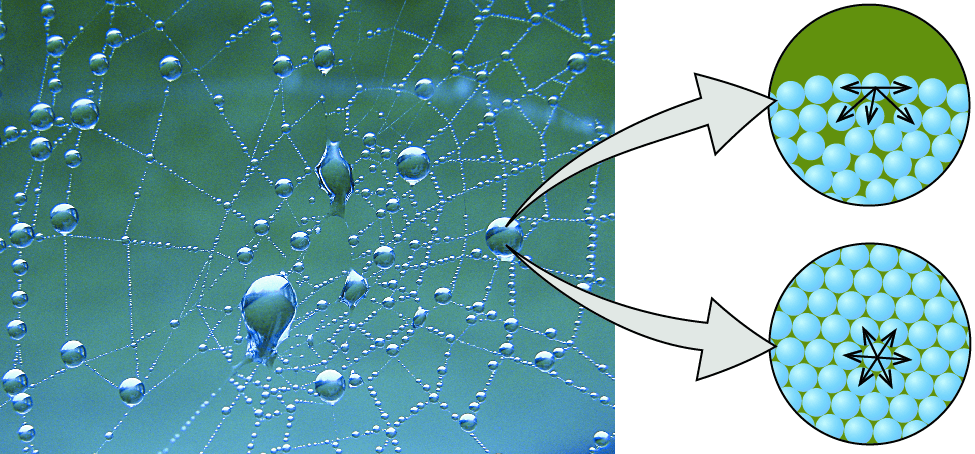
- 水分子之間會互相吸引,稱為 cohesion
- 這是因為水分子間的 hydrogen bonds
- 常見例子是水向下滴時的水滴狀
- 另一個例子是 surface tension
- 想像容器的最上方的水,因為上方就是空氣
- 空氣沒辦法和水吸引,所以最上方的水分子只能互相吸引
- 所以他們的 hydrogen bond 比下方的水還要強
Adhesion of water
- Water 雖有強大的 cohesion 特性,但在特定情況也會去貼近其他 molecules
- 這種去和其他 molecules 互相吸引的特性稱為 adhesion
- 例如玻璃杯中上緣的水,會呈現 concave meniscus 的特性
- 因為水分子被兩側玻璃中的分子吸引 (polar of glass is greater than water)
- 另一個例子是 capillary action
- 水分子被玻璃管吸引,並且往上爬

Temperature and state changes in water
- 水分子中的 Hydrogen bonds 造成了許多的現象
- effectiveness of evaporative cooling
- low density of ice
- temperature changes, freezing, vaporization
Solid, liquid, and gas
- 水在三種狀態下都有獨特的 chemical characteristics
- 這和 hydrogen bond 有非常大的關係
- 水的三種形態的特徵跟生物學息息相關
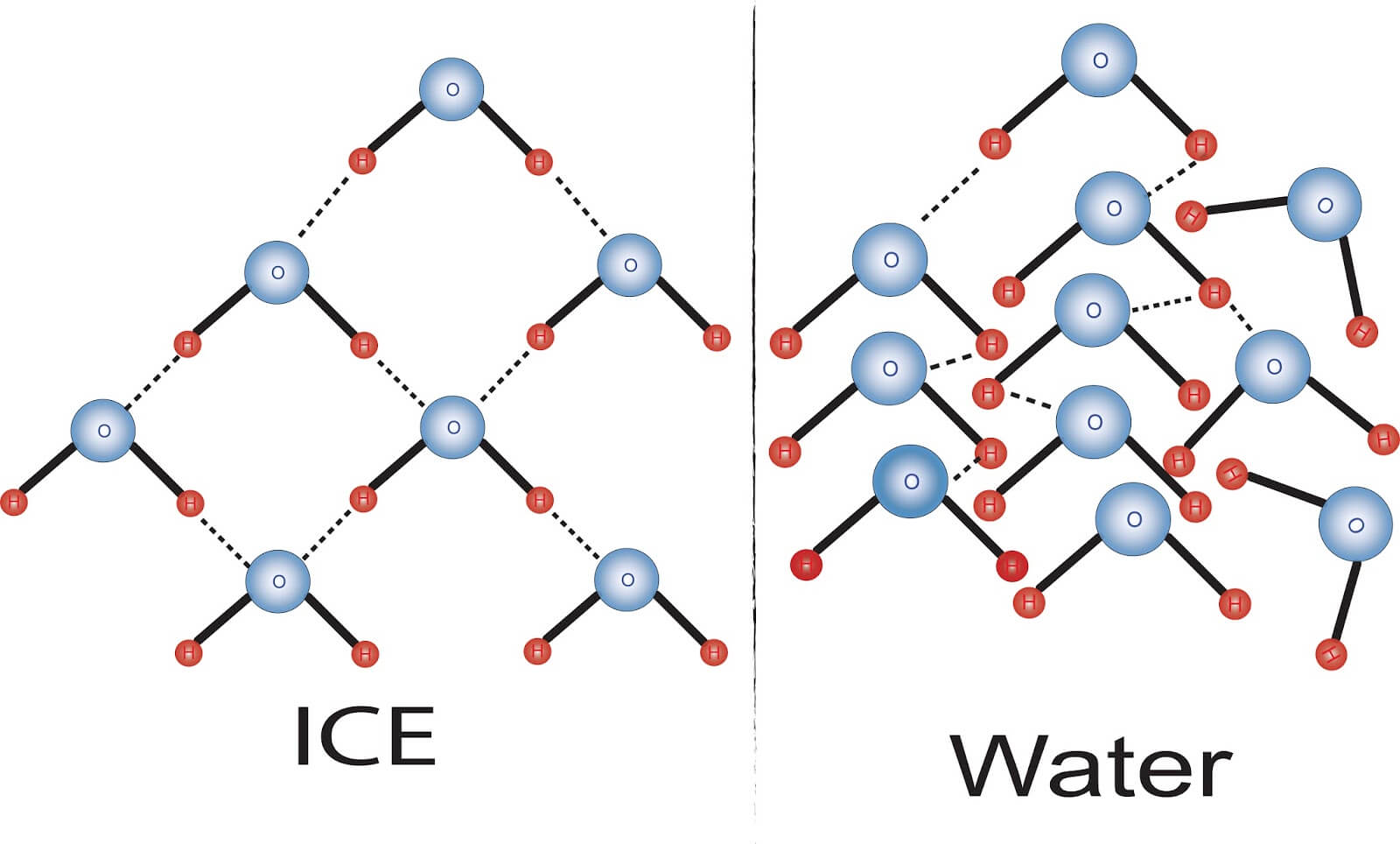
- 當水在液態時
- Hydrogen bonds 被重複組成又分開
- 原因是來自 heat 造成的 energy of motion (kinetic energy)
- 當溫度變高 (boiled)
- kinetic energy 將 hydrogen bonds 完全破壞
- 使 water molecules 逃到空氣中
- 這就是我們看到的 water vapor, steam
- 當溫度變低 (freeze)
- water molecules 透過 hydrogen bonding 成結晶的形狀
- 也是因為幾乎沒有 heat energy 能破壞 hydrogen bonds 了
- 這些因素讓 ice 跟 liquid water 比起來較不密集 (less dense)
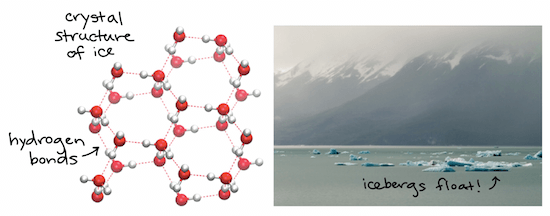
Density of ice and water
- 水在固態時,分子間的距離會被推的更遠
- 也就是當水結冰時 water 會 expand
- 水以外的 liquid 因為溫度下降,所以 molecules 就不會被 kinetic energy 破壞
- 這時候固化 (solid),變得比 liquid 更加 pack tightly, greater density
- 水是例外,在固化時,將有 lower density
- 因為 ice less dense 的特性,所以讓他能夠浮在 liquid water 上
- 因為 freeze 會讓體積變大,所以物質的內容物將會衝破表層
- e.g., soda bottle cracking in the freezer
Heat capacity of water
- 要讓水的溫度上升需要大量的 heat
- 要用來破壞 hydrogen bonds
- 我們稱水有非常高的 specific heat capacity
- 這個 capacity 就是計算物質 1 克需要多少 heat 來升上 1 度
- 而要把 1g 水升 1 度所需的 heat 又稱作 calorie
- 因為水有 high specific heat capacity
- 水能讓溫度的變化最小化
- water's capacity is five times greater than sand
- land cools faster than sea after sunset
- warm-boolded animals distribute heat through their bodies
Heat of vaporization of water
- 水同樣需要大量 heat 讓水蒸發
- 我們稱水同樣有非常高的 heat of vaporization
- 1g 的水變成氣體所需的 heat
- 通常 water's heat of vaporization 在 540 cal/g at 100 °C
- 水分子離開的表面會變得 cooler
- 這個現象稱作 evaporative cooling
- 因為最高的 kinetic energy 消失在蒸發中,原本的水分子能量變少溫度變低
- 所以人類的汗有 99% 的水,在蒸發時會降溫身體,保持溫度平衡
Acids, bases, and pH
- 我們都知道酸和鹼,但到底要怎麼真正定義他們倆,以下是簡短答案
- 酸 : 高濃度的 hydrogen ions ,高於純水
- 鹼 : 低濃度的 hydrogen ions ,低於純水
Autoionization of water
- Hydrogen ions 會自動在純水中小機率的生成出來
- 透過 dissociation (ionization) 生成,又稱作 autoionization of water
- l = liquid
- aq = aqueous solution (water-based)
- 透過 dissociation (ionization) 生成,又稱作 autoionization of water
- 式子中,水有小機率分解產生相同份量的 hydrogen ions 和 hydroxide ions
- 因為 H 的 electron 被 O 吃掉,H 剩一個 proton 變成正電,成為 hydrogen ions
- hydroxide ions 會保持不變飄在水中
- 但 hydrogen ions 會去跟其他水分子結合,得到 hydronium ions
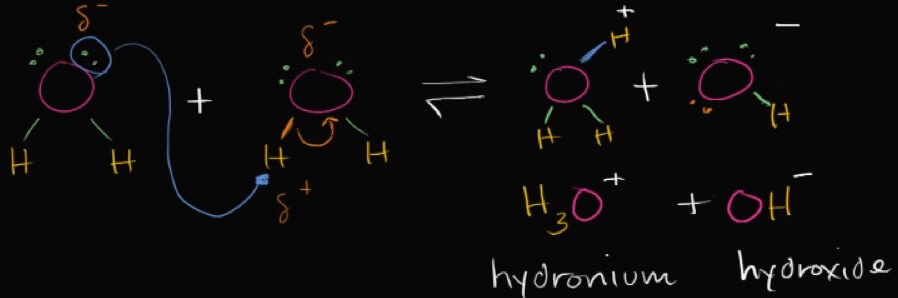
- 所以這個小機率分解的機率到底有多小
- 在純水時,分解機率為 (moles per liter)
- 而一公升純水中的水分子約有
- 所以 autoionized water molecules 要在純水中出現的機率非常的低
Acids and bases
我們可藉由和純水相比的 hydrogen ion 濃度來決定溶液是酸還是鹼
- 當 濃度高於純水時是 acidic solution
- greater than
- 當 濃度低於純水時是 basic (alkaline) solution
- less than
- 當 濃度高於純水時是 acidic solution
因為這個表達法太難記了,所以科學家想出 pH 來表達 hydrogen ion 的濃度
- pH 取濃度的 negative log
所以你用純水的濃度算可以得到 pH = 7
- known as neutral pH
- 身體裡大多的血、組織液都是 neutral pH
acid 會增加 hydrogen ions 濃度,pH 值降低
- 因為會多分解出 hydrogen atoms 並 donate 自己給其它水分子
base 則會減少 hydrogen ions 濃度,pH 值增加
- 因為會多分解出 hydroxide ,迅速的移除掉 hydrogen ions
酸性越強,便越快分解產生
- e.g., hydrochloric acid 在水中能完美分解成 hydrogen 和 chloride ions,所以讓他成為強酸
- tomato juice, vinegar 則沒辦法像鹽酸一樣很好的分解,所以是弱酸
鹼性越強,則是越快分解產生 可以吸收
- e.g., sodium hydroxide 是在水中能完美分解的強鹼
The pH scale
- 用來排名 solution 的 acidity or basicity (alkalinity)
- 因為是使用 logarithmic,所以 1 pH 的改變是 10 倍的 濃度改變
- 大於 7 的視為 acidic,小於 7 的視為 basic (alkaline)
- 有可能出現超出 0-14 範圍的液體
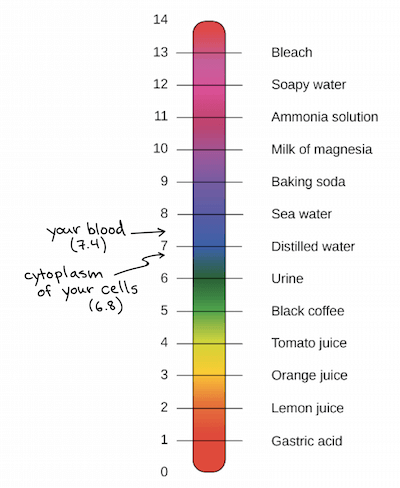
- 人類的 cell (6.8) 和 blood (7.4) 都接近中性
- 雖然極端的 pH 通常對人體有害,但 stomach acid 是非常酸性的 (1 to 2)
- 胃是怎麼解決這個問題 ?
- 答案 : Disposable cells
- 胃中直接接觸胃酸和食物的細胞,通常會在 7 至 10 天就會被新的取代掉
Buffers
- Buffers 會幫人類保持血液或體液的 pH 值範圍,避免瞬間改變
- 當有太多 ions 時,buffer 會吸收他們,讓 pH 值上升
- 當 ions 太少時,buffer 會將自己的 捐出來,pH 下降
- Buffers 通常是一個 conjugate acid-base pair
- 例如人體有一個維持血液 pH 的 buffer 他包含 carbonic acid 還有他的 conjugate base 即 bicarbonate ion
- 當 carbon dioxide 進入血液和水組合時會形成 carbonic acid
- 通常是 carbon dioxide 經過 muscles, lungs 在血液的形態
- 在 muscles 生成,在 lungs 又轉回水和 當成廢物排掉
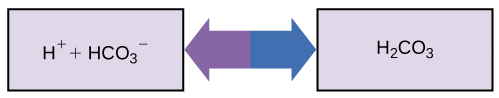
- 如果有太多的 ,式子就會被推向右邊
- 透過 bicarbonate ions 吸收 來形成 carbonic acid
- 同樣的, 若太少,式子就會被拉回左邊
- carbonic acid 分解成 bicarbonate ions,然後 donate 給身體
- 如果沒有這些 buffer system,那麼人體的 pH 將會亂七八糟,無法存活